10 Causes of Geographic Tongue
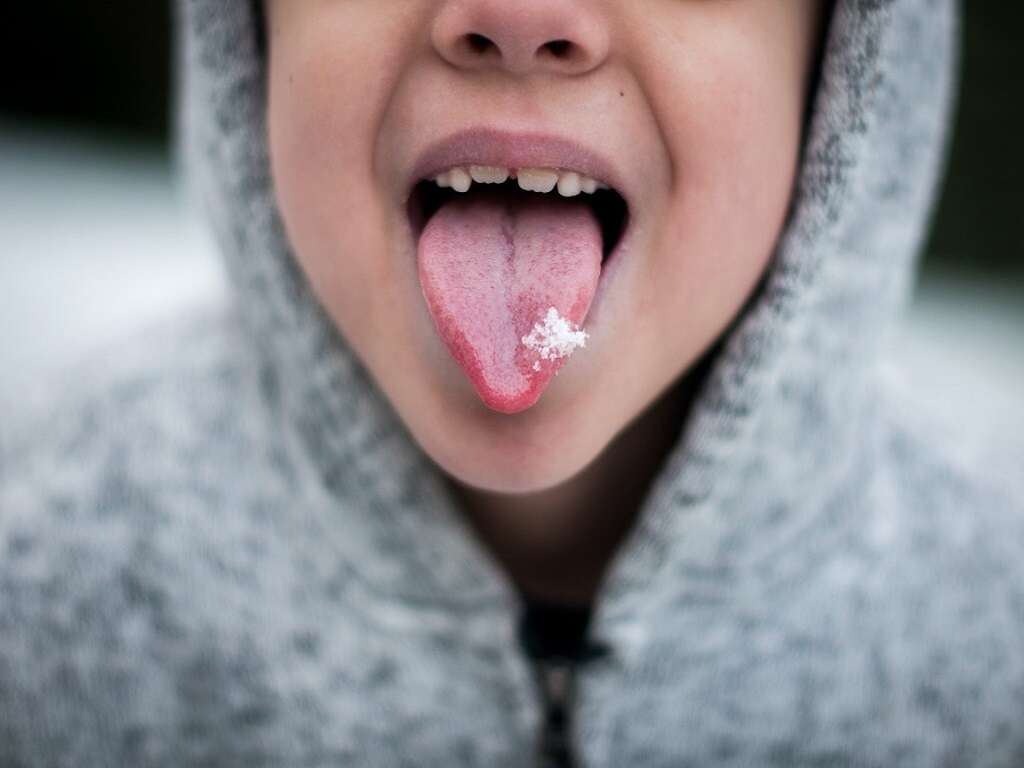
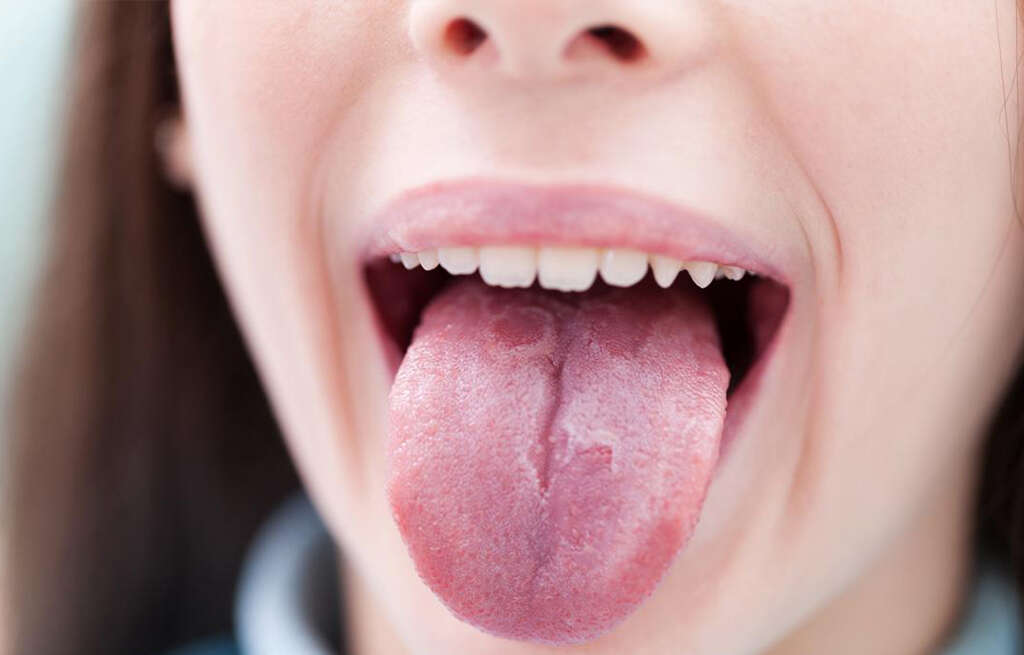
Geographic tongue, also known as erythema migrans, is an inflammatory condition that affects the tongue. It is mostly seen on the dorsal surface of the tongue. It is quite common, affecting 2 to 3 percent of the population.
