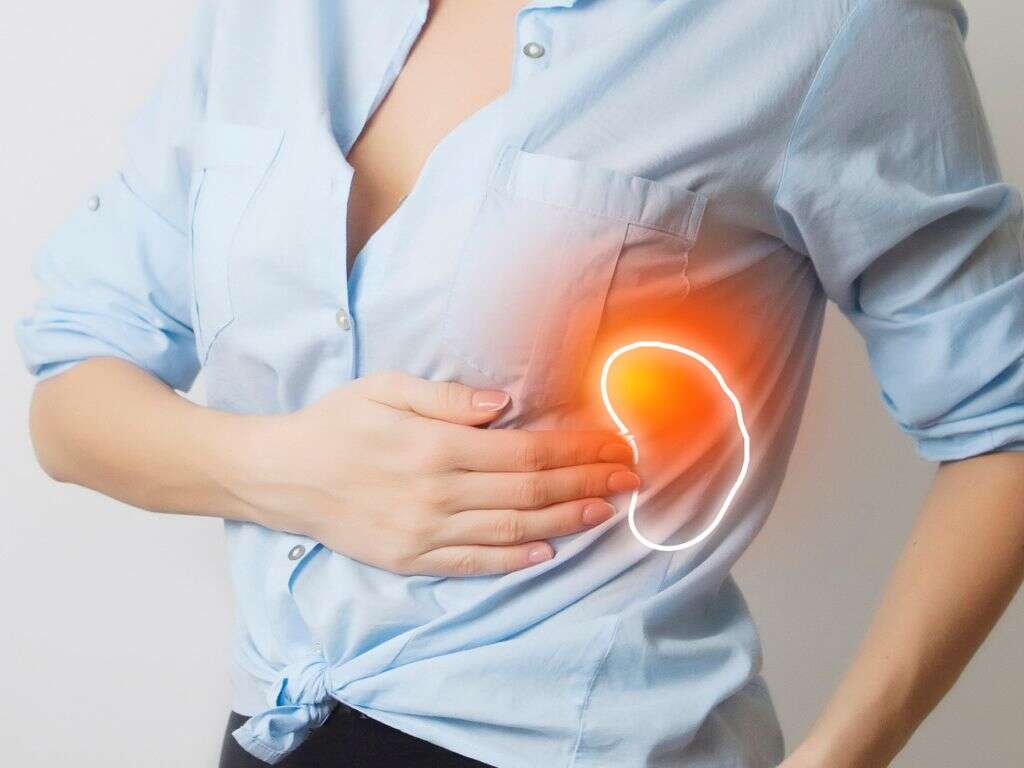
10 Enlarged Spleen Symptoms
The spleen is located in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, just below the ribs. It plays an important role in our immune system by helping to clear pathogens in the bloodstream. It also produces certain compounds like immunoglobulin G which are very important for the proper functioning of our immune system. Additionally, it is also involved in filtering and removing abnormal red blood cells (RBC).
Usually, the spleen is not palpable in adults. Therefore, a palpable spleen might be a sign that something is wrong with the size of this organ. Splenomegaly is the medical term used to describe an abnormally big spleen. It can be caused by many conditions such as infectious diseases (mononucleosis), blood-related disorders (thalassemia major or spherocytosis), congestive disorders (cirrhosis and congestive heart failure), and other conditions like sarcoidosis and some forms of lymphomas. The treatment is usually focused on managing the underlying condition that is causing the spleen to be enlarged and to prevent complications. Patients with an enlarged spleen have a higher risk of splenic rupture, therefore, it is important to avoid any activities that could lead to abdominal trauma.

1. Abdominal Discomfort
Abdominal discomfort is the most common symptom associated with an enlarged spleen. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions but it is usually seen in symptomatic patients with splenomegaly.
Patients may complain of discomfort in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, but this is not always the case. Due to the large size of the affected spleen, it can push other surrounding organs, causing the typical diffuse feeling of abdominal discomfort.

2. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. The location and characteristics of the pain can help to distinguish between different pathologies and it can be very useful information to the clinicians in order to provide an accurate diagnosis.
Usually, most patients complain about abdominal discomfort, but depending on the cause and the size of the spleen, mild abdominal pain might also appear. The pain is usually but not exclusively limited to the upper left quadrant of the abdomen. If the pain is too intense, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible to rule out any complications.

