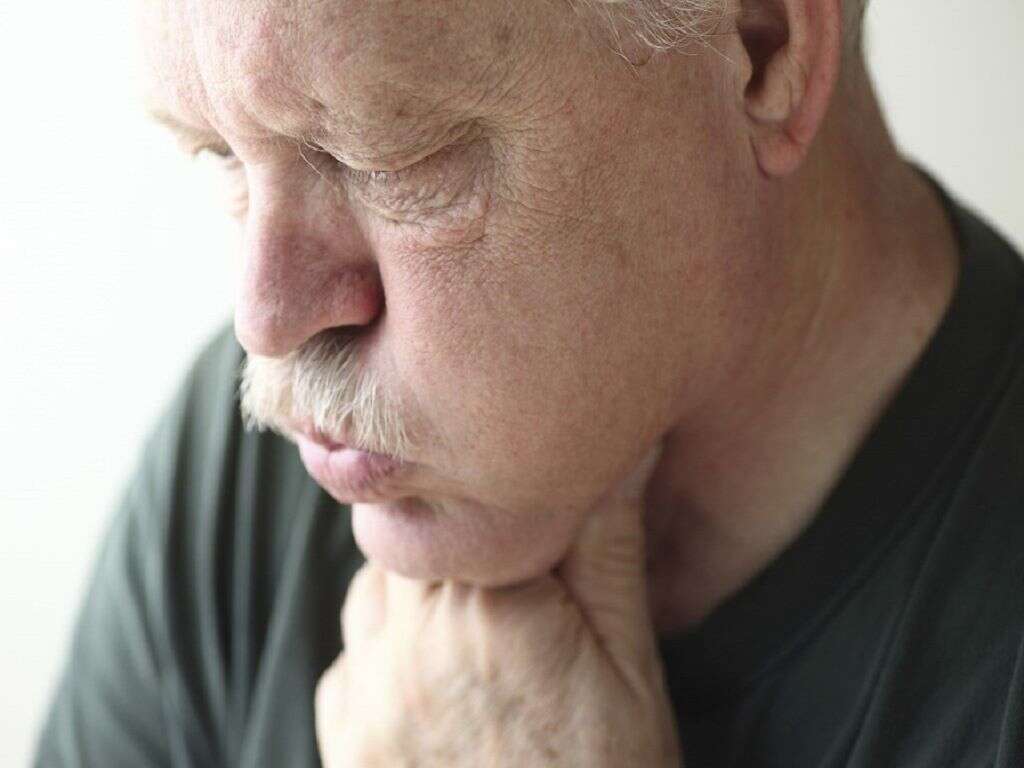
10 Enlarged Thyroid Symptoms
An enlarged thyroid, also called a goiter, occurs when the thyroid gland, which is located in the front part of the base of the neck, increases in size.
A goiter can be caused by a number of conditions including underproduction or overproduction of thyroid hormones, Graves’ disease, inflammation of the thyroid, also called Hashimoto’s disease, and thyroid cancer. However, many cases of enlarged thyroid occur due to iodine deficiency. This leads to the underproduction of thyroid hormones and ultimately to an enlarged thyroid.
A goiter affects more females than males, especially those in their thirties and forties.

Symptom #1: Tightness in the Throat
The location of the thyroid gland in front of the neck makes it easily noticeable in case of an overgrowth. Because of swelling, the thyroid gland can press against the windpipe, also known as the trachea, and cause breathing difficulty. Tightness in the throat may develop progressively over a period of time.
The swelling due to a goiter can lead to difficulties in swallowing as well. When these symptoms appear, they are a strong indicator of a thyroid disorder and medical attention should be sought. Additionally, thyroid-related swellings can occur among patients receiving radiation therapy around the neck.

Symptom #2: Fatigue
Unexplained tiredness, even when you have taken ample rest, can easily be due to functional problems with your thyroid. Due to its central role in determining the rate of metabolism in the body, decreased performance of the thyroid, and hence lowered hormone levels, can lead to less energy being produced for body functions.
As a result, one gets sluggish in performing their activities and are easily fatigued. The unusual feeling of tiredness can also be explained by the fact that thyroid hormones facilitate the body’s use of glucose, the major energy source, by enhancing the work of insulin hormone, which promotes the entry of glucose into cells.

