10 Chlamydia Symptoms For Women
We hear a lot about the importance of safe sex, and for very good reasons. For one thing, there’s the chance of unwanted pregnancies, which can be a real problem for people that are not in a position to bring up children. There is also the risk of catching a disease, some of which can be very dangerous for us.
Among the most common of all sexually transmitted diseases is chlamydia. It is a disease that is relatively mild and also easy to treat so catching it should not be too concerning. Regardless, it remains a good idea to protect yourself against it, and against other sexually transmitted diseases.

1. No Symptoms
Most people that have chlamydia will not even be aware they have it at all. It is common for there to be no symptoms whatsoever, leaving the patient oblivious to the fact they have an infection. This means that people should not be complacent about the disease if they have been taking risks.
Even though you might not have a problem, it doesn’t mean that other people won’t. Not having symptoms also does not mean that you cannot pass it onto other people. If you do suspect that you might have been exposed to the disease recently then you should arrange to get it checked out.
2. Discharge
Discharge is one of the most common symptoms of chlamydia, especially in women. Discharge is not uncommon in women because of how the vagina self-lubricates, but the discharge associated with chlamydia is a rather different type.
Vaginal discharge is usually clear and watery. Discharge that is caused by chlamydia, however, is usually white or yellow in color. The discharge caused by chlamydia is also likely to be much thicker in consistency, while it can also have a very foul-smelling aroma. These symptoms are a clear sign of some sort of infection and should encourage you to speak with a doctor.

3. Back Pain
Some patients will also develop a pain in their lower back. Some patients describe the pain as one that’s similar to those caused by urinary tract infections. In addition to the back pain, some patients will also experience a pain in the abdominal region.
The abdominal pain is often described as a dull pain, or an experience that feels as though they have a cramp. The pain is usually located lower down in the abdomen area in the pelvic region. Either of these symptoms should encourage the patient to see a medical professional if they have not done so already.

4. Rectal Pain
The rectum is the final stage of our digestive system. It is through here that our stools pass before finally reaching the anus. This part of the body can also become infected and, when it does, it can become quite painful for the patient.
In some cases, a chlamydia infection here is the result of transmission by way of unprotected anal sex. At other times, the infection will have started in the vagina and then spread to the rectum. In addition to the pain, the patient might notice a discharge that is mucus-like in terms of appearance and consistency.

5. Fever
Because chlamydia is caused by a bacterial infection, our immune system will step in to try and deal with the problem. One thing the immune system will do to stop the disease is to make the body hotter. If the body is too hot for the bacterium then it can slow it down, or even kill it altogether.
This warming up of the body is a phenomenon known as a fever, and most of us will have experienced it at least once in their lives. In cases of chlamydia, the fever will be quite mild although it can become higher in some cases.

6. Bleeding
Approximately once a month, women will bleed from their vagina. This is due to the inner lining of the uterus being shed in order for it to be replaced by fresh lining. This is a process known as menstruation and it happens in pretty much all healthy women.
Despite this, it is not normal for vaginal bleeding to occur in between periods. If there is bleeding when menstruation is not expected it might be a sign of something being wrong. This can be the result of inflammation inside the vagina, while it can also sometimes be caused by penetrative sex.

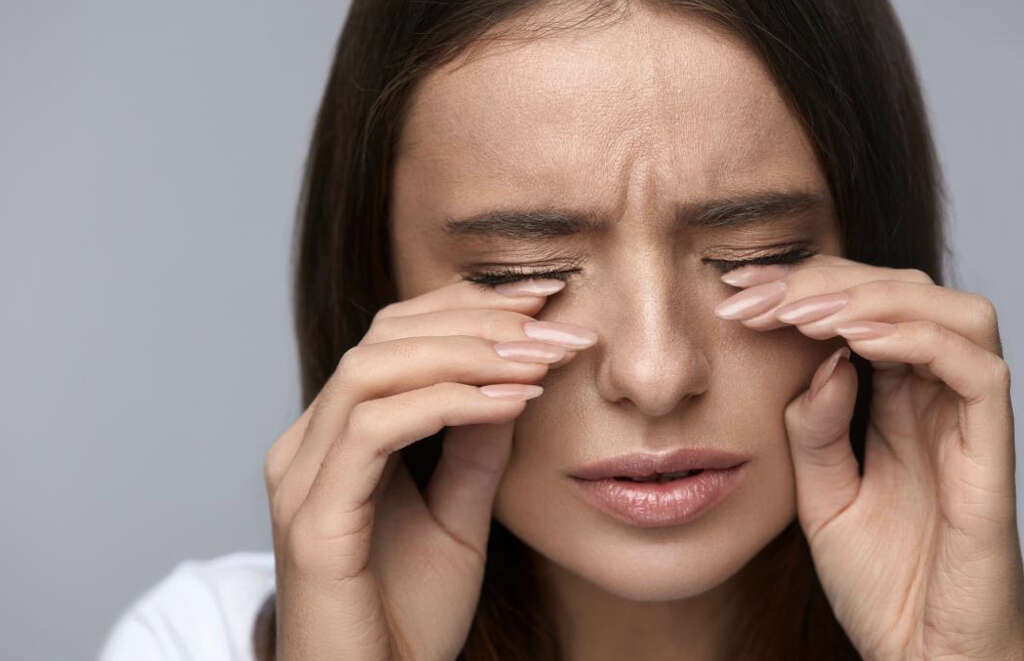
7. Irritated Eyes
The bacterium that causes chlamydia can also get infect somebody’s eyes. This is quite rare and usually happens when the patient has had the sexual bodily fluids of an infected person in one of their eyes. It is known as chlamydia conjunctivitis, and it can cause some very unwelcome symptoms.
Patients with chlamydia conjunctivitis are likely to find that their eyes are irritated. They can be red and sore and also have a discharge coming from them. Chlamydia conjunctivitis can also cause the patient to become more sensitive to light than they usually would be. It is a condition that should be treated to help prevent damage to the eye.

8. Pain During Intercourse
Intercourse can be painful for some women, for a number of potential reasons. One of these reasons is that they have an infection like chlamydia. The vagina might also feel irritated after sex, and they might also experience bleeding from their genitals.
Some people with chlamydia will also find that they need to urinate more frequently than they usually would. The urine can also have a cloudy appearance and it may also have an unusual odor. What’s more is that the patient might experience a burning sensation when they urinate. These are symptoms that should encourage anybody to see a professional.

9. Complications
Chlamydia is usually only a mild disease, while many people will experience no symptoms whatsoever. If the condition is left untreated, however, then more serious complications can develop. Thus, it is always a good idea to get it checked out even if you are otherwise healthy.
If chlamydia is allowed to go untreated then the infection can spread and cause a condition known as pelvic inflammatory disease. An uncontrolled infection may even spread to the fallopian tubes and the uterus, potentially making the patient infertile for the rest of their life. Fortunately, treatment for chlamydia is straightforward so complications are usually avoided.

10. Treatment
Chlamydia is a disease that is relatively easy to treat. As a bacterial infection, antibiotics are usually the preferred choice and there are two main options. One option is doxycycline, which is given as a one-week course. The other is azithromycin, and this is given to the patient in a single dose.
It is important to refrain from sex for two weeks to help prevent spreading the disease further. It is also still necessary to take precautions because having had the disease already does not make you immune to it. Provided adequate protection is taken, however, there is no reason for the symptoms to return again.