10 Causes of Skin Rashes
A skin rash is any sort of skin inflammation. The normal skin color or texture will change and the skin becomes scaly, bumpy, or itchy.
In most cases, a skin rash is not dangerous and it tends to resolve on its own. Medications commonly recommended for the treatment of a skin rash include anti-itching creams, oral antihistamines, and moisturizing lotions.
But what causes a skin rash in the first place? Continue reading about the 10 most common causes of a skin rash.

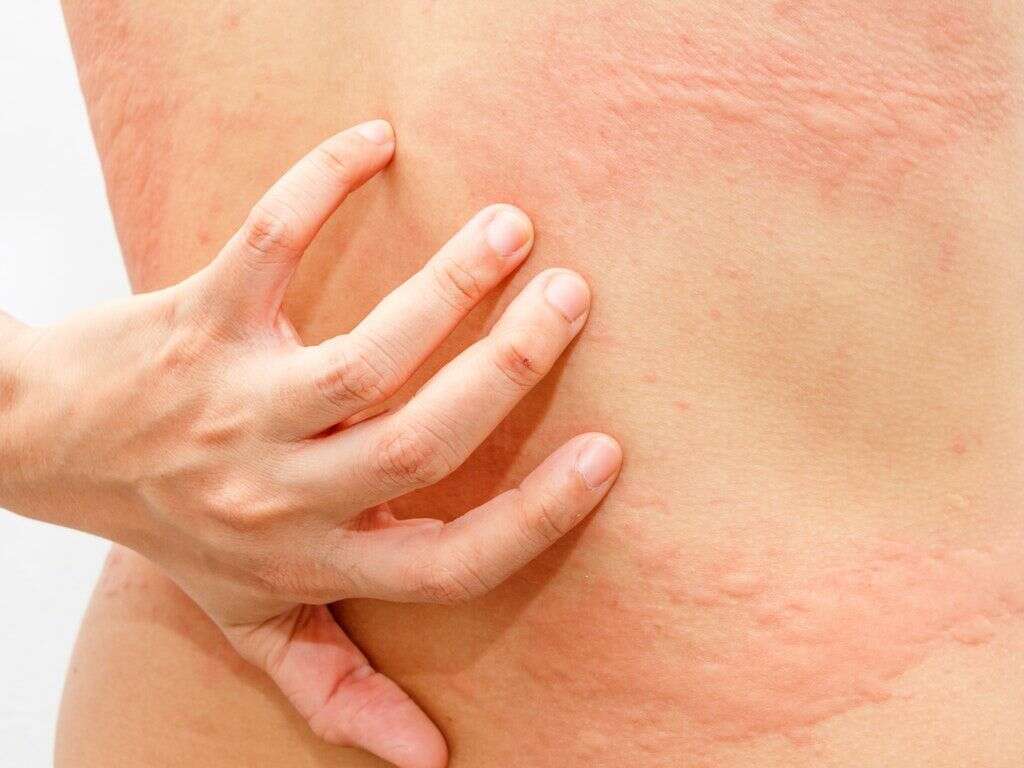
Cause #1: Urticaria
Urticaria, otherwise commonly known as hives, is characterized by raised and erythematous wheals that develop because of the release of vasoactive substances, especially histamine from mast cells. It can be either acute or chronic. Acute urticaria lasts fewer than 6 weeks, while chronic urticaria is characterized by recurring episodes that last longer than 6 weeks.
Urticaria can be triggered by many mechanisms, which are divided into allergic and nonallergic. However, in about one-half of urticaria cases, the triggering factor cannot be identified.
