10 Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition where there is pain affecting the trigeminal nerve. Trigeminal neuralgia can be divided into typical and atypical neuralgia. The typical form results in sudden, severe, and shock-like pain on the affected side of the face lasting from seconds to minutes. Multiple episodes or attacks can occur over a few hours. In the atypical form, patients usually experience a constant burning pain that may be less severe. Episodes of these attacks can have multiple triggers such as a touch to the face, shaving, drinking, eating, brushing teeth, a breeze blowing on the face, smiling, talking, and more, which can negatively impact the patient‘s quality of life.
Both typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia can occur in the same individual. Since it is a debilitating issue, it can also lead to depression. While the mechanism of how trigeminal neuralgia occurs is unclear, it is thought to be attributed to the loss of myelin sheath of the trigeminal nerve. The diagnosis can be made based on the symptoms the patient experiences after other possible causes are ruled out. The treatment of trigeminal neuralgia usually involves medication such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, baclofen, pimozide, and others.
Surgery is also an option for those who do not experience alleviation of symptoms with medication. Approximately one in every 8,000 individuals suffer from trigeminal neuralgia. It is usually seen in individuals over the age of fifty and is more commonly seen in women compared to men.

Cause #1: Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a disease where demyelination of the nerve cells in the spinal cord and brain occurs. This results in the disruption of communication in the nervous system resulting in mental, physical, and psychiatric symptoms. Examples include double vision, muscle weakness, blindness in one eye, and difficulty with coordination.
Trigeminal neuralgia is one of the early symptoms observed in multiple sclerosis. Since multiple sclerosis is a disease that causes demyelination, myelin deterioration of the trigeminal nerve can result in trigeminal neuralgia.
Cause #2: Stroke
A stroke occurs when there is poor blood flow to the brain resulting in cell death. Stroke can be divided into hemorrhagic (bleeding) and ischemic (decreased blood flow) types. Signs and symptoms of stroke include dizziness, inability to move one side of the body, slurring of speech, loss of consciousness, and issues with vision, among others.
A stroke can cause trigeminal neuralgia if it affects where the trigeminal nerve enters at the lower part of the brain. Some risk factors of stroke include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, and smoking.

Cause #3: Tumor
A tumor is a mass of abnormal growth of tissue. It can refer to a solid or fluid filled cyst. Examples of tumors that may cause trigeminal neuralgia include a meningioma or arachnoid cyst. The compression of the nerve from the tumor may injure the protective myelin sheath of it resulting in hyperactive and erratic functioning.
This means slight stimulation of the area supplied by the nerve may result in pain. It may also hinder the ability of the nerve to stop transmitting pain signals even after the stimulation has ended.
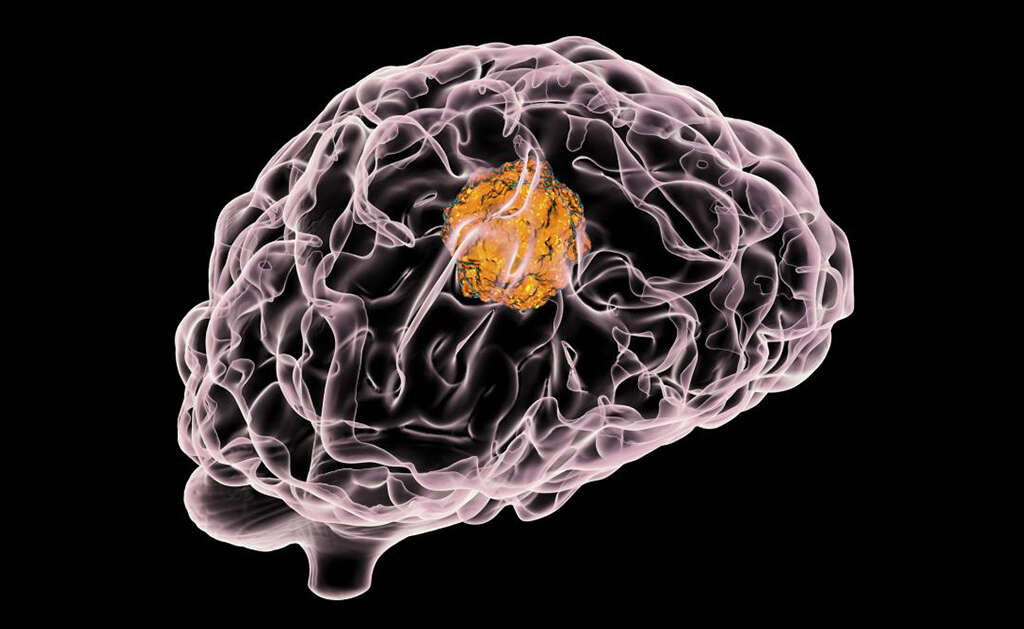
Cause #4: Arteriovenous Malformation
Arteriovenous malformation refers to a network or connection of abnormal arteries and veins that bypasses the capillary system. While many are asymptomatic, they can also cause serious issues such as bleeding and intense pain. Most arteriovenous malformations are congenital.
The signs and symptoms for an arteriovenous malformation depend on the location of the malformation. Most are discovered as part of an incidental finding. Those in the brain can result in neurological deficit, epilepsy or pain. If one happens to compress the trigeminal nerve, it can also cause trigeminal neuralgia.
Cause #5: Aneurysm
An aneurysm refers to a weakened spot on the wall of a blood vessel causing it to bulge outward like a balloon. It can be an acquired or hereditary condition. The risk of rupture increases as the aneurysm increases in size. This can lead to uncontrolled bleeding.
While an aneurysm can occur anywhere, lethal examples include abdominal aortic aneurysms and aneurysms in the circle of Willis. The presence of an aneurysm that happens to compress the trigeminal nerve can result in trigeminal neuralgia.

Cause #6: Aging
Aging is a natural process where one becomes older. This term is used especially for humans. In humans, aging leads to changes in physical, psychological and social aspects. It is also the greatest known risk factor for many diseases.
While experts are still unclear how aging occurs, it is thought to be attributed to the damage concept where damage accumulation such as DNA oxidation can result in the failure of biological systems. Trigeminal neuralgia can be a result of aging.

Cause #7: Scleroderma
Scleroderma refers to a group of autoimmune disorders that can cause changes in the muscles, skin, vessels, and organs. The disease can involve the skin and other organs with symptoms of tiredness, thickened skin, stiffness, and cold extremities. While the cause is unknown, some think that it may be due to an abnormal immune response.
The risk factors of scleroderma include genetic factors, positive family history, and exposure to silica. Trigeminal neuralgia has also been observed in scleroderma patients.
Cause #8: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease which can present with multisystem symptoms. It is a disease that affects individuals of any age. Common symptoms of SLE include fever, painful joints, swollen joints, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, tiredness, and rash.
It is thought that SLE is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While rare, trigeminal neuralgia has been reported to be one of manifestations seen in SLE.
Cause #9: Trauma
Trauma is a term that can refer to traumatic injury such as physical injury as a result of external force. Trigeminal neuralgia caused by trauma is also known as posttraumatic trigeminal neuropathy.
It occurs if pain is localized to the distribution of the trigeminal nerve less than six months after the traumatic event. The trauma can be thermal, mechanical, chemical, physical, or caused by radiation. Head trauma can also result in trigeminal neuralgia.

Cause #10: Surgery
Surgery is defined as the use of instruments and techniques to repair, improve, or treat a pathological disease or injury.
In surgeries such as wisdom tooth removal, it can result in trigeminal nerve injury that can cause trigeminal neuralgia. While most nerve injury is temporary, severe damage to the nerve can cause permanent damage.