10 MCTD Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Mixed Connective Tissue Disease.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 2 June 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/mixed-connective-tissue-disease/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20375152
- 2. Team, Wellness. '5 Ways to Fight Fatigue With Food.' Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, 19 Aug. 2020, health.clevelandclinic.org/5-ways-to-fight-fatigue-with-food/
- 3. 'Mixed Connective Tissue Disease.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 2 June 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/mixed-connective-tissue-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20375147.
- 4. 'Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD).' NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), 5 July 2017, rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/mixed-connective-tissue-disease-mctd/
- 5. Nugent, Caitlin C. 'H2 Blockers.' StatPearls /[Internet/]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 20 Mar. 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525994/
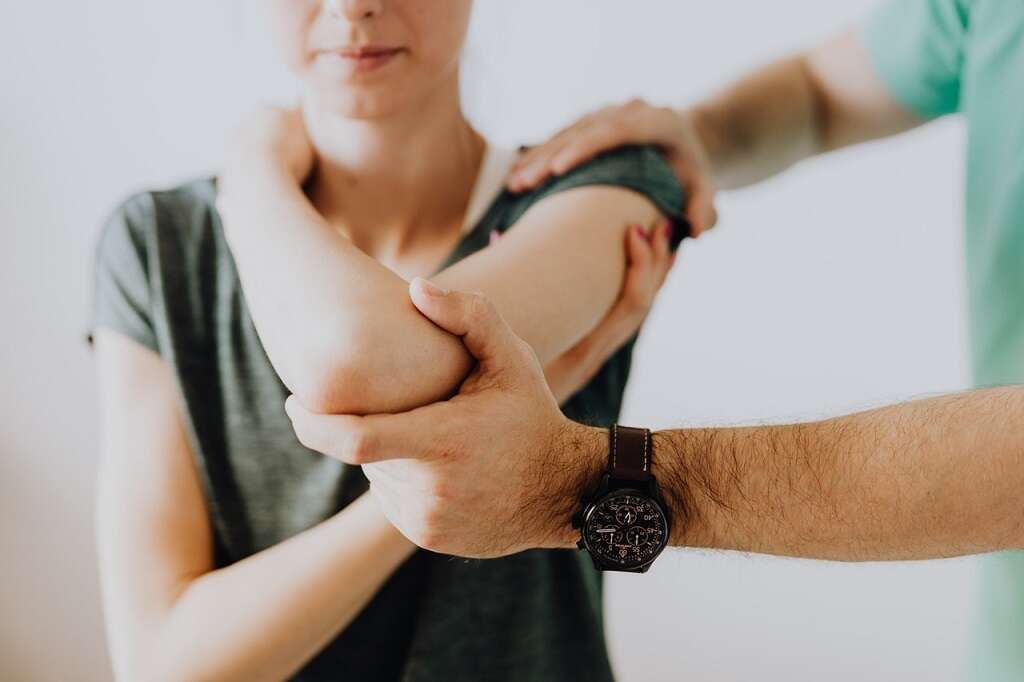
Joint Swelling
Swollen joints are another common symptom of MCTD. The swelling can occur due to an increase in fluids that envelope the affected joints. Along with the swelling, an individual may also experience stiffness and pain in the joint. The joint may also appear bigger in size or misshapen.
Along with arthritis, other common causes of joint swelling can include ankylosing spondylitis, which causes joint inflammation, and inflamed tendons, also known as tendinitis. Individuals should seek medical attention if the swelling is accompanied by a fever.
Advertisement