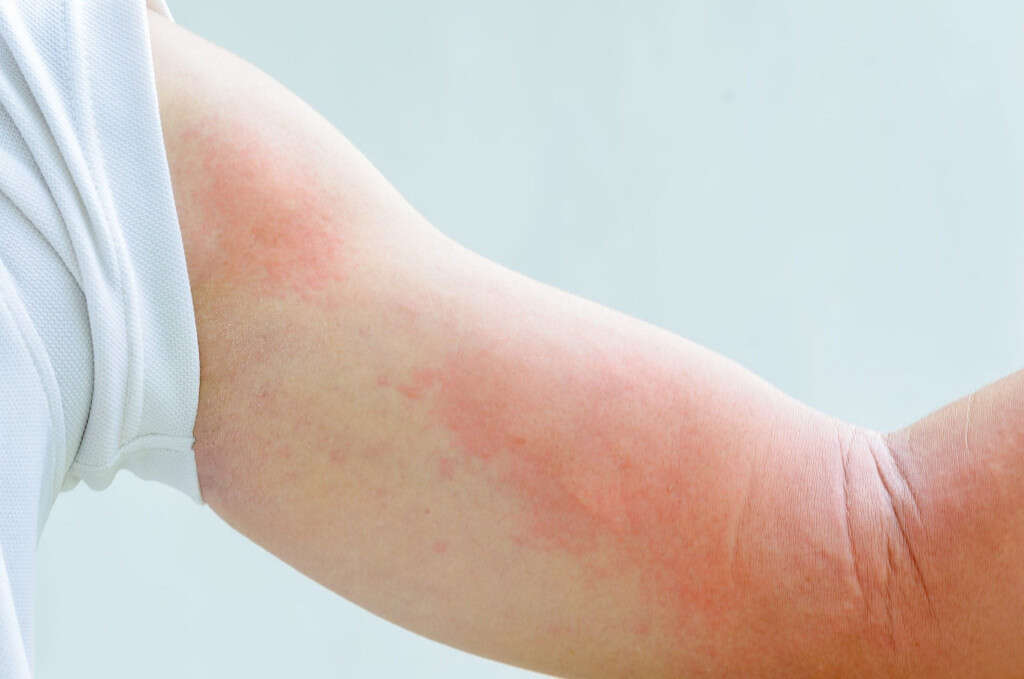
Cause #2: Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Another common cause of a skin rash is allergic contact dermatitis. It is a delayed type of hypersensitivity reaction that occurs due to a contact with an irritant or allergic substance.
In those who are already sensitized, the allergens will activate the antigen-specific T cells. Typically, it requires repeated exposure to the allergen in order for a person to become sensitized and it usually requires exposure of 24–48 hours before the skin rash starts appearing.

Cause #3: Eczema
Eczema or atopic dermatitis is a chronic and relapsing pruritic condition. Infants and children are most affected. Eczema is often associated with asthma and allergic rhinitis. It usually resolves during childhood, but in some cases, it can persist even in adulthood. The underlying cause of eczema is not known. It is believed that genetics and environmental factors have a major role in the development of eczema.
