10 Throat Cancer Symptoms
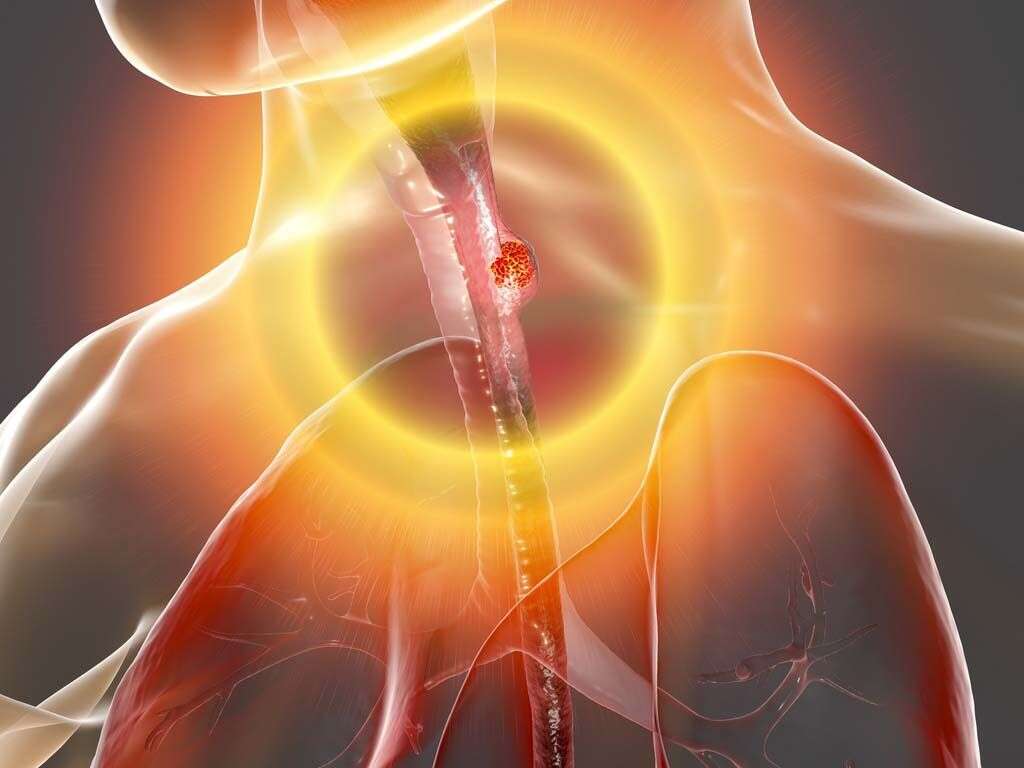
Throat cancer can be divided into two main types: pharyngeal cancer and laryngeal cancer. Pharyngeal cancer is further divided into three types: nasopharynx cancer, oropharynx cancer, and hypopharynx cancer. Risk factors of throat cancer include excessive alcohol consumption, tobacco use, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Epstein-Barr virus infection, and human papillomavirus infection. The risk of developing throat cancer increases with age in most patients over age sixty-five. Men are also more likely to develop throat cancer than women.
The diagnosis of throat cancer depends on the patient’s history, physical examinations, imaging tests, and biopsy. The survival rate depends on the location of the cancer and its stage. The stages of throat cancer are based on the TNM staging system (the size of the tumor, the presence of cancer in the lymph nodes, and metastasis). In 2009, as many as 30,676 cases of oropharyngeal and oral cavity cancer were reported in the United States, along with 24,900 cases of pharyngeal and laryngeal cancer.
Symptom #1: Cough
A cough is a repetitively occurring reflex that aims to clear the airway and breathing passages from irritants, fluids, microbes, and foreign particles. It is a common and nonspecific symptom that is observed in various infections. Smoking, choking, air pollution, gastroesophageal reflux disease, asthma, chronic bronchitis, post-nasal drip, lung tumors, and throat cancer can also trigger a cough.
There are three phases of cough: the inhalation phase, forced exhalation with a closed glottis, and the violent release of air after the opening of the glottis.

Symptom #2: Voice Changes
Voice changes are one of the earliest symptoms of throat cancer. In throat cancer, voice changes occur if the larynx, which includes the vocal cords, is compromised. Hoarseness is one of the commonest complaints that patients have when they are diagnosed with laryngeal cancer.
If a person has voice changes as well as risk factors of throat cancer, such as smoking, excessive drinking, and gastroesophageal reflux disease, it is best to seek medical attention to rule out throat cancer.

Symptom #3: Difficulty Swallowing
Difficulty swallowing can present as the sensation that there is food stuck in the throat. Patients may often choke on food. The medical term for difficulty swallowing is dysphagia. In the early stages of throat cancer, the symptom is often mild and gradually worsens over time as the opening of the throat gets smaller.
Patients tend to change their diet and eating habits without realizing it as swallowing becomes more difficult. Affected individuals tend to take smaller bites of food and chew their food slowly and more carefully. As the tumor enlarges, they may progress to softer and more fluid foods.

Symptom #4: Weight Loss
Weight loss is frequently a constitutional symptom of cancer. Other associated symptoms include loss of appetite, cachexia, and fatigue. Weight loss in throat cancer patients may result from loss of appetite, early satiety, difficulty swallowing, depression, and an increase in metabolism due to the cancer.
The weight loss may also occur due to the atrophy of the muscles as patients become less active in their daily routines. Affected patients are not able to eat enough to maintain their weight.

