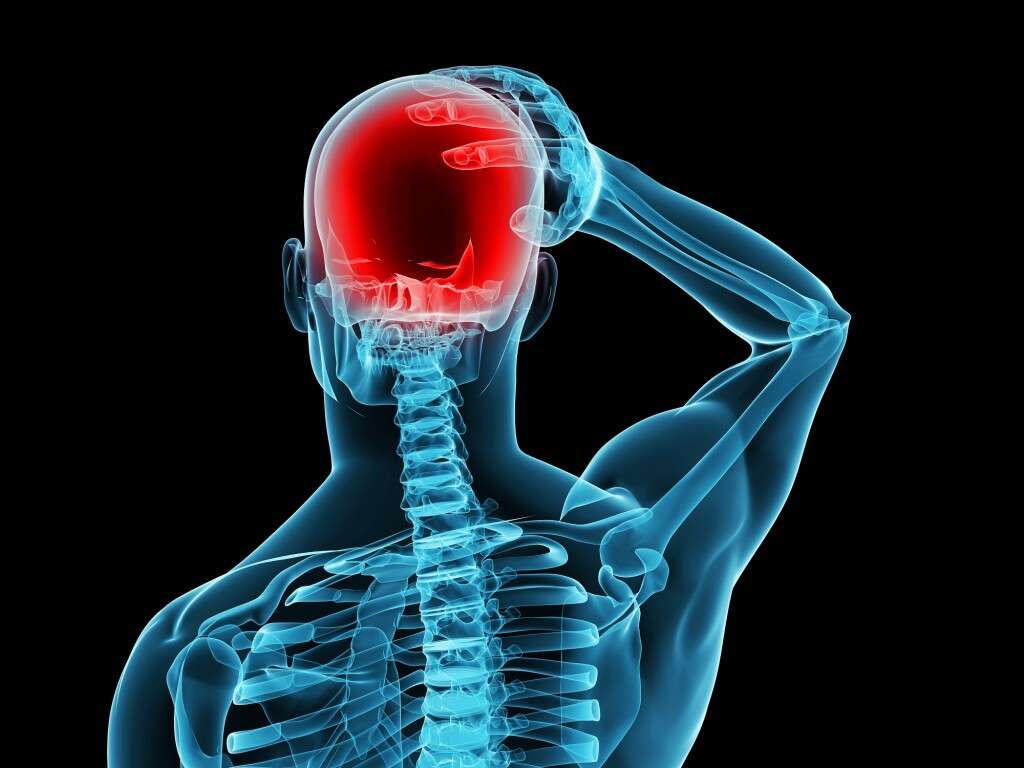
10 Hydrocephalus Symptoms
Hydrocephalus is a condition where there is excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain leading to increased intracranial pressure. In infants, a rapid increase in head size may be seen. It is a condition that can be acquired or due to birth defects such as neural tube defects that causes aqueductal stenosis. Other examples that can cause hydrocephalus are intraventricular hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, brain tumors, meningitis, traumatic brain injury, and more. Hydrocephalus can be divided into normal pressure, ex-vacuo, communicating, and non-communicating hydrocephalus.
The diagnosis of hydrocephalus can be made via physical examination and confirmed through medical imaging. Treatment usually involves the placement of a shunt through surgery. However, shunts can also cause complications such as underdrainage, overdrainage, infection, obstruction, or mechanical failure which may require the replacement of the shunt. Many patients with hydrocephalus who receive treatment go on to live normal lives. It has been estimated that approximately 1 to 2 per 1,000 individuals have hydrocephalus.
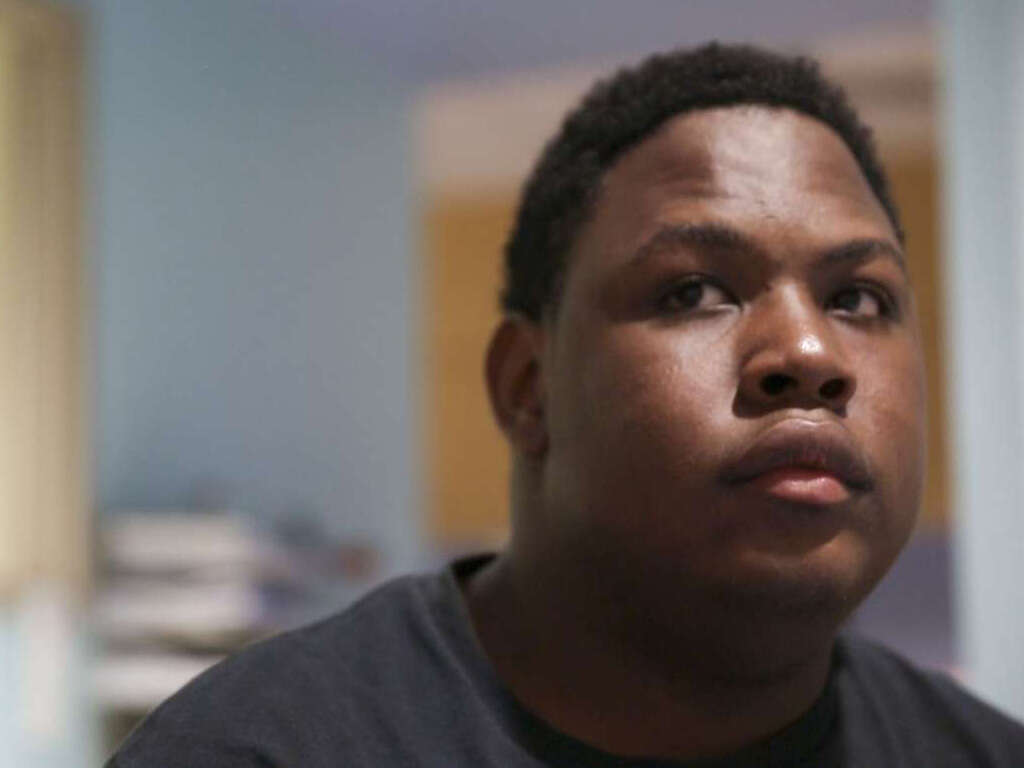