Eczema can be either acute, subacute, or chronic. Acute eczema is characterized with erythema, vesicles, bullae, weeping, and crusting of the skin. Subacute eczema is characterized by scaly plaques, papules, round erosions, and skin crusts. Chronic eczema is characterized by thickening of the skin, scaling, as well as hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation of the affected skin.
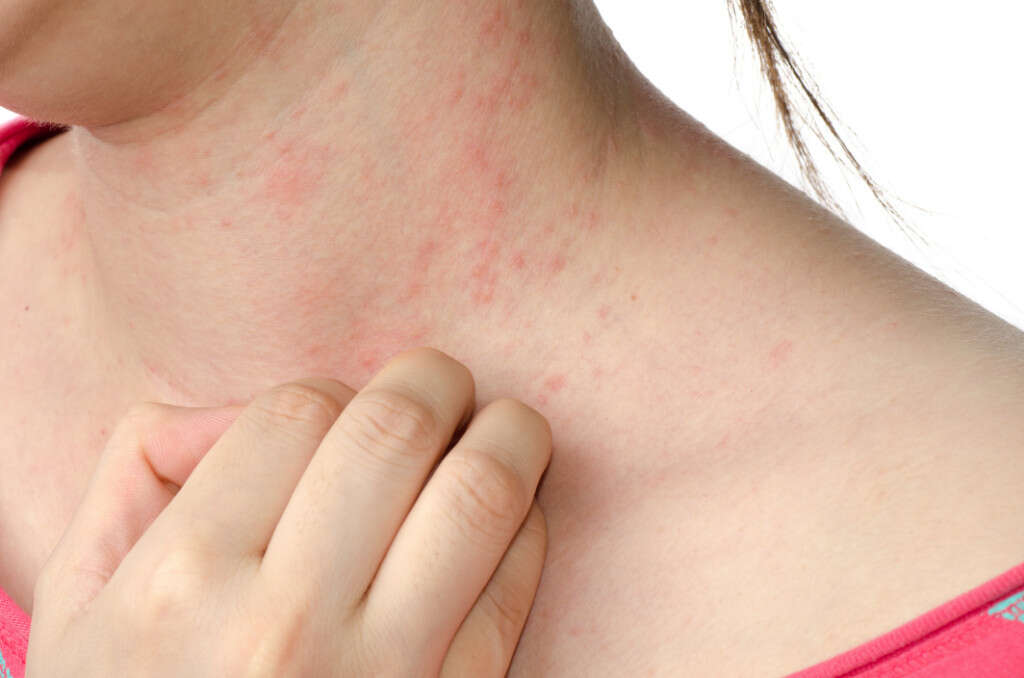
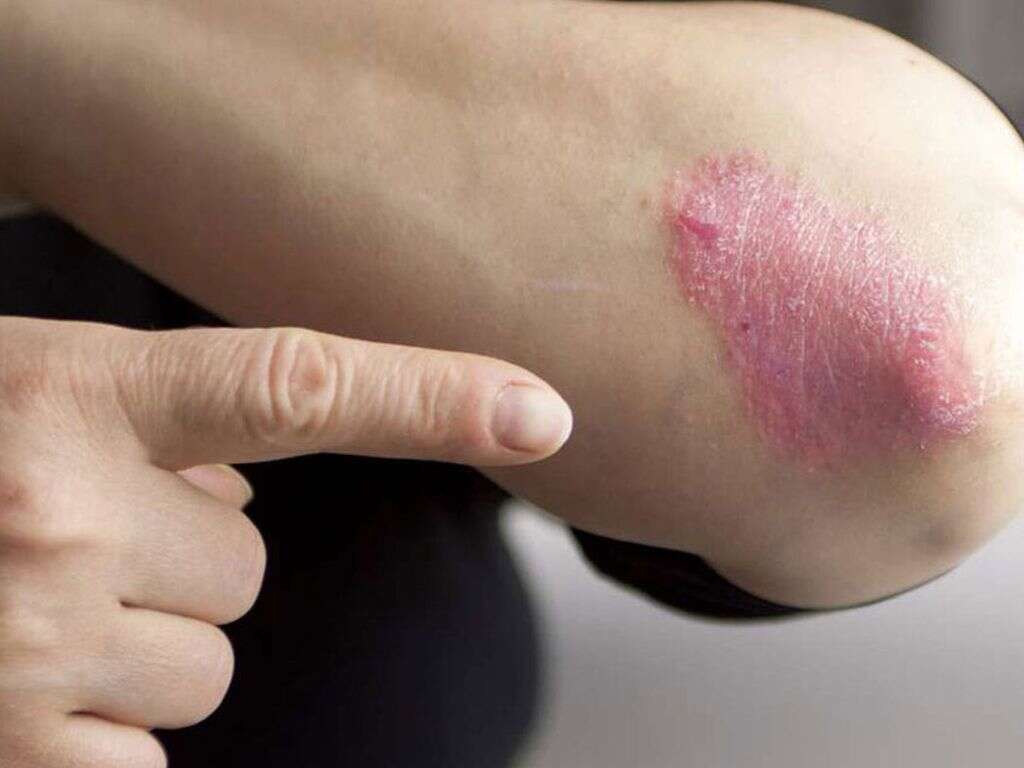
Cause #4: Psoriasis
One of the most common causes of a skin rash is psoriasis. Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the skin. It is characterized by intermittent relapsing and remission periods. It can develop at any age usually affecting the scalp, the elbows, the knees, the nails, hands, feet, and trunk. Estimates show that about 2% of people worldwide suffer from psoriasis.
Psoriasis is categorized as mild, moderate, and severe. Mild psoriasis affects only less than 3% of the body, moderate psoriasis affects less than 10% of the body, while severe cases of psoriasis are those that affect over 10% of the body.

