10 Blood Clot In Arm Symptoms
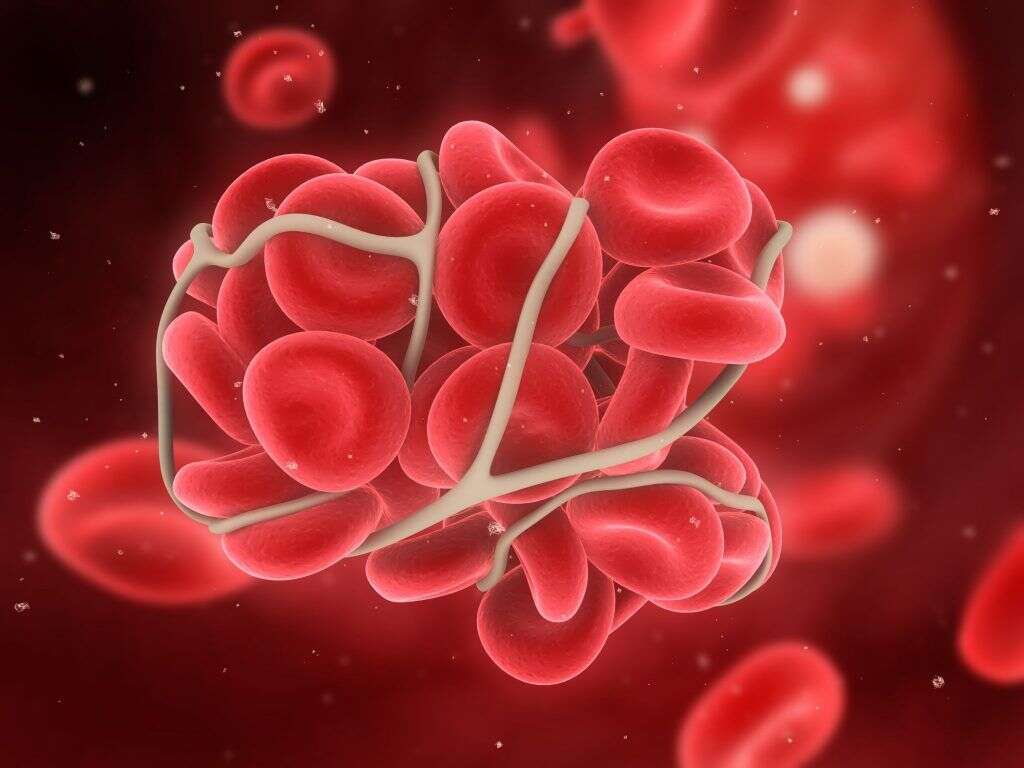
A blood clot, or thrombus, occurs when blood coagulates as part of hemostasis. There are two components in a blood clot: the red blood cells forming a plug and aggregated platelets. When the clot occurs, there is a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein.
In normal cases, a blood clot is a healthy response to injuries as it functions to prevent excessive bleeding. However, when it occurs in a blood vessel, it can be dangerous as the clot obstructs the flow of blood to the other healthy blood vessels. Causes of a blood clot formation can be attributed to endothelial injury, blood stasis, and hypercoagulability.
Severe blood clots may not be common and only 10 percent of blood clots involve the deep veins of the arms. It is important to recognize blood clot symptoms as it helps you to seek immediate medical attention.
Symptom #1: Swelling
Swelling is most evident when the blood clots occur in the deep veins. The clots are usually located in the subclavian and axillary veins. These large veins are veins that extend through the upper arm, going through the armpit, shoulder, and into the chest. These veins are important as they carry most of the blood from the arm back to the heart. When there is obstruction, the blood is unable to flow back to the heart and results in obvious swelling of the arm and hand.
If the blood clot occurs in the superficial vein, the swelling is usually localized and can be attributed to the inflammation of the vein. In arterial blood clots, swelling is uncommon and usually appears when there is extensive cell death.

