Jock Itch Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Jock itch is an uncomfortable itch that affects the inner parts of the thighs and the crotch area. The infection is usually caused by fungi or yeasts, which thrive well in the warm, moist atmosphere of the groin. Fungal jock itch presents with a ring-shaped rash that has a slightly raised border. For this reason, it is sometimes called the ringworm of the groin.
The microorganisms responsible for jock itch live on the skin, usually without causing any problems. However, when moisture and warmth increase for prolonged periods of time, these microorganisms multiply rapidly and cause an itch. Jock itch is especially common in physically active individuals, who are more likely to sweat. It also occurs often in obese people and those who wear very tight clothing. Jock itch is more common in men than in women 1http://www.aafp.org/afp/2014/1115/p702.html. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and remedies of jock itch.
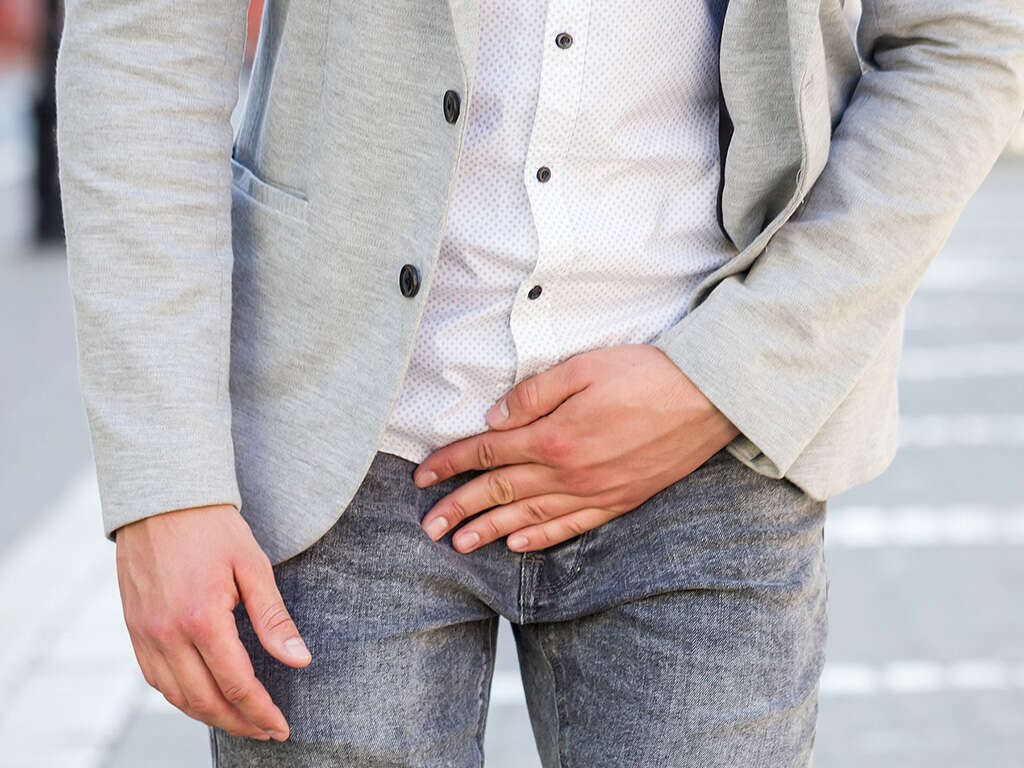

Cause #1: Ringworm Fungus
Ringworm fungus, also called tinea, is the most common cause of jock itch. The fungus thrives well in a warm, moist atmosphere. Therefore, people who are physically active, such as athletes, are more at risk because they are more likely to sweat and remain warm.
This provides the ideal conditions for the fungus to overgrow. Sharing contaminated clothing and equipment also can increase the chances of infection. For this reason, exercise equipment must be disinfected regularly. People also should not share towels or other garments.

Cause #2: Bacteria
Bacterial infections, such as impetigo and erythrasma, can also cause itching in the groin area. Erythrasma is caused by bacteria known as Corynebacterium minutissimum while impetigo is caused by Staphylococcus bacteria. Erythrasma appears more often in obese people and those with diabetes. Impetigo is more common in children.
Erythrasma is more like jock itch because it usually occurs in areas where skin touches skin, such as the groin and under the breasts. While impetigo can affect the groin, it is more likely to occur in other areas, including the armpits, lips, face, and arms. To avoid spreading the infection, minimize touching other people and avoid sharing clothes. Since they are bacterial infections, erythrasma and impetigo are treated with antibiotics.
