10 Adenovirus Symptoms
Adenoviruses are common viruses that can cause a variety of issues such as cold-like symptoms, bronchitis, sore throat, diarrhea, pneumonia, conjunctivitis, and more.
An adenovirus infection can affect individuals of all ages. However, those who have weakened immune systems, or existing cardiac or respiratory disease, are more likely to have a more severe form of the disease. The adenovirus is an extremely hardy virus that can survive long durations outside a host. There are 52 serotypes of adenovirus and it has therefore been recognized as the etiologic agent of various syndromes.
Transmitted via direct inoculation (i.e. to the eye) , fecal-oral route, bodily fluids (i.e. blood) , and aerosolized droplets, the virus can affect various organ systems. Adenovirus is commonly isolated in both infants and children. In immunocompetent hosts, severe morbidity and mortality are rare.

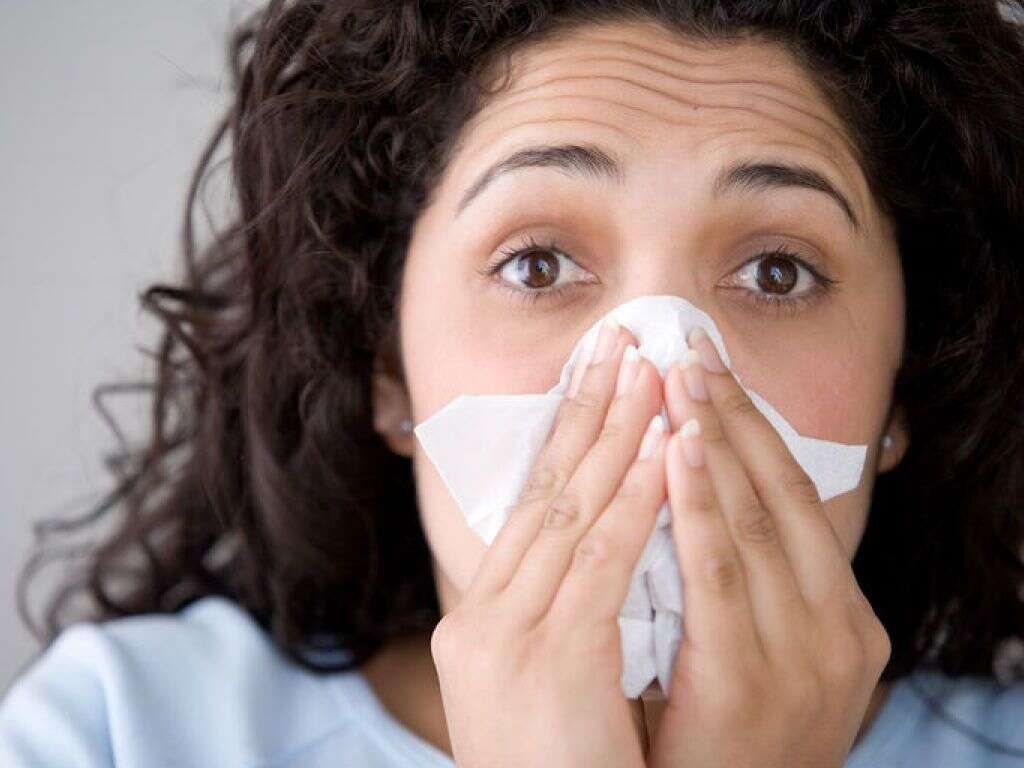
Symptom #1: Fever
Fever or pyrexia occurs when the set point of body temperature in the central nervous system is abnormally elevated. The increase results in a feeling of coldness and more muscle contractions in an effort to generate and conserve heat. A fever can be caused by various conditions, including infections (viral, bacterial, parasitic, fungal). Different manifestations of adenovirus infection can cause a fever. Some of these syndromes are acute respiratory disease (ARD), pharyngoconjunctival fever, acute hemorrhagic nephritis, and gastroenteritis.
The treatment of fever is generally unnecessary. However, once the cause of the fever has been established by a physician, certain medications can be prescribed to lower body temperature and improve other associated symptoms.

Symptom #2: Diarrhea
Diarrhea can be defined as having at least three loose bowel movements a day. It can last several days, resulting in dehydration. Some signs and symptoms of dehydration include loss of skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, decreased urination, tachycardia, and more.
