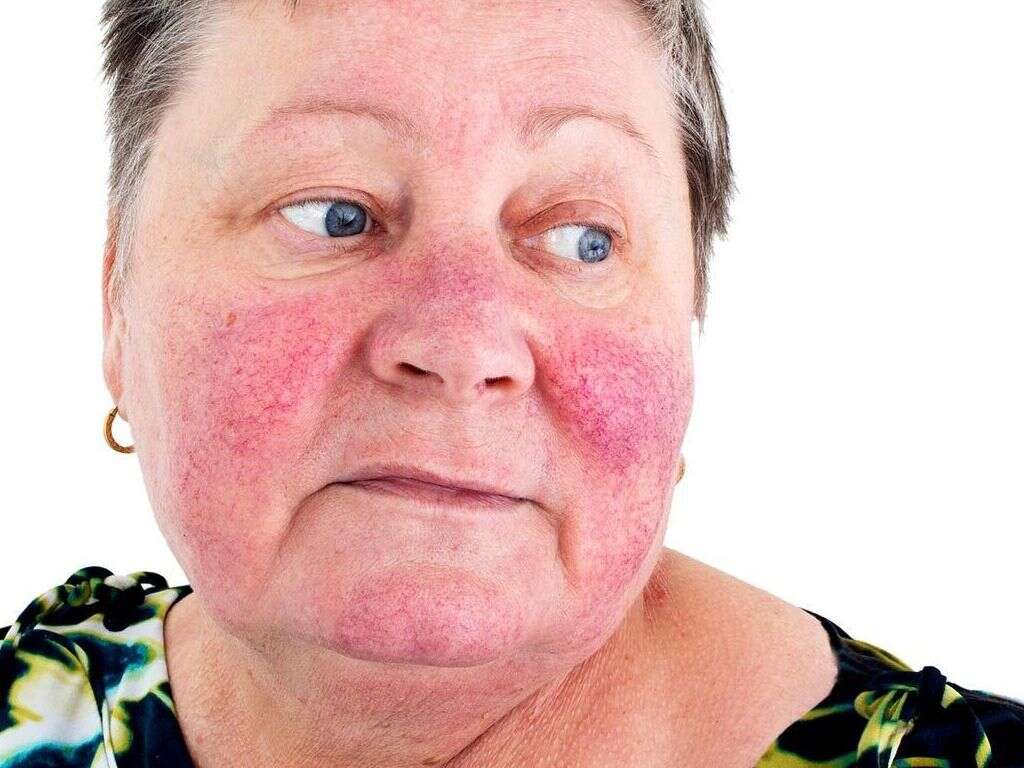
10 Autoimmune Disease Symptoms
An autoimmune disease is a condition in which a person’s immune system begins to function differently than it should, causing problems in the body. In effect, the immune system is actually attacking its host when its job should be protecting it from invaders. The main issue in an autoimmune disorder is the way that the immune system sees the cells of the body. In a healthy immune system, there is no problem differentiating between foreign, invading cells and those of the host’s body. Unfortunately, if you have an autoimmune disease then your immune system actually sees some of your own cells as invaders and begins to attack them.
There are many, many different forms of autoimmune diseases. Some of them can be quite serious and result in the need for hospitalization, and others are quite mild and only cause visible symptoms that don’t damage a person’s health – an example of this being vitiligo, an autoimmune condition in which the pigment of the skin is destroyed leaving splotches of lighter skin. Some autoimmune systems will attack a single organ – diabetes is a good example of these, an autoimmune condition which affects the pancreas. More serious conditions like lupus affect the whole body and can cause a whole host of unpleasant and dangerous effects.
Doctors and researchers still haven’t fully identified exactly what leads to the miscommunication in an autoimmune disease. What is known is that some people are much more likely to develop these conditions than others. Unfortunately, women are about twice as likely to develop these conditions as men. If you think that you might be struggling with an autoimmune disease, then check out this list of symptoms. It could help you determine whether or not you need treatment.

Symptom #1: Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom that runs among many of the autoimmune disorders that a person can develop.
As your immune system taxes your body of energy by sending out immune cells to attack it, you will likely lose some of your energy. This can make it difficult for you to maintain your daily routine or accomplish everything that you want to get done.

Symptom #2: Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is a condition in which a person can’t consume gluten, a protein that’s found in many grains such as wheat and rye. When gluten is present in the intestines, the immune system considers it a pathogen and attacks it, which can lead to inflammation and related symptoms.
Celiac disease affects about 1% of the people in the US, but it’s important to note that Celiac disease is different than a gluten sensitivity which affects even more people. The latter causes similar symptoms but doesn’t actually involve the immune system.