Cause #3: Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis, also known as allergic contact eczema, can cause a rash in the crotch area or elsewhere. Allergic contact dermatitis is a skin reaction that is provoked when a chemical or other material comes into contact with the skin. Materials that may provoke allergic contact dermatitis include some soaps, detergents, and fabric softeners.
In most cases, allergic contact dermatitis will clear once the skin is no longer in contact with the allergen. If it is suspected that the jock itch is the result of allergic contact dermatitis, try to keep clear of the suspected substance that may be causing the rash. If this does not help, consult a dermatologist for assistance.

Symptom #1: Itchy Skin Rash
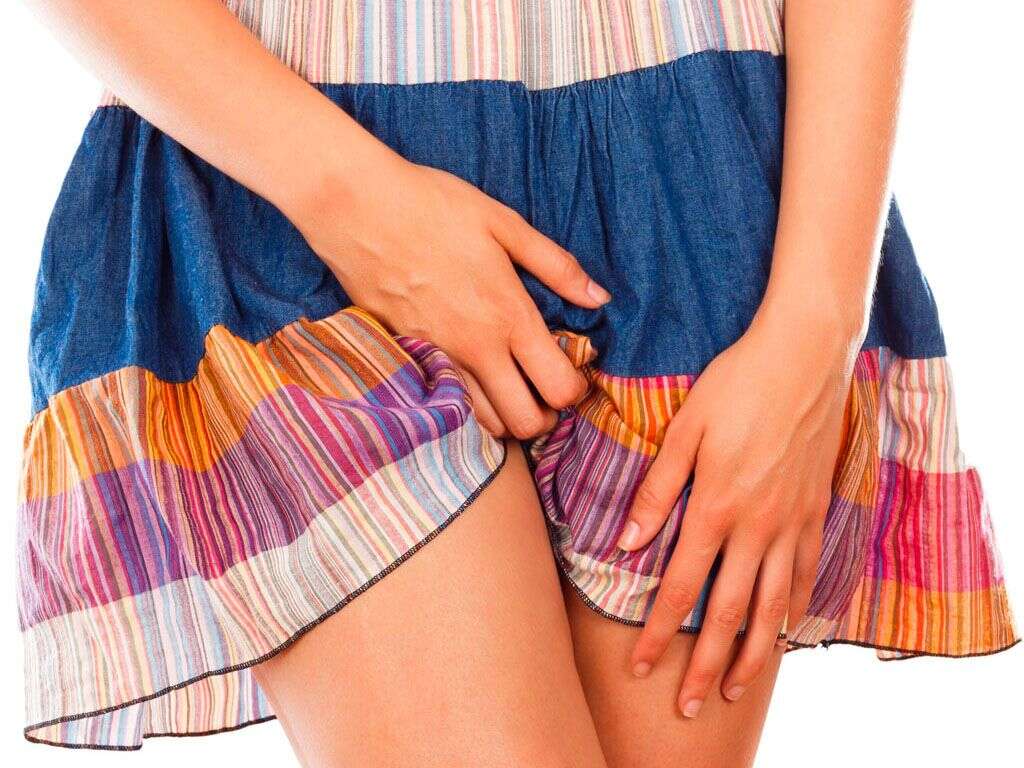
An itchy skin rash in the groin area is the most characteristic symptom of jock itch. The rash usually begins in a fold of skin before spreading to other areas because moisture and warmth are more likely to be trapped in the folds. Therefore, these areas provide ideal conditions for the microorganisms that cause jock itch to grow.
A jock itch rash is a dry, reddish, and scaly area surrounded by a round border of tiny, raised pimples. Scratching the itchy rash may worsen the condition if the scratching breaks the skin, causing increased irritation and pain. In addition, breaks in the skin expose the skin to other microorganisms, including bacteria, that may cause other infections.