Symptom #3: Palpitations
Among the many organs and systems that thyroid hormones influence is the heart. Thyroid hormones play a part in the control of the force and rate of contraction of heart muscles. Elevated levels of thyroid hormones, in the case of hyperthyroidism, increase the rate of heartbeats and blood pressure. One can feel their heart pounding or can manifest other forms of heart palpitations.
Urgent medical attention is necessary to ensure that heart functions and blood pressure are well controlled while investigating the underlying cause for the hyperactive thyroid. If the thyroid is underactive, then the opposite set of symptoms comprising decreased heart rate and low blood pressure usually occur.

Symptom #4: Increased Appetite
High levels of thyroid hormones impose greater demands for nutritional sources on the body. As the rate of utilization of food is increased, there is an urge to eat more. Besides the direct effect on the rate of metabolism, thyroid hormones also influence the rate of digestion. Depending on the type of food you eat, the increased food intake might lead to weight gain, weight loss, or no change in weight.
Additionally, other factors, including exercising and having other medical conditions, can determine the effects on weight. An increased appetite, therefore, can be a symptom of hyperthyroidism.

Symptom #5: Increased Sweating
Higher rates of metabolic activities in the body in a person with an overactive thyroid gland can lead to increased energy production. There is thus enhanced heat production. As a result, the body feels heated-up and, therefore, devises a way to cool itself down.
Consequently, the body’s temperature regulatory mechanisms cause an increase in the flow of the blood closer to the surface of the skin. The blood vessels near the skin surface dilate to facilitate the exchange of heat between the body and the surroundings. Sweat glands also produce more sweat to help the body lose more heat in a quest to maintain a healthy temperature.

Symptom #6: Weight Loss
As mentioned earlier, the thyroid gland produces chemical substances referred to as hormones that play a role in controlling growth and metabolism. Metabolism is the process by which the body takes in and utilizes nutrients to produce energy.
Unexplained weight loss can result due to hyperthyroidisms, as the increased metabolism causes nutrients to be processed differently. On the other hand, hypothyroidism is associated with weight gain.

Symptom #7: Hyperactivity
Enhanced speed of metabolism follows elevated levels of thyroid hormones. Thus, a person with an overactive thyroid can be extremely active. Besides influencing the cellular metabolism, an overly active thyroid can influence the mental status of an individual, making them react disproportionately to stimuli or situations.
When you find yourself or a loved one becoming very irritable, nervous, unable to sleep, restless, or even anxious without any tangible or rational cause, you should consider establishing if all is well with the thyroid gland function. Similarly, a thyroid gland with depressed activity will lead to a general slowing of mental functions and physical activities.

Symptom #8: Heat Hypersensitivity
Thyroid hormones, due to their role in regulating the rate of metabolism in the body, are responsible for temperature control and reaction to temperature variations. When the goiter is caused by a hyperactive gland, the consequence is heightened metabolism in cells, accompanied by production of a lot of energy.
High energy production leads to increased heat, which may cause heat discomfort. On the other hand, an underactive thyroid will make the metabolism rates of the body to be too low. When little energy and, therefore, little heat is produced in the body, it becomes difficult to bear conditions of low temperature. This can lead to intolerance of cold environments.
Symptom #9: Constipation
Slowing down of the body’s metabolism due to hypothyroidism can manifest as reduced intestinal movements. Contraction of the muscles of the intestines propel the contents and aid in the passing of stools. If slowed contraction of these muscles is prolonged, a person can get constipated.
So, if you suffer from constipation, which you cannot relate to any disease, medication, or food, you should probably go for tests to find out if you have thyroid issues. If, on the other hand, you have an overactive thyroid gland, increased intestinal movements and diarrhea can occur. Whereas medications to treat constipation and diarrhea are readily available, it is important to address the root causes of the respective conditions.

Symptom #10: Hair Loss
Have you noticed an increased amount of hair on your comb and you are not aware of any health condition you may have, and you are not on any treatment that could have this effect? Maybe you need to see a doctor to find out what could be the cause of your hair loss. Thyroid problems that cause a goiter can cause hair loss.
Cases of hair loss have been reported among people who have either an underactive or a hyperactive thyroid. It is, however, relieving to note that hair growth is usually restored once the thyroid dysfunction is corrected. This observation affirms the critical role that thyroid hormones play in regulating growth and differentiation of almost every tissue in the body.