The most common cause of diarrhea is an infection due to viruses, parasites, or bacteria. In these cases, the transmission is usually from contaminated food or water. However, noninfectious causes of diarrhea also exist (i.e. celiac disease, lactose intolerance, irritable bowel syndrome). Adenovirus is one of the viral pathogens that can cause diarrhea. Most commonly, serotypes 40 and 41 can cause acute inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract (gastroenteritis). It is a common cause of watery diarrhea and fever in infants (i.e. daycare), that usually lasts no more than one to two weeks. However, it is less common than rotavirus infection in infants and it can also affect adults.

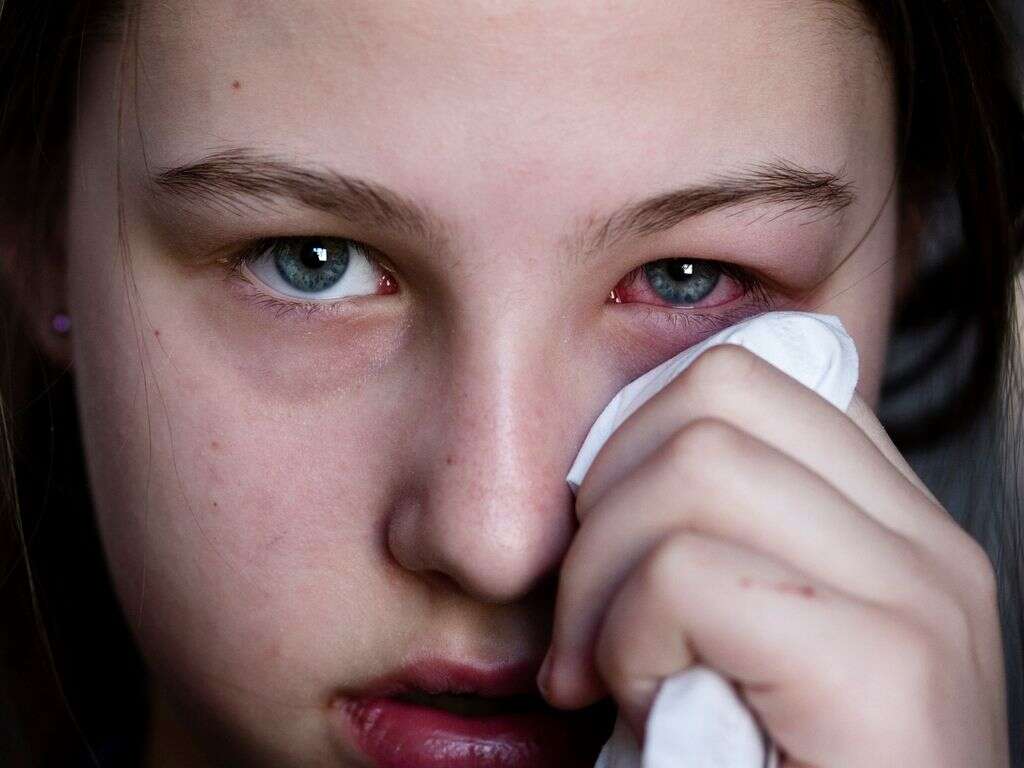
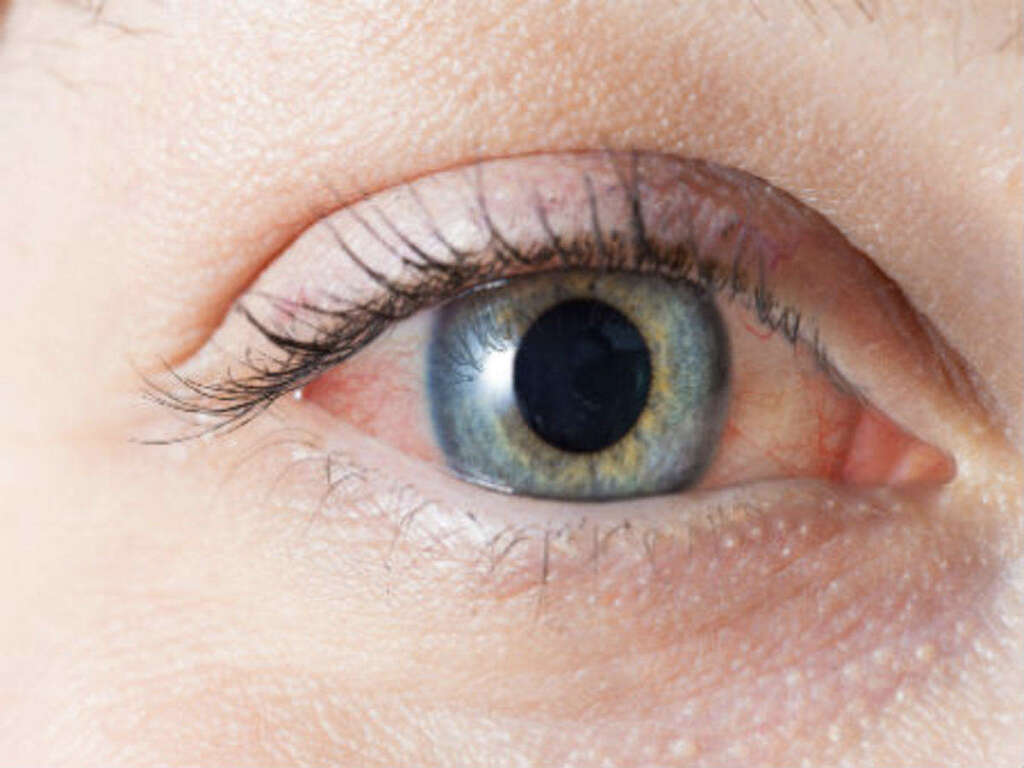
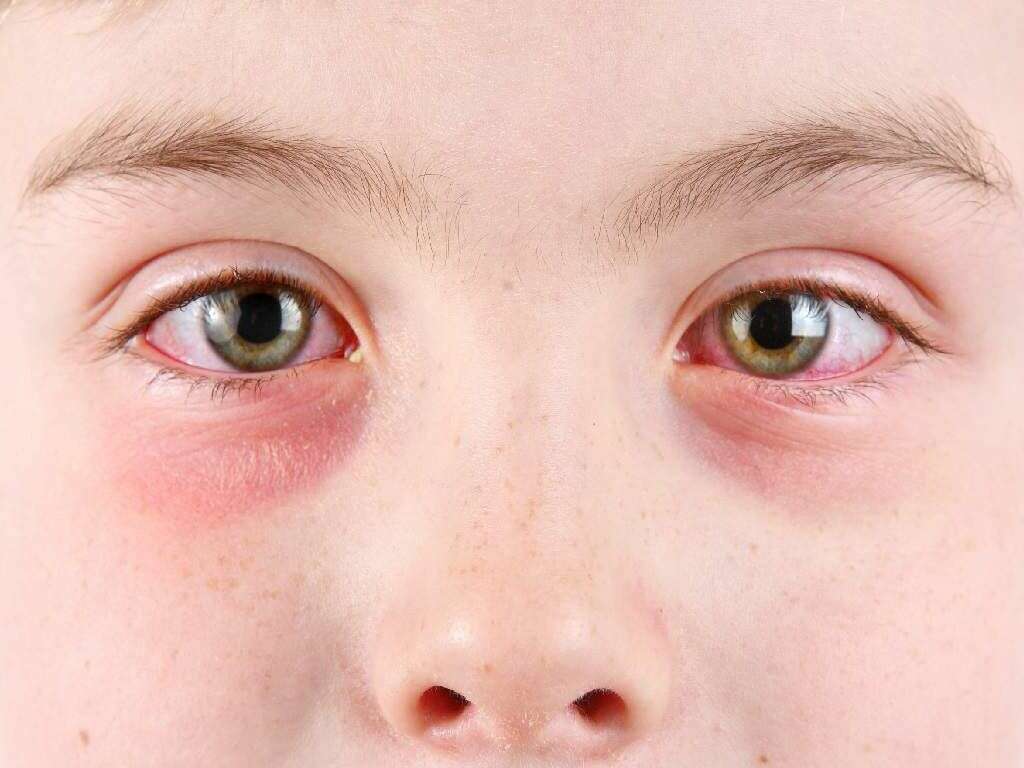
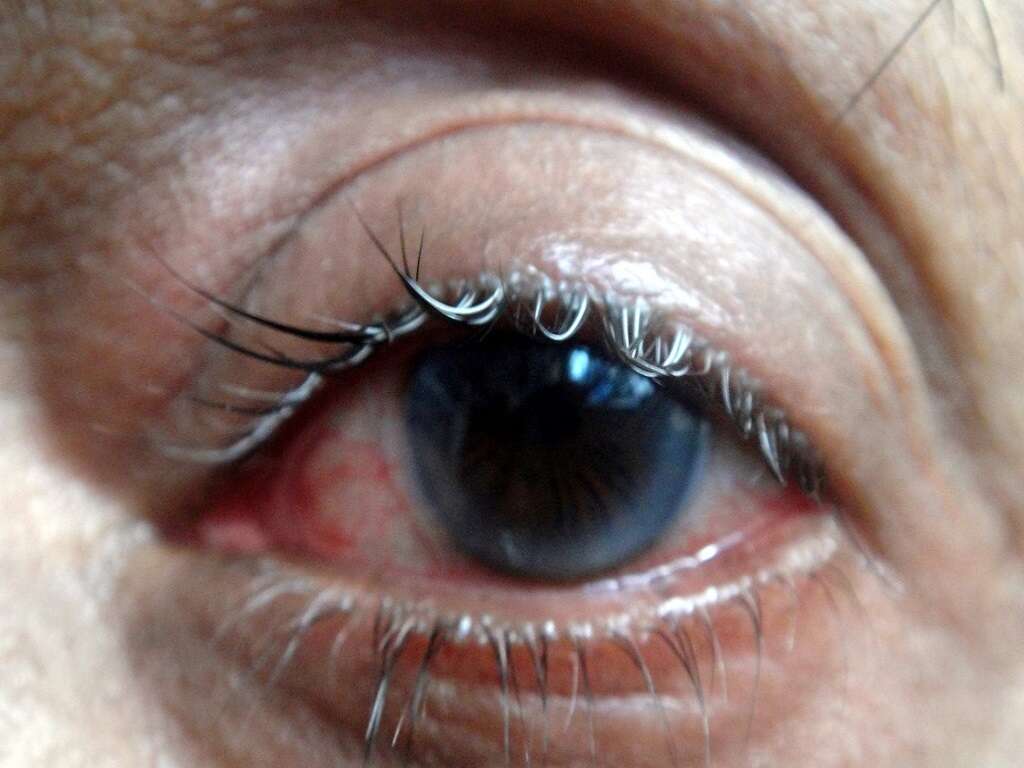