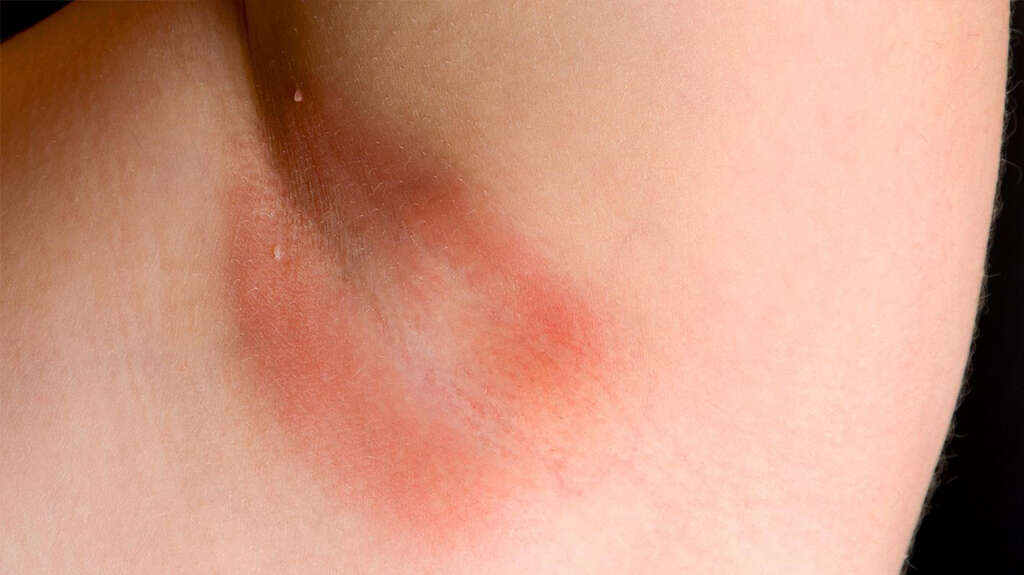
Symptom #2: Skin Irritation
Jock itch that presents with skin irritation in the groin area may be a symptom of contact dermatitis or eczema. It is estimated that about fifteen million Americans suffer from some form of eczema 2https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic_understanding_eczema. In eczema cases, itching may start before there is any sign of a rash. Scratching the itch leads to a rash that may spread to other areas.
The rash may present as patches of reddish or gray skin. With time, the rash changes into tiny, fluid-filled bumps, which may ooze and form a crust on the skin’s surface. Jock itch caused by contact eczema may disappear if the skin no longer comes into contact with the material that provokes it
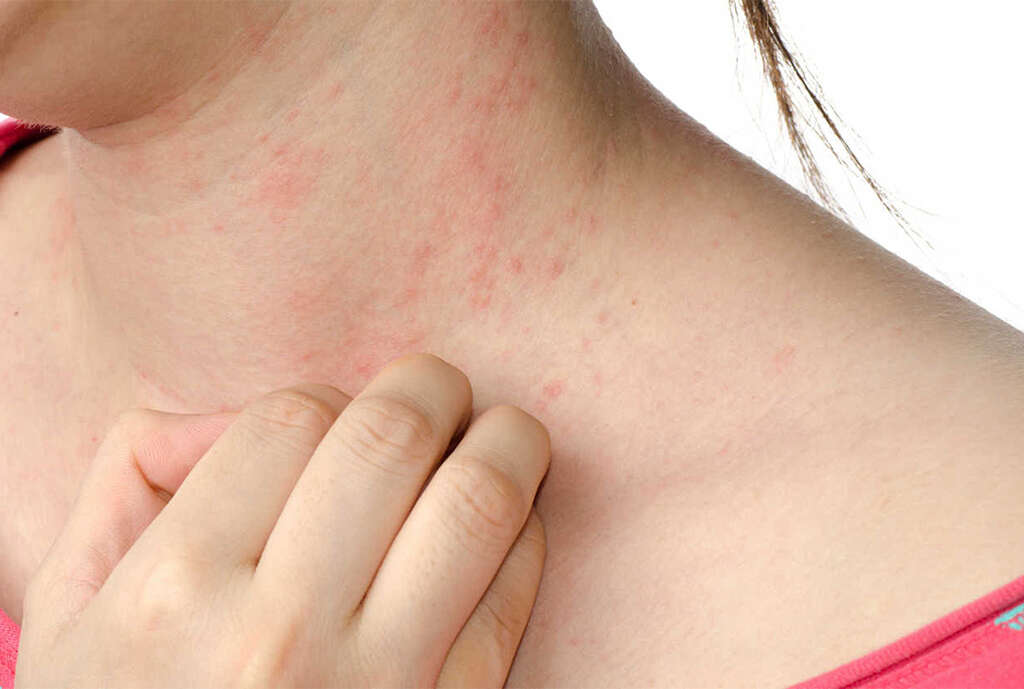
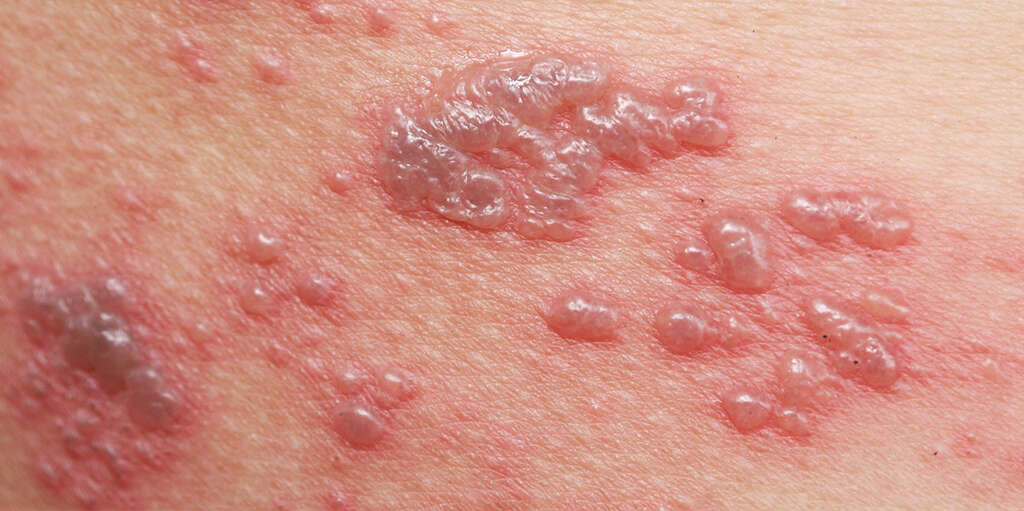
Symptom #3: Blisters
Jock itch may present with red spots or blisters, especially when bacteria is the cause. For example, in impetigo, the condition starts as sores that develop into blisters. Eventually, the blisters may burst open, oozing a yellowish fluid that forms a honey-colored crust on the skin’s surface.
As the crust forms, itching may escalate. Scratching an itch removes the crust, which causes bleeding and pain. Swelling of the lymph glands in the crotch area may also occur. When the wounds heal, they leave behind red marks, but they ultimately fade away and leave no scars.
Symptom #4: Hair Loss and Change in Skin Color
Jock itch can cause pubic hair loss in the affected area. When the infection affects a hair follicle, the follicle may no longer have the capacity to support hair growth. If a large area of the groin is affected, pubic hair loss may leave stubble or partial baldness. This condition is temporary, however, and the hair will usually grow back once the jock itch is treated.
Additionally, skin in the affected area may change color, becoming darker or lighter than the rest of the skin. Most of the discoloration clears once the jock itch heals. However, the skin discoloration may persist for weeks or months.

Jock Itch Remedy #1: Shower after Working Out