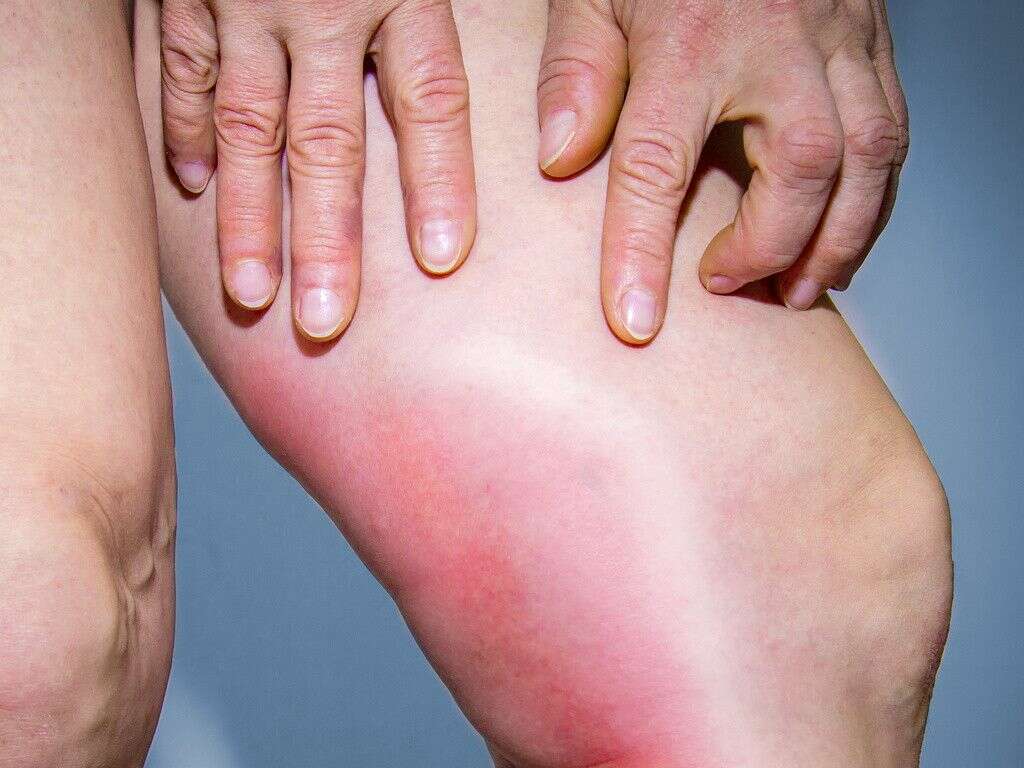
Symptom #2: Redness
When there is a venous blood clot in the arm, redness can occur due to pooling of blood and inflammation. It is one of the most common symptoms seen among patients with a blood clot. In most, it may be the only symptom present.
Redness is sometimes associated with other symptoms such as pain, tenderness, and swelling. Seek medical attention if you believe you have a blood clot.
Symptom #3: Pain
Pain is a common symptom of a blood clot. When the clot is small, the pain may be mild. When the clot is large or obstructs an artery, the pain can become intense and debilitating.
Arterial blood clots are much more painful as the arterial blockage decreases oxygen delivery to tissues that are supplied by the artery, resulting in loss of function and death of the tissue. Blood clots that occur in the superficial veins usually cause pain in the surrounding areas of the clot. Clots located in the deep veins typically cause more widespread pain and can affect most of the arm. The pain is usually mild in the beginning and progressively becomes more severe.
It should also be noted that sometimes blood clots are not painful at all.
Symptom #4: Change in Temperature of the Arm
When there is a venous blood clot in the arm pooling of blood occurs. Warmth is one of the main characteristics of the presence of a blood clot. Inflammation may also contribute to the warmth of the limb.
Converse to a venous blood clot, an arterial blood clot in the arm will block fresh blood to the distal parts of the extremity. This will cause a cooling of the skin in the arm.
Symptom #5: Bluish Discoloration
Pale or bluish discoloration along with coolness of the limb usually occurs when blood clots form in an artery.
This is due to the lack of blood flow to the limb.