Symptom #3: Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis or pink eye occurs when the inner surface of the eyelid and outermost layer of the white part of the eye is inflamed, causing the eye to appear reddish or pinkish. Other associated symptoms include itchiness, pain, tearing, and burning. Some patients may also experience the affected eye to be “stuck shut” in the mornings.
The most common infectious causes of conjunctivitis are viral followed by bacterial. Adenovirus infection is one of the causes of conjunctivitis. Most commonly, serotypes 3,4, and 7 can cause fever and conjunctivitis, associated with upper respiratory symptoms (sore throat and dry cough) This manifestation of adenovirus infection is also referred to as pharyngoconjunctival fever and can affect children of school age. Moreover, serotypes 8, 19 and 37 can cause epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. This manifestation of the infection occurs in epidemics because it is highly contagious (i.e. through contaminated hands or objects), and can also cause inflammation of both the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye. Prevention of any type of conjunctivitis can be achieved by washing your hands often and avoiding touching your eyes with your hands.
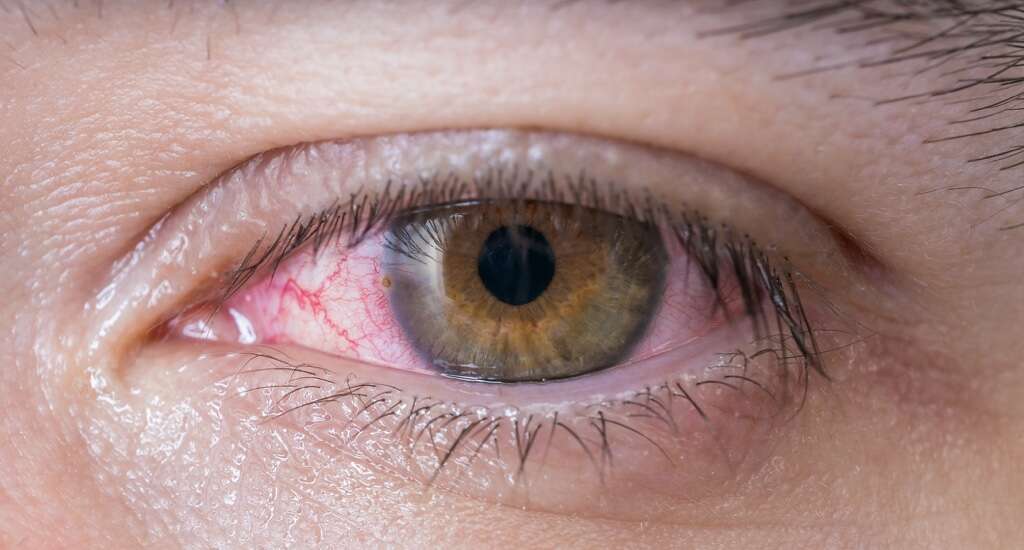
Symptom #4: Sore Throat
Sore throat occurs when there is irritation or pain in the throat. A sore throat can be caused by tonsillitis, pharyngitis, or trauma. It is a very common issue that is seen in acute viral pharyngitis (i.e. adenovirus infection). Adenovirus infection can manifest as acute respiratory disease (ARD), which may cause fever and upper respiratory symptoms (i.e. runny nose and dry cough), including pharyngitis and tonsillitis. It is usually self-limited, with an average duration of 3 to 5 days. Finally, as mentioned above, an adenovirus infection can also manifest as pharyngoconjunctival fever causing a sore throat.