Symptom #5: Loss of Appetite
Loss of appetite is a lack of desire or reduced affinity for food. Cancer may be the cause of the symptom, especially if it is a cancer that involves the gastrointestinal tract. Cachexia and a metabolic change that occurs because of the cancer are other possible causes.
Cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy, can further complicate the condition. Side effects such as dry mouth, difficulty chewing, trouble swallowing, and mouth sores also contribute to appetite loss. The serious weight loss and muscle atrophy that may result can lead to physical weakness and decreased immune function. Affected patients should see a nutritionist.

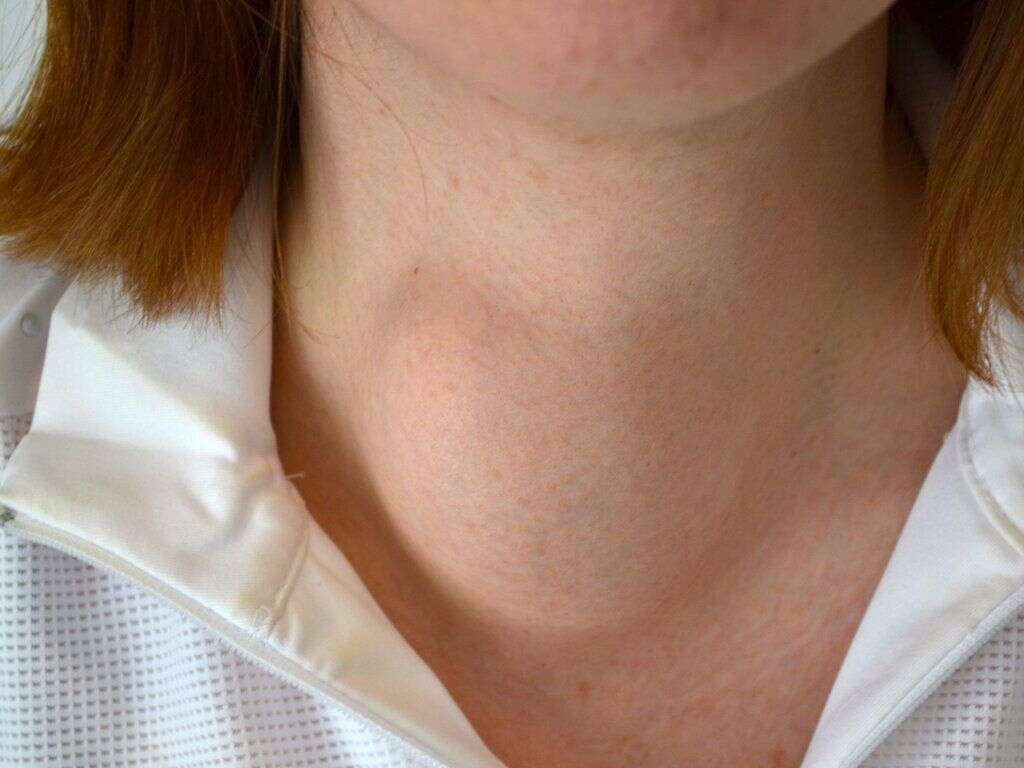
Symptom #6: Neck Lump
A lump on the neck is also known as a neck mass. The lumps can be either small or visibly large. While some neck lumps are harmless, some can be a sign of a serious condition, such as cancer or infection. In throat cancer, the neck lump could be the cancerous growth itself or it may be enlarged lymph nodes.
Lymph nodes filter pathogens, foreign materials, and cancer cells. Lymph nodes adjacent to the cancer are also one of the first sites where cancer spreads.
Symptom #7: Earache
An earache or ear pain can be one of the early symptoms of mouth or throat cancer. It can also be a symptom of an upper respiratory tract infection, such as acute otitis media.
However, an earache that is persistent and does not resolve with ear drops or antibiotic treatment warrants an appointment with the doctor to rule out malignant causes. Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) may also occur.
Symptom #8: Persistent Sore Throat
A sore throat is pain, discomfort, or irritation of the throat. Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and trauma are common causes of sore throats. Most sore throats are caused by an infection, and the symptom usually resolves once the infection is cured.
However, in patients with throat cancer, the sore throat is often persistent and does not go away. Other symptoms, such as fever, that often appear with a sore throat are also not present in patients with cancer.

Symptom #9: Difficulty Breathing or Wheezing
Difficulty breathing is also known as dyspnea and shortness of breath. It is a common issue for patients with throat cancer. Laryngeal cancer that affects the movement of the vocal cords can make breathing difficult. In these cases, it takes an extra effort for patients to breathe, which requires accessory and scalene muscles.
They may also develop wheezing or stridor, especially if the tumor causes the opening of the vocal cords to narrow. There are many causes of stridor, such as foreign bodies, infections, subglottic stenosis, laryngospasm, and vocal cord palsy. Visualization of the airway may be necessary to confirm the cause of the stridor.

Symptom #10: Constant Need to Swallow
Having a constant need to swallow or clear the throat is an early symptom of throat cancer. The presence of a tumor causes the patient to feel as if there is a lump in the throat, which results in the constant need to swallow.
It is a nonspecific symptom that can often be confused with other harmless conditions, such as a sore throat. However, patients with these issues should seek medical attention to rule out serious conditions, such as throat cancer.