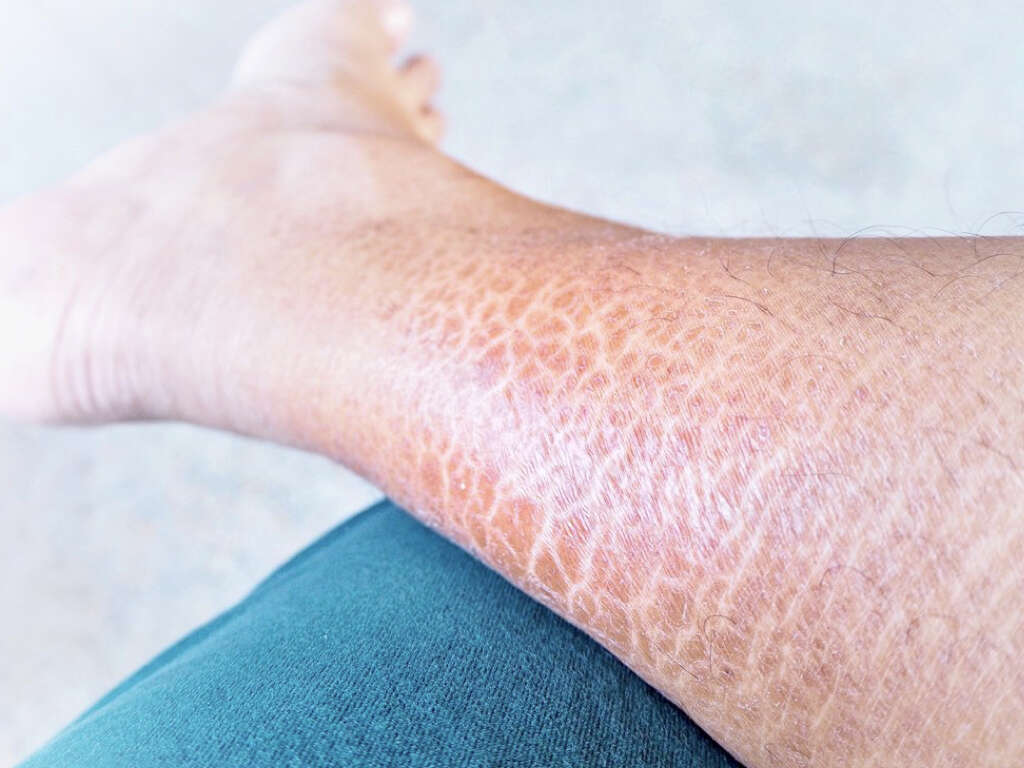
Cause #5: Tinea Corporis
Tinea corporis or ringworm is another skin condition that leads to a skin rash. It is caused by fungi named Trichophyton, Microsporum, or Epidermophyton. Fungi are transmitted to humans by direct contact or through fomites. This skin infection is more likely to develop in humid and warm climates. It can also spread from one part of the body to the other.
It normally appears as a scaly rash, very itchy, and with raised borders in the shape of the ring. The skin inside the ring can be either scaly, dotted with red bumps, or it can be clear. Even though tinea corporis is associated with a lot of itching, sometimes the rash does not itch and only the red color is present.

Cause #6: Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin disease caused by an infestation of mites. A scabies infestation is something quite common occurring all around the world. This skin disease can affect anyone at any age even though those in nursing homes, schools, and other facilities are more likely to develop scabies.
Scabies is transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact. Once infected, it causes a skin rash that is composed of small and red bumps and blisters affecting specific areas of the body, usually the area between the fingers, the wrists, the elbows, the knees, the areas around the nipples, around the umbilicus, the genital area, and the buttocks, as well as the axillary folds. The rash is more likely to be noticeable in infants and young children.

Cause #7: Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin disorder that is characterized by an inflammation of the hair follicles. Infection of these hair follicles is also possible. Viruses, bacteria, fungi, or parasites can cause folliculitis. It starts as a skin rash characterized by small red bumps, or yellow tipped or white tipped pimples. Over time, as the inflammation of the hair follicles progresses, crusty sores can develop. One or many hair follicles can be affected at the same time.
Risk factors that increase the possibility of developing folliculitis include shaving, ingrown hairs, wearing tight clothes, acne, dermatitis, skin injuries, using an unclean hot tub, using an unclean swimming pool, having a weaker immune system due to HIV/AIDS or cancer, and being overweight.