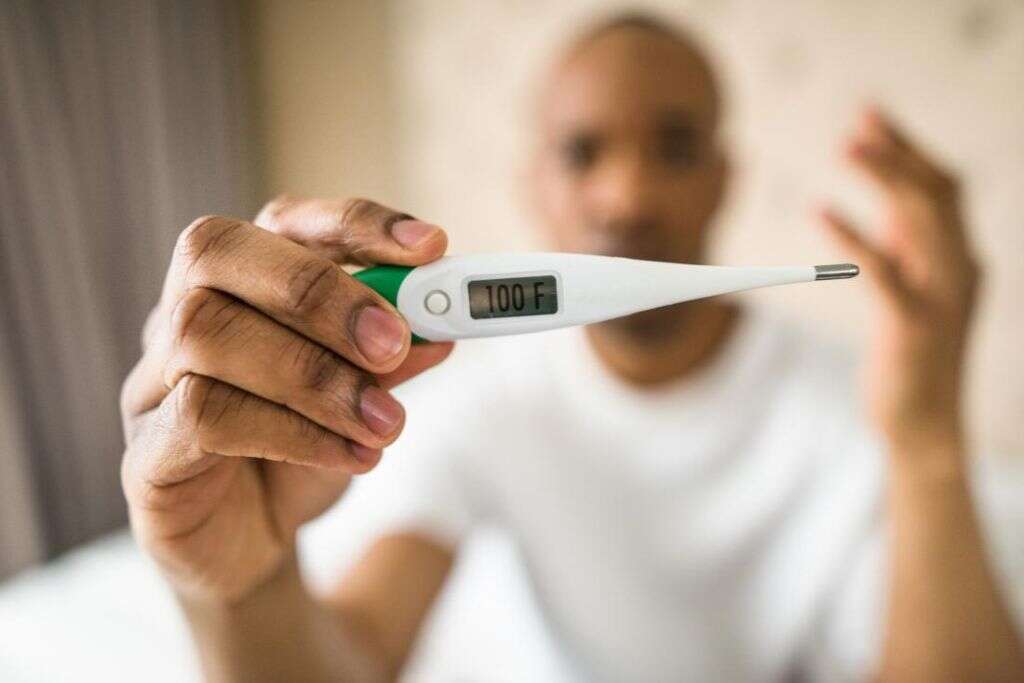
Symptom #6: Fever
Some patients with blood clots may also experience a fever. In any type of blood clot, a mild fever up to 100.4°F is a normal part of the body’s response.
When the temperature is higher, it may suggest an underlying infection located in the vein (also known as septic thrombophlebitis) or other areas.
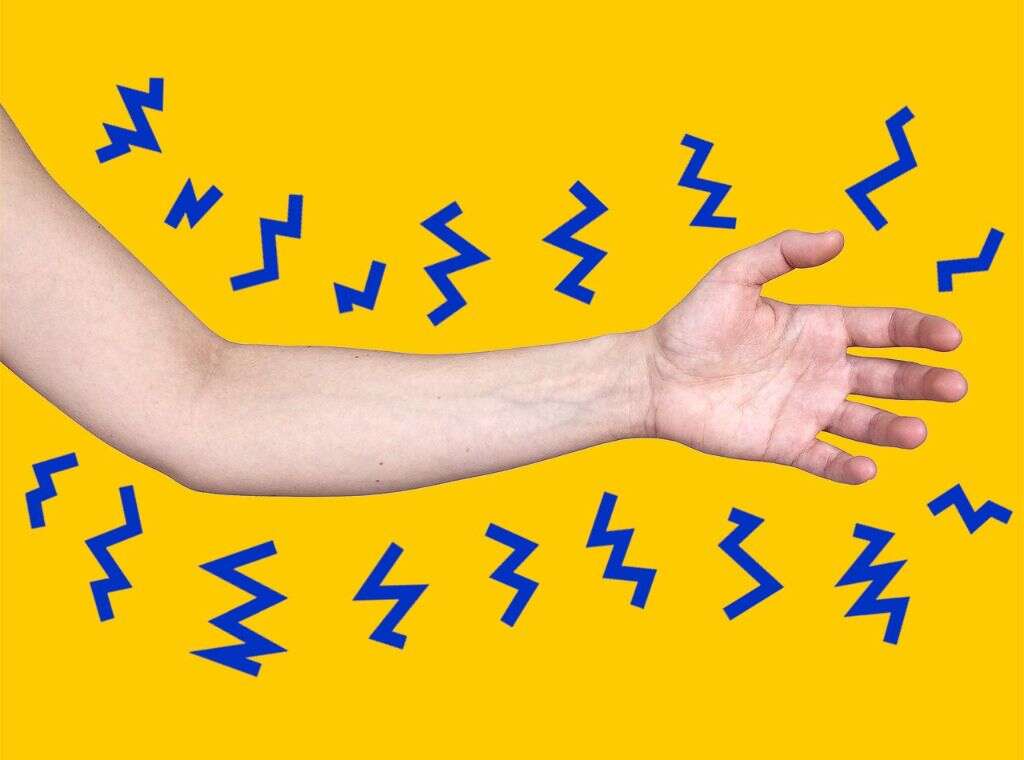
Symptom #7: Paresthesia
Paresthesia refers to an abnormal dermal sensation where there is numbness, tingling, chilling, burning, or prickling without an apparent physical cause. Paresthesia can be chronic or persistent and can be due to various causes. It is generally painless and is most commonly felt in the extremities.