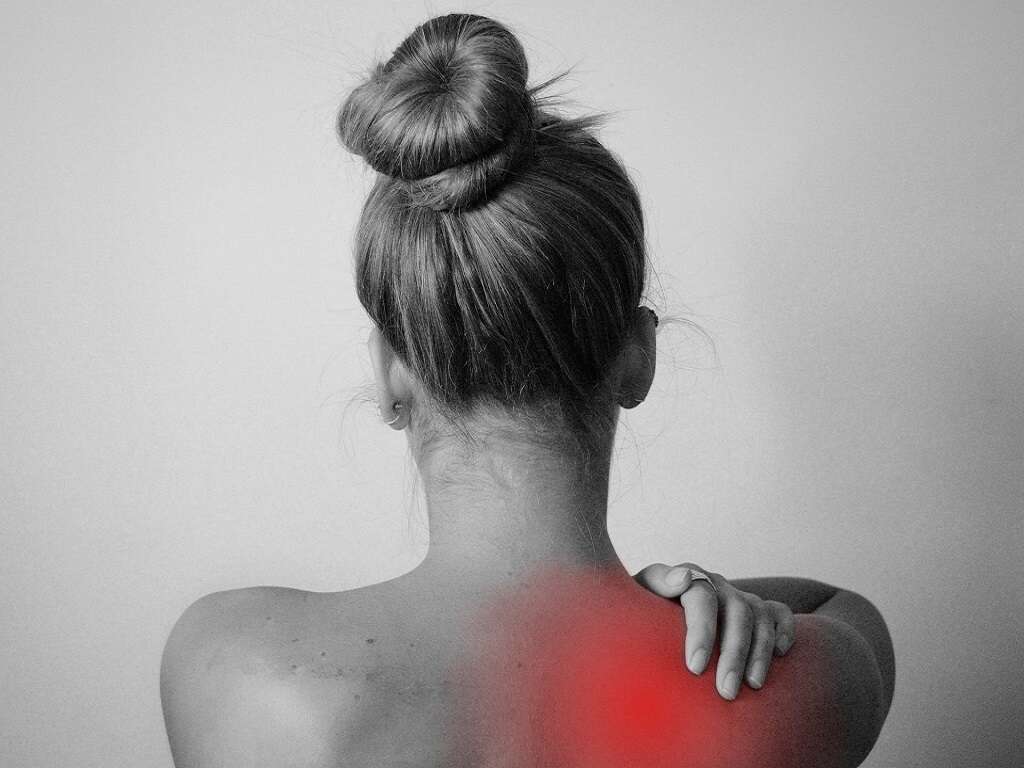
Symptom #3: Muscle Soreness
Another symptom that can target someone when they are developing an autoimmune disease is muscle soreness.
Soreness can affect many of the muscles in the body and can be felt as a lingering soreness or a dull ache. This is usually an early symptom of an autoimmune disease.
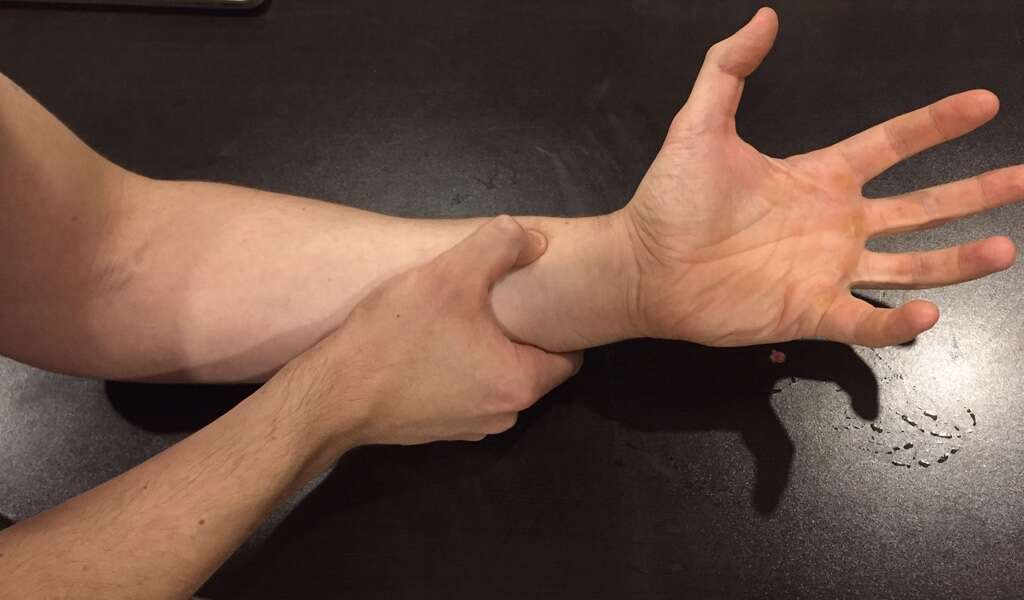
Symptom #4: Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a condition in which the immune system actually begins to attack the blood vessels in the body. This attack can lead to the blood vessels becoming inflamed. As they become inflamed, they become tighter and more constricted, making it more difficult for the body to transport blood.
Since blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the different tissues and organs in the body, this can manifest as a number of symptoms ranging from fatigue to impaired organ function. If you suspect that you are developing vasculitis you should see a doctor.
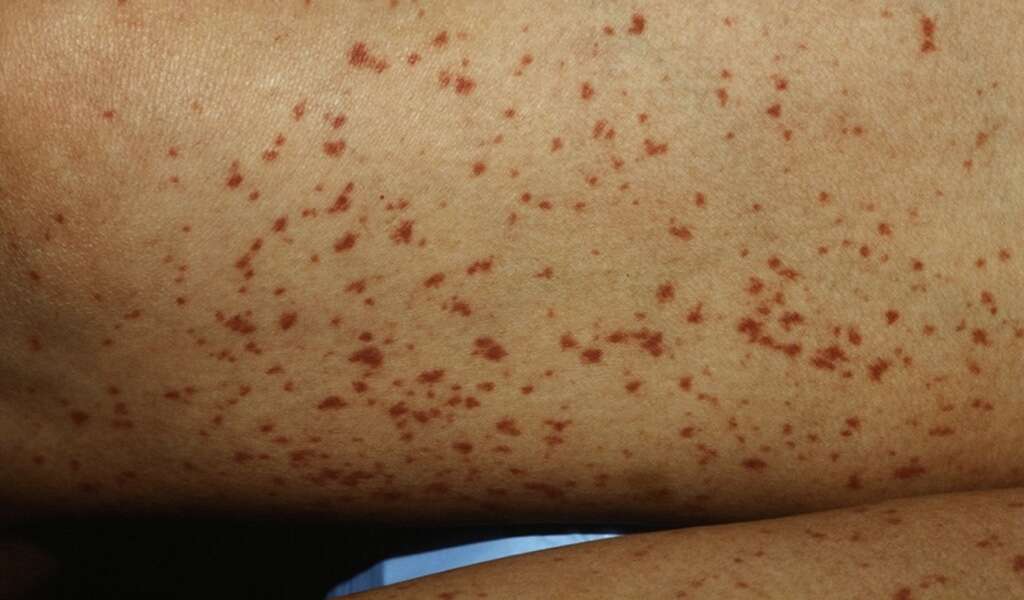
Symptom #5: Weight Gain
Weight gain is another sign of an autoimmune disorder. In some cases this can be a result of developing Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, a condition in which the thyroid glands are unable to produce the proper amount of the hormones that they need to.
In addition to experiencing a swollen thyroid and weight gain, people experiencing this particular autoimmune problem may also become very sensitive to cold and begin to lose hair at an early age.