Symptom #1: Headaches
Headaches are a common issue that is observed in about 20 percent of the population. It refers to pain that can be felt anywhere in the region of the head and neck. There are many types of headaches such as migraines, tension type headaches, cluster headaches, and more. Those with frequent headaches may experience depression as it can affect employment and relationships.
Examples of conditions that can cause headaches include dehydration, stress, sleep deprivation, fatigue, viral infection, head injury, concussion, dental issues, temporomandibular joint disorders, and more. In hydrocephalus, headaches may be due to the increased intracranial pressure.

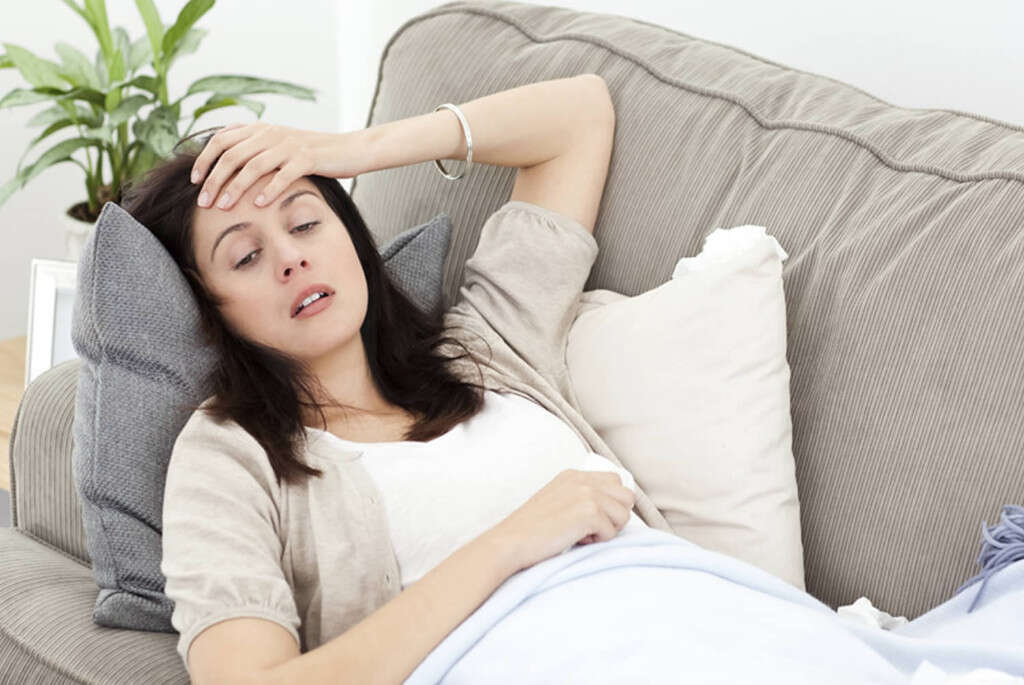
Symptom #2: Nausea
Nausea refers to an unpleasant and uncomfortable sensation where there is an urge to vomit. Although nausea does not result in pain, it can be a debilitating issue as there is discomfort that can be felt in the upper abdomen, chest, and throat. Nausea is the body’s way to discourage the individual from repeating situations or triggers that may have caused the unpleasant sensation.
Nausea can be a powerful sensation that elicits revulsion towards triggers. It is a common and non-specific symptom that is commonly seen in gastroenteritis, gastritis, pregnancy, motion sickness, hypoglycemia, food poisoning, and more. It can be managed using antiemetics.

