10 Peptic Ulcer Symptoms
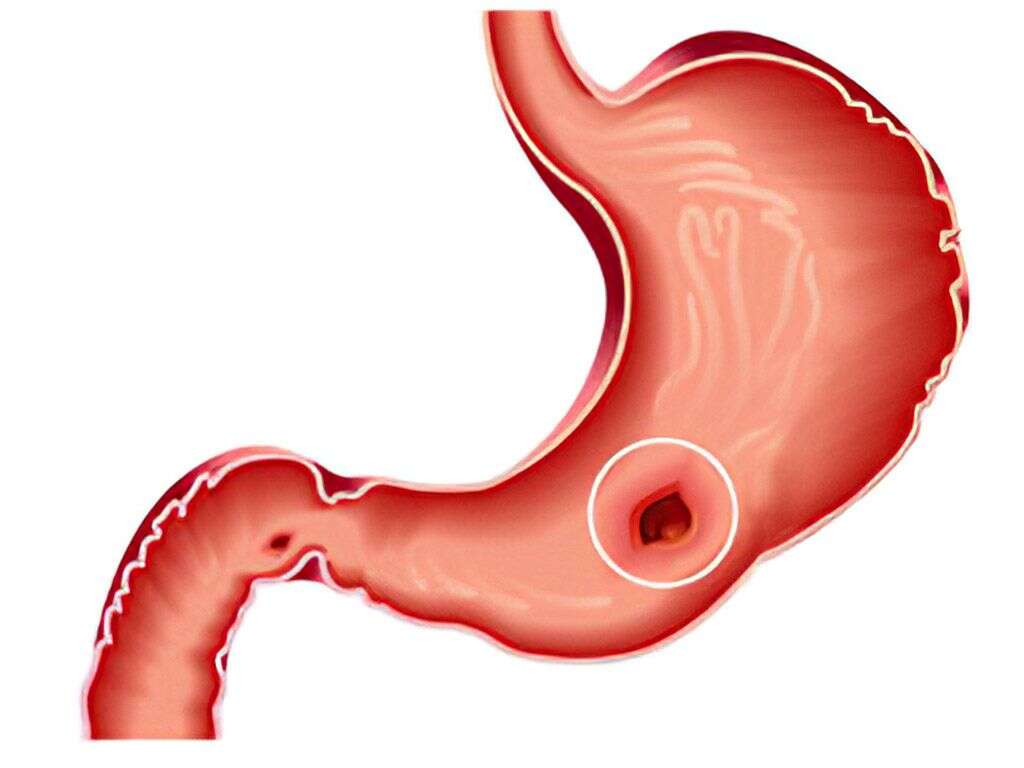
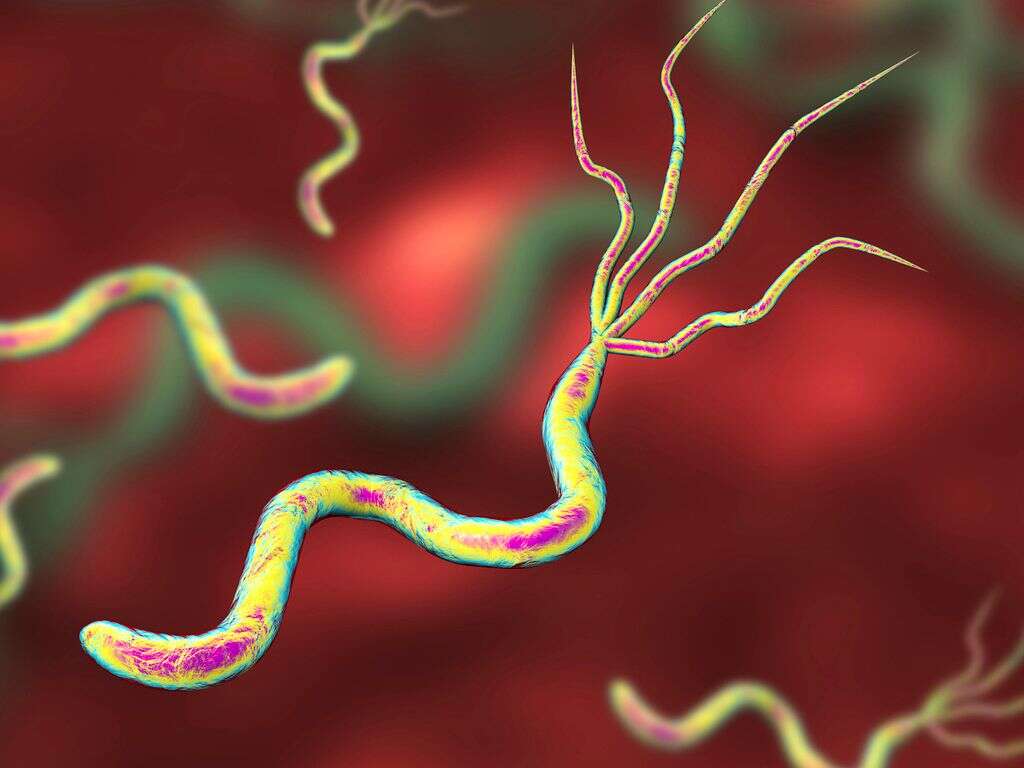
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) occurs when there is a break in the stomach lining, lower esophagus, or first part of the small intestine. An ulcer that occurs in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The commonest causes of PUD are the bacteria Helicobacter pylori and the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)i.e. ibuprofen, naproxen. Other contributing factors include tobacco smoking, severe physiologic stress, unknown genetic factors, and hypersecretory states (i.e. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome). PUD might lead to complications in approximately 20-25% of patients, such as bleeding, obstruction of the stomach, and perforation.
The diagnosis of PUD can be confirmed with an endoscopy. A chest radiograph can be useful to detect perforation. A Helicobacter pylori infection can be confirmed by testing the blood for antibodies, testing the stool for the bacteria, a urea breath test, or a biopsy of stomach tissue. The treatment and management of the disease involve quitting smoking, stopping the use of NSAIDs, avoiding alcohol intake, and taking medications (such as a protein pump inhibitor i.e. omeprazole or an H2 receptor blocker i.e. famotidine) to lower the production of stomach acid. Bleeding peptic ulcers can be treated through endoscopic procedures.
Approximately 4 percent of the global population have peptic ulcers. In 2015, peptic ulcers resulted in 267,500 deaths and about 87.4 million individuals had new ulcers. Approximately 10 percent of people develop an ulcer at some point in life.
Symptom #1: Upper Abdominal Pain
One of the most common symptoms of a gastric or duodenal ulcer is pain in the upper abdomen that occurs in the middle of the night or pain that improves or worsens after eating. The pain is often described as a dull ache or burning sensation. Most patients find relief after taking antacids orally.