Symptom #6: Nervousness and Fast Heartbeat
Some autoimmune disorders can cause your body to ‘rev up’ its metabolism, causing it to use more energy. One such example is Graves’ disease, another autoimmune complication that targets the thyroid gland.
In this condition, however, the thyroid actually begins to produce too many hormones as opposed to too little. This causes your body to use more energy and can lead to feelings of nervousness, a quick heartbeat, a sensitivity to heat, and weight loss.

Symptom #7: Bowel Problems
Autoimmune diseases are known to affect the bowels. In fact, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, or IBS, is a term used to describe the various symptoms that can be caused by an autoimmune disorder that targets the intestinal lining.
Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are two conditions that can be caused by autoimmune problems. Both conditions are known to contribute to diarrhea, discomfort, cramping, bloating and gas. Anti-inflammatory compounds can help people manage these conditions in certain cases.

Symptom #8: Lupus
Lupus is a very serious autoimmune disease that targets many different organs in the body.
While lupus was initially regarded as a skin condition because it can produce a nasty rash, recent research has identified this rash is actually a result of all the different organs that it affects: the kidneys, the brain, and the heart, just to name a few. Additional symptoms can include pain in the joints and serious fatigue.
Symptom #9: Numbness and Tingling
Feeling numbing or tingling in the arms and legs is one of the more common symptoms associated with the development of an autoimmune disease. This is particularly true if someone is developing multiple sclerosis (MS) a very serious autoimmune condition that can prove fatal.
People with MS experience damage to the myelin sheath – the protective layer that surrounds the cells of the nervous system. Damage to nerve cells can lead to numbness, tingling, pain, and many other symptoms.
Symptom #10: Skin Problems
Some autoimmune diseases are known for causing skin problems. Psoriasis is a good example of an autoimmune disease that contributes to skin problems – in this case, skin cells begin to multiply far too quickly, and they can form dry, scaly patches.
Often associated with this are itchiness, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. There are many topical anti-inflammatory lotions that can be useful to help someone with psoriasis manage their conditions. Fortunately, psoriasis is not fatal and can be put into remission with proper care.