The lesions often appear to be well demarcated and concentrated on the lateral or tip of the tongue. The erythema (redness) is thought to be due to the atrophy of the papilla. The atrophic areas are then surrounded by elevated, serpentine, or scalloped whitish borders. These depapillated and smooth areas migrate with time. The name of the condition thus originates from the map-like appearance on the tongue where patches resemble islands of an archipelago. The lesions are generally asymptomatic, although some patients experience a burning sensation when eating spicy foods.
Although geographic tongue has been around for many years, the exact etiopathogenesis of the condition is still unknown. However, it has been associated with the following factors.
Cause #1: Stress
Stress describes a feeling of pressure and strain thought to be a type of psychological pain. Small amounts of stress have been thought to be beneficial as it helps increase productivity and performance and small amounts of stress can help with adaptation and motivation. However, excessive stress can cause bodily harm as proven by various studies. Excessive stress can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, mental illness, ulcers, and more.
Various studies have found an association between stress and geographic tongue. Stress can occur during both positive and negative changes in life such as divorce, separation, death in the family, marriage, retirement, pregnancy, and so on.

Cause #2: Diabetes
Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders where there is high blood sugar for an extended duration. Patients with diabetes often experience polydipsia, polyuria, frequent urination, increased hunger, and more. It has been associated with increased risks of stroke, heart disease, foot ulcers, weight loss, kidney disease, and damage to the eyes.
Diabetes can be generally divided into type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Management of diabetes includes having a healthy diet, regular exercise routine, avoiding tobacco use, medications, insulin, and weight loss. Diabetes has been proposed to be a possible cause of geographic tongue.

Cause #3: Hormonal Disturbances
Hormones are chemicals in the body that are produced by the endocrine glands. They travel to tissues and organs resulting in reactions. Hormones help in the regulation of the heart rate, appetite, metabolism, sleep, growth, development, sexual function, reproductive cycles, stress, mood, and body temperature.
Both men and women can be affected by imbalances of growth hormones, insulin, adrenaline, and steroids. Other imbalances that are gender specific include testosterone, progesterone, and estrogen levels. Hormonal imbalances can cause symptoms such as changes in heart rate, dry skin, difficulty sleeping, weight gain, weight loss, sensitivity to the heat or cold, blood sugar, thirst, depression, and so on. It has also been proposed to be a possible cause of geographic tongue.

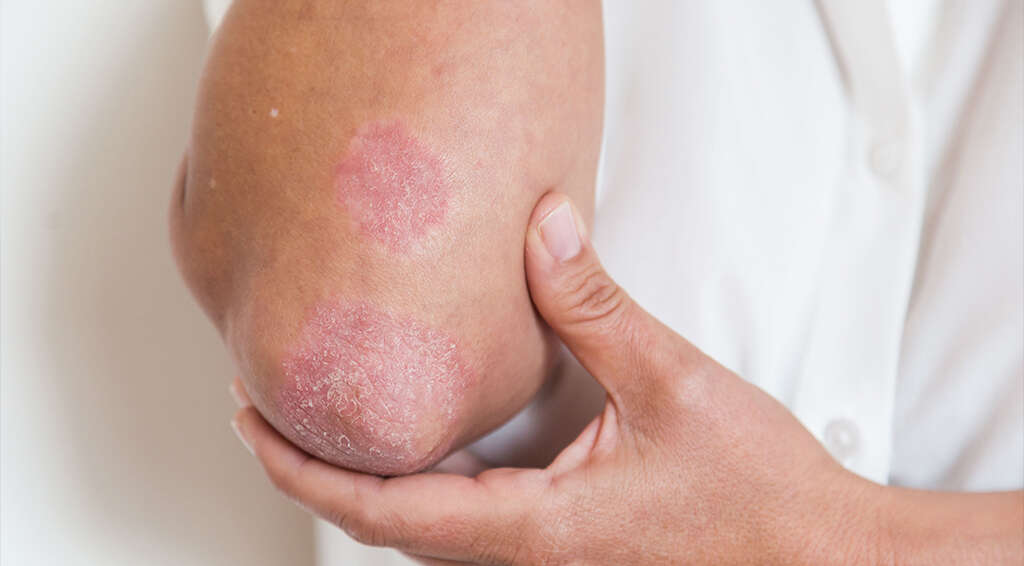
Cause #4: Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition where there are patches of abnormal skin. The patches are usually scaly, red, itchy, and dry. The severity varies ranging from small and localized patches to complete involvement of the body. Psoriasis can be divided into 5 types: guttate, plaque, pustular, erythrodermic, and inverse. Psoriasis can also affect the fingernails and toenails.