Cause #8: Drug Rash
A skin rash commonly occurs as a side effect of a certain medication, like antibiotics or diuretics, for example. The rash starts as red spots that tend to spread and emerge with one another covering large areas of the body.
Sometimes, it takes weeks for the skin rash to become noticeable, while in other cases, the red spots on the skin become noticeable after a couple of hours or immediately after taking a new drug. Discontinuation of the drug that caused the drug rash will clear up the rash within a couple of days in most cases.
Cause #9: Impetigo
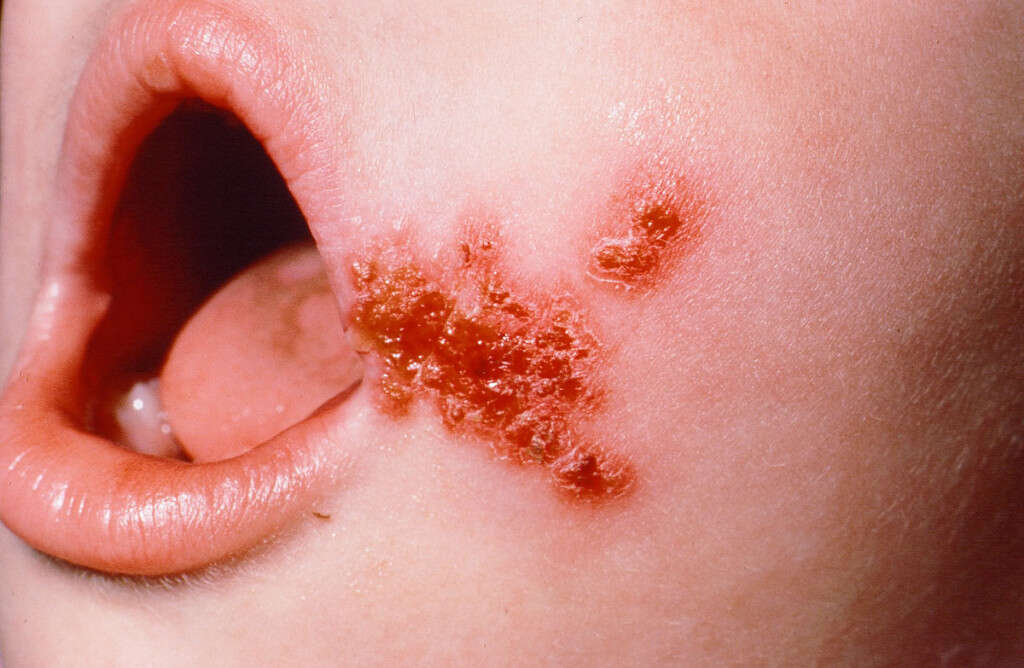
Another common cause of skin rash is impetigo. It is a highly contagious skin infection commonly noticeable in infants and children. Impetigo appears as red sores on the child’s face. These sores are usually present around the mouth and nose, as well as on the hands and feet. These sores burst and develop crusts, after oozing for a few days. Itching and soreness are generally mild.
In certain cases, larger blisters may develop, affecting the trunk of infants and children. This form of impetigo is otherwise known as bullous impetigo. Ecthyma, is another and more serious form of impetigo, which is characterized by painful and fluid-filled sores, as well as pus-filled sores. These sores turn eventually into deep ulcers as deeper skin layers are affected. Treatment consists of antibiotics.
Cause #10: Roseola
Roseola, or as it is otherwise known as the sixth disease, is a viral infection most common among children under the age of 2. Adults are not affected by roseola. Signs and symptoms include high fever, a runny nose, and a sore throat. Once the fever ends, the skin rash becomes noticeable. The skin rash in roseola usually starts on the torso before spreading to other body parts, like on the arms, legs, neck, and face. Roseola rash appears as small pink spots, which can be either raised or flat. Some spots may even have a lighter ring or halo around them.
Roseola is not a serious condition and it usually resolves within a week. However, roseola is a contagious viral infection caused by herpes virus 6 or herpes virus 7 that is spread through infected respiratory secretions. Infants and children usually get it from other children in daycare centers.