In the United States, there are as many as 2.4 million visits to the emergency department annually due to throat-related complaints. Other causes of sore throat include gastroesophageal reflux disease, infectious mononucleosis, and streptococcal pharyngitis.

Symptom #5: Nausea and Vomiting
Gastroenteritis or infectious diarrhea occurs when there is inflammation of the stomach and small intestines. Patients affected may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea. There can also be fever, fatigue, and dehydration. Gastroenteritis can be caused by bacteria, parasites, fungus, and virus.
In children, rotavirus is the most common cause of gastroenteritis. Other common causes include norovirus, campylobacter, and adenovirus. It can be prevented by drinking clean water and practicing adequate hand hygiene.
Symptom #6: Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath or dyspnea is an uncomfortable sensation of not being able to get enough air. Affected individuals often complain of chest tightness, and an increased effort required to breathe normally. As mentioned before, patients with adenovirus infection can exhibit symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Furthermore, patients can also experience tracheobronchitis, bronchiolitis, and pneumonia. Thus, dyspnea is one of the most common symptoms associated with these viral lower respiratory infections.
Shortness of breath is a symptom that can also be seen in cardiac ischemia, asthma, congestive heart failure, interstitial lung disease, anxiety, panic attacks and more.

Symptom #7: Cough
A cough is a repetitive and sudden protective reflex which helps to clear the airways from microbes, foreign particles, fluids, and more. Frequent coughing usually indicates that there is an underlying disease.
Through evolution, many pathogens have caused the host to cough to help spread disease to new hosts. Coughing can be caused by a respiratory tract infection, lung tumors, post nasal drip, asthma, bronchitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, side effect of medications, and more. The treatment for a cough would depend on the underlying cause. In this case, an adenovirus infection can cause upper and lower respiratory tract infections resulting in cough.

Symptom #8: Dysuria
Dysuria is a medical term that refers to difficult or painful urination (i.e. burning sensation). Cystitis is an infection of the lower urinary tract (i.e. bladder) that frequently causes dysuria, frequent urination, hematuria (blood in the urine), and more.
The most common cause of cystitis is a bacteria called Escherichia coli, but it can also be caused by a virus. Adenovirus infection can manifest as a self-limited acute hemorrhagic cystitis, that affects mostly children and teenagers (boys more than girls). However, it can also affect adults with a compromised immune system (i.e. AIDS or post-transplantation patients).

Symptom #9: Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy refers to lymph nodes that are abnormal in consistency, size, number, or texture. It is a nonspecific sign which can be seen in various conditions such as common cold, influenza, autoimmune diseases, cancers, and more.
Most cases of lymphadenopathy are idiopathic (unknown cause) and self-limiting. In an infection, the lymph nodes have a function as part of the immune system and “trap” cells that pass through containing pathogens, leading to enlargement of the organ. In adenovirus, lymphadenopathy is mostly observed in children who experience respiratory and ocular infections.

Symptom #10: Flank Pain
Flank pain is a sensation of discomfort in the upper abdomen, below the ribs and above the pelvis on each side.
Patients with adenovirus infection (i.e. serotypes 11 and 21) can experience nephritis, or the inflammation of renal tissue. This can occur in patients who receive hematopoietic stem cell transplants, and it can manifest with fever, flank pain and hematuria (blood in urine).