Symptom #2: Belching
Belching is also known as burping. It refers to the release of gas from the digestive tract through the mouth. It generally occurs when air is swallowed then expelled after eating or drinking (particularly carbonated beverages like soft drinks and beer).
Belching is very common and can be a symptom of other gastrointestinal diseases as well.

Symptom #3: Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is a sensation of unease and discomfort that often includes an urge to vomit. Vomiting is the involuntary and forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth and sometimes the nose. It is also known as barfing, puking, or emesis.
Both nausea and vomiting are common and nonspecific symptoms that are often observed in various conditions, such as pregnancy, food poisoning, infection, and peptic ulcer disease. Patients with a chronic untreated duodenal ulcer may present with nausea and vomits after food intake due to a gastric outlet obstruction.

Symptom #4: Poor Appetite
Poor appetite is a nonspecific symptom that can be seen in various conditions, such as acute viral hepatitis, atypical pneumonia, appendicitis, cancer, chronic pain, chronic kidney disease, dehydration, dementia, fever, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease.
Treatment depends on the underlying cause.

Symptom #5: Bloating and Abdominal Fullness
Bloating and abdominal fullness refers to a full, tight, and distended abdomen. It is a very common symptom that can be seen in most gastrointestinal disorders. Some causes of bloating include lactose intolerance, food allergy, overeating, premenstrual syndrome, aerophagia, irritable bowel syndrome, constipation, menstruation, and diverticulosis.
The treatment and management of bloating depend on the underlying cause. Nevertheless, dietary modifications and certain medications may alleviate the discomfort.
Symptom #6: Heartburn
Have you ever experienced a burning sensation in your chest or throat hours after a fatty or heavy meal? That sour taste that remains in your mouth is no more than your stomach acids backing up into your esophagus. If this happens frequently, it’s called gastro-esophageal reflux (GERD).
However, heartburn may also be a common symptom in patients with peptic ulcer disease. It must not be mistaken with the severe dull and burning pain of PUD (epigastric or stomach area), given that they can occur at the same time.

Symptom #7: Hematemesis
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood that usually originates from the upper gastrointestinal tract. Some causes of hematemesis include Mallory-Weiss syndrome, erosion of the esophageal or stomach lining, vomiting of ingested blood from the nose or throat, tumors of the esophagus or stomach, radiation poisoning, gastroenteritis, and peptic ulcers.
Hematemesis is treated as a medical emergency since excessive blood loss can lead to shock.

Symptom #8: Melena
Melena refers to dark, tarry, and black feces that are associated with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. The feces can have a characteristic and strong odor from the hemoglobin in the blood, which has been altered by intestinal bacteria and digestive enzymes. The most common cause of melena is peptic ulcer disease. It can also occur as a complication of anticoagulant medications, malignant tumors, hemophilia, and Mallory-Weiss syndrome.
Iron supplements can also cause a grayish-black stool that should be distinguished from melena. Melena is a medical emergency, and urgent care is needed to rule out serious, life-threatening causes. Treatment will depend on the underlying cause.

Symptom #9: Acute Peritonitis
Peritonitis refers to the inflammation of the peritoneum, which lines the inner walls of the abdomen and covers the abdominal organs. In acute peritonitis, there may be severe pain, fever, and abdominal distension. It can lead to complications, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome and shock.
Acute peritonitis can occur in peptic ulcer disease, especially if there is a perforation due to the ulcer. Other causes of acute peritonitis include pancreatitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, stomach ulcer, ruptured appendix, and cirrhosis.

Symptom #10: Weight Loss
Weight loss is a common symptom seen among patients with gastric ulcer disease. Due to the associated symptoms of the condition, such as upper abdominal pain, belching, nausea, vomiting, and bloating, the affected individual may lose weight over time.
However, in patients with a duodenal ulcer, there may be weight gain since eating food may relieve the pain from duodenal ulcers.