Psoriasis is not a contagious condition and it can be treated with vitamin D3 cream, steroid creams, immune system suppressing medications, and ultraviolet light. Psoriasis has been associated with increased likelihood of other conditions such as cardiovascular disease, psoriatic arthritis, lymphomas, and geographic tongue.
Cause #5: Allergies
Allergies are caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to substances that are usually harmless in the environment. This can result in allergic asthma, hay fever, atopic dermatitis, food allergies, anaphylaxis, and more. Patients with allergies may experience an itchy rash, runny nose, red eyes, sneezing, shortness of breath, and sneezing.
Treatment for allergies include avoiding allergens, using medications such as antihistamines or steroids, and injectable epinephrine (adrenaline) in severe reactions. Allergies have been reported to be one of the predisposing factors for geographic tongue.
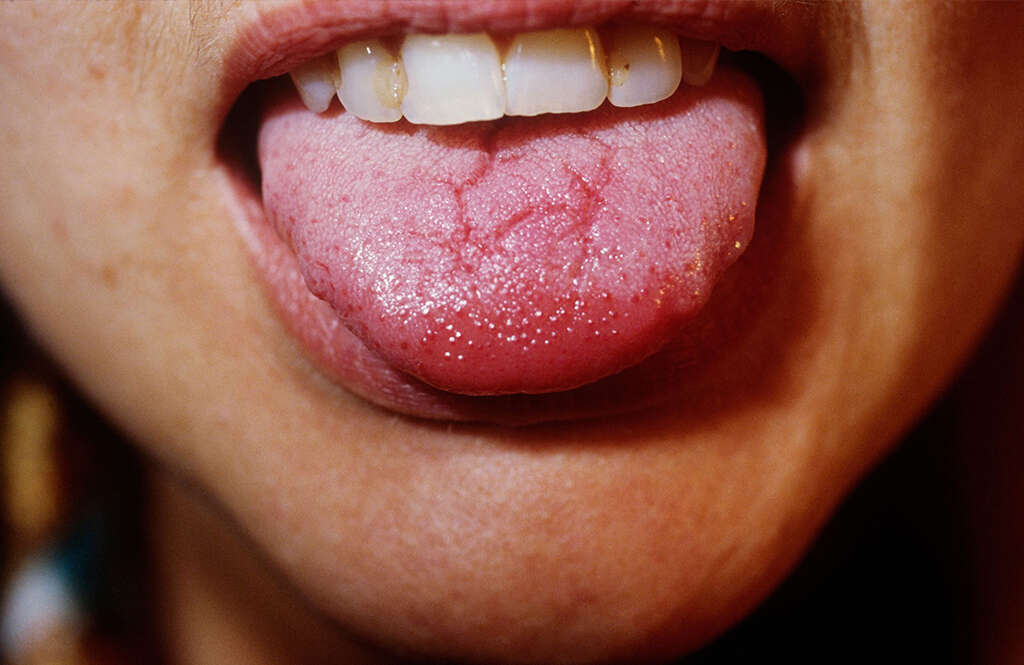
Cause #6: Hereditary Disorder
A hereditary disorder occurs when there are abnormalities in the genome passed on from a person to their offspring. Hereditary disorders can be caused by mutations or changes in the DNA passing on to the next generation if it occurs in the germline.