3. Early Satiety
Early satiety can be described as requiring less amount of food in order to reach the usual level of food-related satiety. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions. Usually, this symptom can be seen in common gastrointestinal tract (GI) disorders like gastritis and gastroenteritis but it can also be associated with more severe conditions like stomach cancer and other disorders that are not necessarily GI-related.
Due to the proximity of the spleen and the stomach, it is common to see the enlarged spleen push against the stomach. This causes can cause the stomach to have a reduced capacity, resulting in early satiety.

4. Loss of Appetite
Hyporexia is the medical term that describes when a person has a reduced appetite. If a person refuses to eat anything due to a total lack of appetite, then the condition is called anorexia. Many conditions can cause a person to lose their appetite, some of them are not even medical related.
This symptom can be related to the compression effect that the enlarged spleen exerts onto the neighboring stomach. It can also be associated with a systemic manifestation of an infectious condition or a malignancy.

5. Fever
A fever is an increase in body temperature. Usually, the temperature should be above 38⁰C (100.4⁰F) in order to be considered as a fever, but this depends on the site where the temperature is being measured. A fever is usually a response of the body to a threat. By increasing the body’s thermostat set point, we start to shiver to generate heat in order to reach the new temperature that has been set.
This symptom is not directly related to the enlarged spleen, rather it might be associated with the underlying condition that causes the splenomegaly. One of the most common causes of an enlarged spleen is an infectious disease such as infectious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein Bar Virus (EBV).

6. Weight Loss
Weight loss is not always something to be worried about, especially if it happens progressively and if it is associated with a healthy change in either food consumption or exercise activity. The problem comes when the weight loss happens unintendedly and/or over a short period. Many conditions are known to cause weight loss, especially if the patient is losing fluids through vomiting or diarrhea. It is important to know that drastic and unintended changes in weight, such as losing over 10 kilograms in less than 6 months can be a sign of a serious medical condition.
For patients with splenomegaly, weight loss can be a result of the associated decreased appetite due to stomach compression. On the other hand, if the weight loss is too drastic, other conditions like leukemia and lymphoma should be ruled out immediately by a health care professional.

7. Fatigue
Fatigue can be described as a general feeling of exhaustion. Usually, this symptom improves with adequate rest, but depending on the source of the problem, it may not improve at all. It can be triggered by exercise, stress, and work-related activities. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions like anemia and anxiety, to name a few.
The spleen is in charge of filtering abnormal red blood cells (RBC). Some blood-related disorders like thalassemia major and spherocytosis can cause the spleen to work over-time, causing it to become enlarged. Fatigue is one of the most common symptoms associated with anemia in these patients.

8. Easy Bruising
Bruising is a normal response to trauma. Nevertheless, not all traumas should cause a bruise. If you find yourself bruising without being able to remember the related trauma or if you find that you are bruising easily to low-force traumas that previously produced no consequence whatsoever, then, you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.
Liver damage and cirrhosis are known causes of splenomegaly. If liver function is compromised, many processes are going to be affected. One of the most common signs of liver damage is easy bruising due to the lack of production of vital compounds involved in coagulation.

9. Shortness of Breath
Dyspnea is the medical term used to describe sudden shortness of breath. It is characterized by having difficulty breathing which may or may not be associated with a feeling of tightness in the chest. Dyspnea is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with both respiratory and circulatory conditions. It is important to state that exercise-induced dyspnea is usually a normal and transitory state of air hunger which is not directly related to a disease, whereas, resting shortness of breath is usually a sign that something might be wrong.
The anemia seen in blood disorders like thalassemia major and spherocytosis can cause a patient to experience shortness of breath. As the oxygen supply to the tissues becomes compromised, dyspnea appears. Both of these blood disorders are known causes of splenomegaly, therefore, in the presence of splenomegaly and shortness of breath, anemia should be considered as a possible cause.

10. Malaise
Malaise is a very subjective symptom that can be described as a general feeling of discomfort or a state of uneasiness that is quite difficult to describe. Due to its subjectivity, it is not a very helpful diagnostic tool, as it is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions.
Malaise is a common symptom associated with splenomegaly. Either directly caused by the enlarged spleen or indirectly related to the underlying cause of the problem, it can be an annoying symptom that may cause the patient to have a disruption in their daily activities.