It is best to prevent jock itch before it happens. To do this, take a shower immediately after working out or engaging in physical activity. Showering washes away the sweat, dirt, and most of the microorganisms on the skin. After showering, dry the body with a clean towel and make sure to wipe off moisture from the crotch.
Additionally, avoid sharing towels and other garments. Instead, wear clean, loose cotton clothing (particularly undergarments) and use clean towels before and after working out. Another way to prevent jock itch is to put on socks ahead of the undergarments. This will ensure that fungus isn’t transferred from the feet to the crotch area. Jock itch can also be treated at home by soaking in a bathtub of water containing one-quarter cup of bleach. Afterward, dry the area and all skin folds with a clean towel.

Jock Itch Remedy #2: Antifungal Cream
If already infected, jock itch can be treated using zinc oxide to keep the crotch dry. By reducing moisture, zinc oxide helps reduce the number of microorganisms on the skin, which will help clear the infection.
However, if zinc oxide does not seem to help, use an antifungal cream. Antifungal creams contain clotrimazole or tolnaftate. They are generally effective and are available over the counter without a prescription. Make sure to buy a cream and not an ointment. Most ointments are greasy and trap moisture on the skin, which makes the infection last longer. Apply only a thin layer of the cream two to three times a day, and the infection should clear in a week or two.

Jock Itch Remedy #3: Prescription Medication
Some cases of jock itch do not clear even after using antifungal creams. This could mean that the cause of the infection is not a tinea fungus or is a resistant fungus. Besides tinea fungus, other causes of jock itch include bacterial infections, psoriasis, and contact dermatitis. In such cases, antifungal products won’t help. If antifungal powders and creams don’t work, consult a dermatologist for diagnosis and treatment with the appropriate jock itch remedies.
If the jock itch is the result of a bacterial infection, a doctor may prescribe a topical or oral antibacterial medication. Oral treatments may also be prescribed in cases of resistant fungal infections. If the jock itch is the result of other conditions, such as eczema and contact dermatitis, the doctor may prescribe an anti-inflammatory medication like hydrocortisone.