Hereditary disorders can be categorized based on how they are passed on to the next generation. Some examples include autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, x-linked dominant, x-linked recessive, y-linked, and mitochondrial. Geographic tongue is also a condition that tends to occur in families, which suggests that the condition may be hereditary.

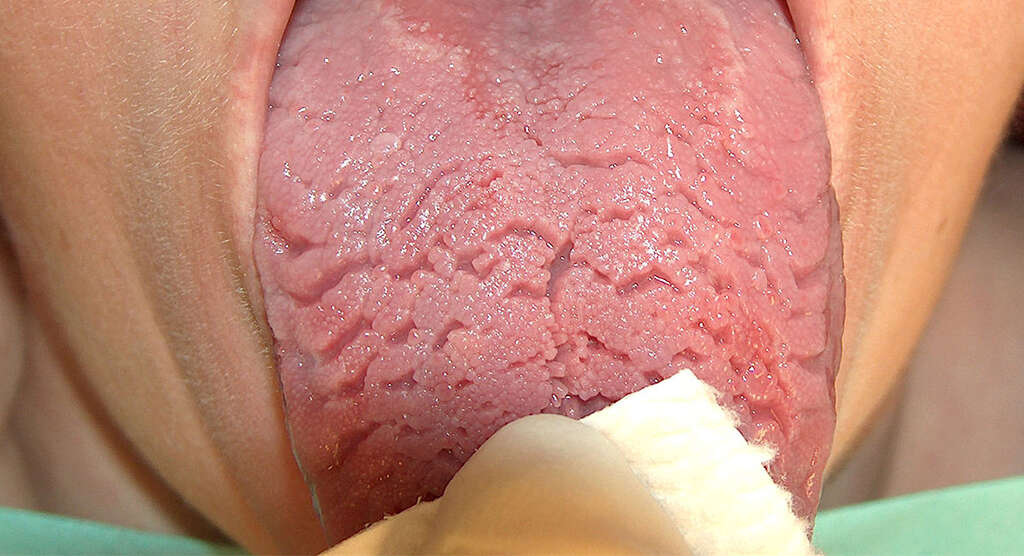
Cause #7: Fissured Tongue
Fissured tongue is also known as plicated tongue, furrowed tongue, scrotal tongue, or lingual plicata. This is a condition where there are deep grooves seen in the dorsal side of the tongue. Although it may appear unsettling, it is a painless condition. However, some individuals may experience a burning sensation.
Fissured tongue is thought to be hereditary as it is often seen among members of the same family. It is quite common, affecting 6.8 to 11 percent of the general population with males more commonly affected. Geographic tongue is also often associated with fissured tongue.
Cause #8: Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Chronic granulomatous disease is also known as chronic granulomatous disorder, Quie syndrome, or Bridges–Good syndrome. It refers to a group of hereditary disorders where the cells of the immune system are unable to form reactive oxygen compounds that function to kill ingested pathogens. This results in the formation of granulomata (a collection of immune cells that walls off substances that the immune system is unable to eliminate) in various organs.
Patients with chronic granulomatous disease will experience recurrent infections due to their reduced capacity to fight organisms that cause disease. Geographic tongue has been reported in association with chronic granulomatous disease.
Cause #9: Down Syndrome
Down syndrome is a genetic condition caused by the presence of a third copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21). This condition is associated with mild to moderate intellectual disability, delays in physical growth, and characteristic facial features. The parents of the patient are usually genetically normal. However, the chances of having a Down syndrome child increases to 3 percent once a woman reaches the age of 45 years old.
Down syndrome can be identified through prenatal screening and genetic testing. Although there is no cure for Down syndrome, the quality of life for those affected can be improved through care and specialized education. It is one of the commonest chromosomal anomalies in humans. Geographic tongue has also been associated with Down syndrome.

Cause #10: Reiter’s Syndrome
Reiter’s syndrome, or reactive arthritis, is a disorder where there is inflammatory arthritis due to cross-reactivity. This means that there is an infection in another part of the body that triggers the response of the immune system.
Reactive arthritis has the characteristic triad of symptoms. Patients usually experience inflammation of the eyes (uveitis or conjunctivitis), inflammatory arthritis of large joints, and cervicitis (women) or urethritis (men). Other symptoms include mucocutaneous lesions. Reiter’s syndrome is a proposed risk factor for geographic tongue.