The most familiar type of paresthesia is often described as “pins and needles” or of a limb that has “fallen asleep.” When there is an arterial blood clot, paresthesia may occur as the muscle and nerve function becomes impaired due to inadequate blood supply.

Symptom #8: Enlarged Veins
If a blood clot is present in a superficial vein, the vein can appear to be enlarged and feel firmer compared to normal. While it may not be obvious initially, the clot can become firmer as it hardens. The vein distal to the clot also starts to appear larger due to the clot creating a damlike effect. If the clot is in the deeper veins, similar changes can still occur but not observed as the veins are located deeper within the arm.
Depending on the veins that are blocked, some blood flow can be diverted through the other veins. This leads to enlarged superficial veins that may be visible on the upper chest, shoulder, and arm.

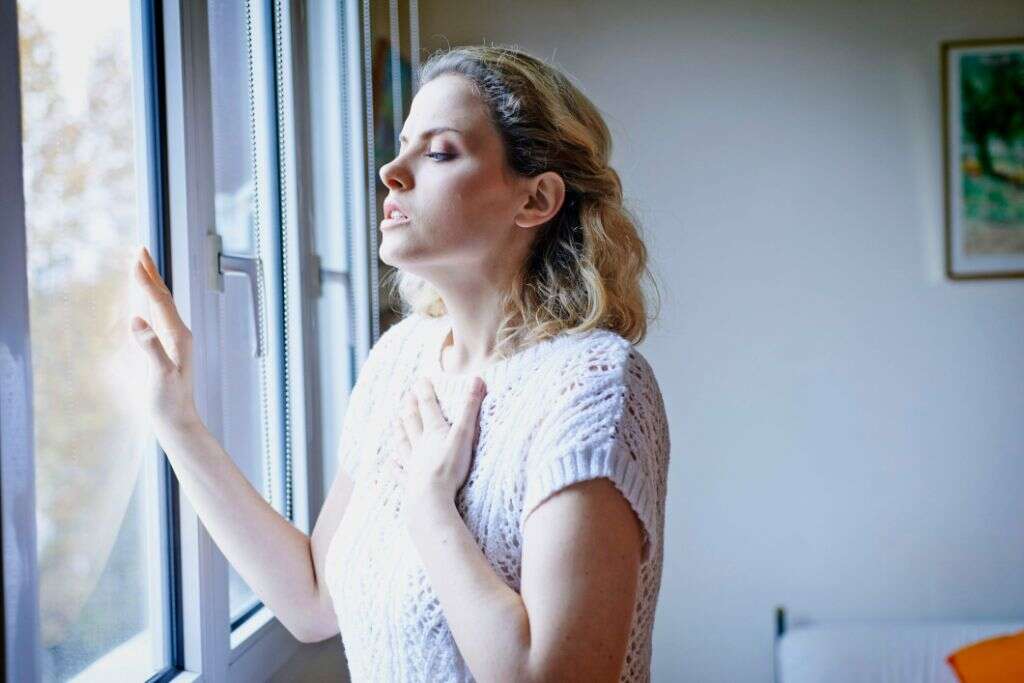
Symptom #9: Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath or dyspnea refers to the feeling where one is unable to breathe well enough. It is a subjective feeling where there is increased chest tightness, increased effort needed to breathe, and air hunger. In most cases, it is due to cardiac ischemia, interstitial lung disease, asthma, pneumonia, congestive heart failure, psychogenic causes, and various respiratory and cardiovascular related causes.
When shortness of breath occurs in a patient who has a blood clot in their veins, it could mean that the clot or part of the clot has lodged in the lungs. Those experiencing this issue should seek immediate medical attention.

Symptom #10: Cramp
A cramp is an involuntary and sudden muscular contraction where the muscle shortens. While it is temporary and usually does not cause any damage, it can be debilitating and cause paralysis-like immobility. It usually resolves on its own after several minutes or hours.
Cramps can occur in both smooth and skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscle cramps can occur when there is electrolyte imbalance, muscle fatigue, or low oxygenation of the tissue. A blood clot in the arm can also cause cramps in the arm as blood flow to some of the muscles in the arm is obstructed.