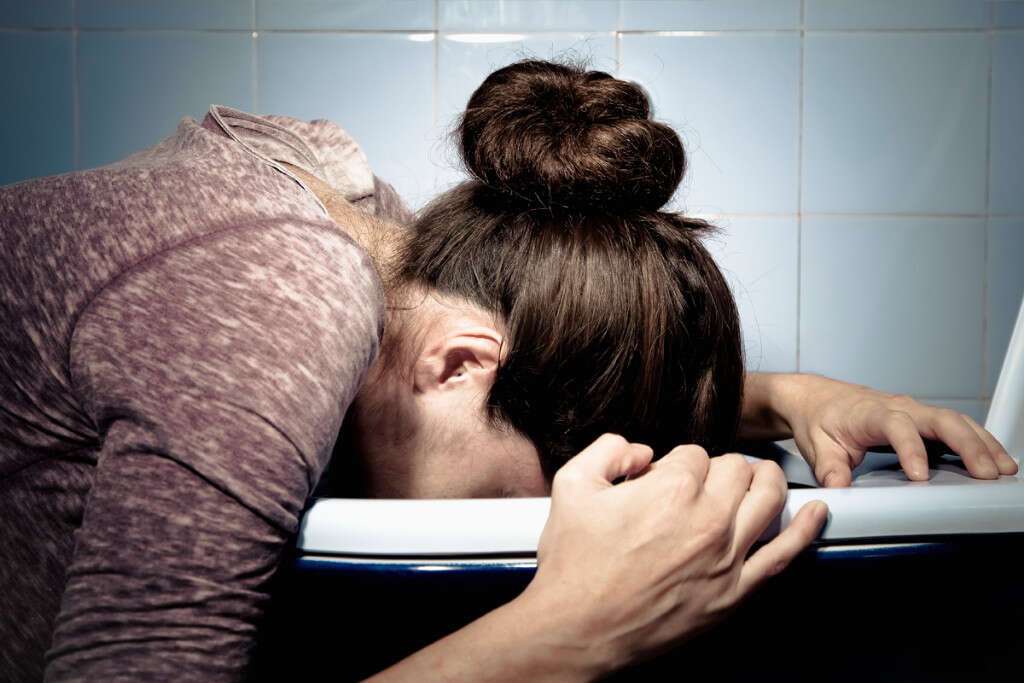
Symptom #3: Vomiting
Vomiting is also known as puking, barfing, or throwing up. It refers to the involuntary expulsion of one’s stomach contents through the mouth and nose. It is a common symptom that can be seen in various conditions such as poisoning, gastritis, elevated intracranial pressure, motion sickness, excessive pain, and more.
The treatment and management of vomiting may include the use of antiemetics such as promethazine, ondansetron, and metoclopramide. If severe dehydration occurs due to vomiting, intravenous fluids may be necessary.

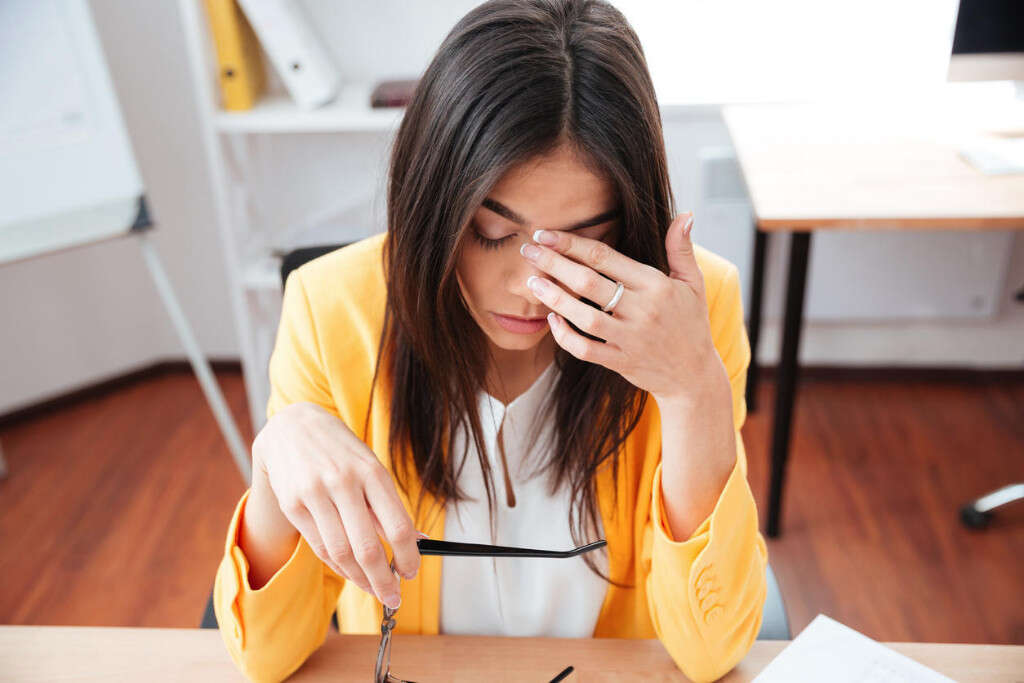
Symptom #4: Somnolence
Somnolence is a term describing drowsiness or sleepiness. It is a sensation where there is a strong desire for sleep. It can also refer to abnormally long periods of sleep. Associated symptoms of somnolence include lack of mental agility, weakness, and lethargy.
Somnolence can be seen in meningitis, hypothyroidism, concussion, hyponatremia, narcolepsy, brain tumor, fibromyalgia, mood disorders, hypercalcemia, head injury, sleeping sickness, hydrocephalus, and more. In hydrocephalus, somnolence may be attributed to increased intracranial pressure.

Symptom #5: Seizures
Seizures are episodes where there can be brief and undetectable to long periods of vigorous shaking that may result in physical injuries. It is an uncontrolled and sudden electrical disturbance in the brain that can alter behavior and levels of consciousness. Causes of seizures include epilepsy, head injury, stroke, meningitis, and more.
Patients who experience seizures can experience uncontrollable jerking of the body, confusion, loss of consciousness, anxiety, loss of awareness, and more. An episode of seizure that has never occurred before should be considered as a medical emergency.

Symptom #6: Irritability
Irritability refers to the tendency for frustration or anger. It can be a growing response to stimuli. Those who are affected are prone to anger, frustration, and are easily aggravated. It is commonly seen in high pressure or stressful situations. When one is short tempered and easily becomes frustrated, they can be considered to be irritable.
It is an emotion that can negatively affect the mood. It is also a term that parents often use to describe their children or infant child. Another expression that may be used interchangeably with the term “irritability” is “being fussy”. In children, irritability often indicates that there may be underlying discomfort.

Symptom #7: Failure to Thrive
Failure to thrive refers to the faltering weight that can be seen in children and infants. It indicates there is either inappropriate weight loss or insufficient weight gain. The child often has a low rate of increasing weight or low weight when compared to the majority of their peers.
Causes of failure to thrive include cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, anemia, cleft palate, hydrocephalus and more. Factors that contribute to failure to thrive in those with hydrocephalus include vomiting, difficulty feeding, excessive sleepiness, and irritability.

Symptom #8: Personality Changes
A person’s personality refers to all the ways how he or she feels, thinks, and acts. It comprises of habits, reactions, and quirks.
Examples of conditions that can result in personality changes include Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body dementia, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, multiple sclerosis, brain tumor, thyroid disease, brain injury, depression, stroke, and more. In hydrocephalus, the involvement of the brain may also cause personality changes.

Symptom #9: Muscle Spasms
Muscle spasms refer to the involuntary and sudden contraction of a muscle. Muscle spasms can occur due to abnormal nerve stimulation or abnormal muscle activity.
Severe spasms can result in tears or strains in tendons, ligaments, and muscles if it exceeds the underlying connective tissue tensile strength. A spasmodic muscle contraction can also be a muscle cramp associated with pain.
Symptom #10: Ocular Issues
In hydrocephalus, patients may experience ocular issues such as blurry vision, double vision, and sunsetting of eyes. Blurry vision refers to the hazy borders of an image while double vision occurs when the patient is seeing two images instead of one. In the sunsetting of eyes, it is a phenomenon observed in young children and infants with raised intracranial pressure.
The eyes appear to be driven downwards with upward gaze paresis. The sclera may be seen between the iris and upper eyelid while part of the pupil may be covered by the lower eyelid.