What Is Orthopnea?
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Vaskar Mukerji: 'Dyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea.' Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd Edition. 1990, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK213/
- 2. 'Pulmonary edema.' Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009
- 3. Rakesh K. Pai, MD, FACC; Martin J. Gabica, MD; E. Gregory Thompson, MD; Adam Husney, MD; Stephen Fort, MD, MRCP, FRCPC: 'Heart Failure Symptoms.' UMHS Michigan Medicine, August 31, 2020, https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tx4082abc
- 4. Biykem Bozkurt; Douglas L. Mann: 'Shortness of Breath.' AHA Journals, July 15, 2003, https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.0000075956.36340.78
- 5. Cara Martinez: 'Shortness of Breath: When to See Your Doctor.' Cedars-Sinai, September 30, 2019, https://www.cedars-sinai.org/blog/shortness-of-breath.html
- 6. 'Heart Failure: Risk Factors.' University Health Care System, https://www.universityhealth.org/heart-failure/risk-factors/
Orthopnea is the medical term for shortness of breath that occurs in the reclining position and is relieved by sitting or standing This differs from dyspnea, which refers to breathing issues an individual experiences in any position. However, it’s similar to paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, which wakes a person an hour or two after they’ve fallen asleep.1Vaskar Mukerji: ‘Dyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea.’ Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd Edition. 1990, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK213/
More blood flows into the lungs when a person lies down. The heart must work harder to pump blood back out to the body. Congestion and fluid retention are also more prevalent in this condition. Impairment of these functions due to a disease can lead to orthopnea.
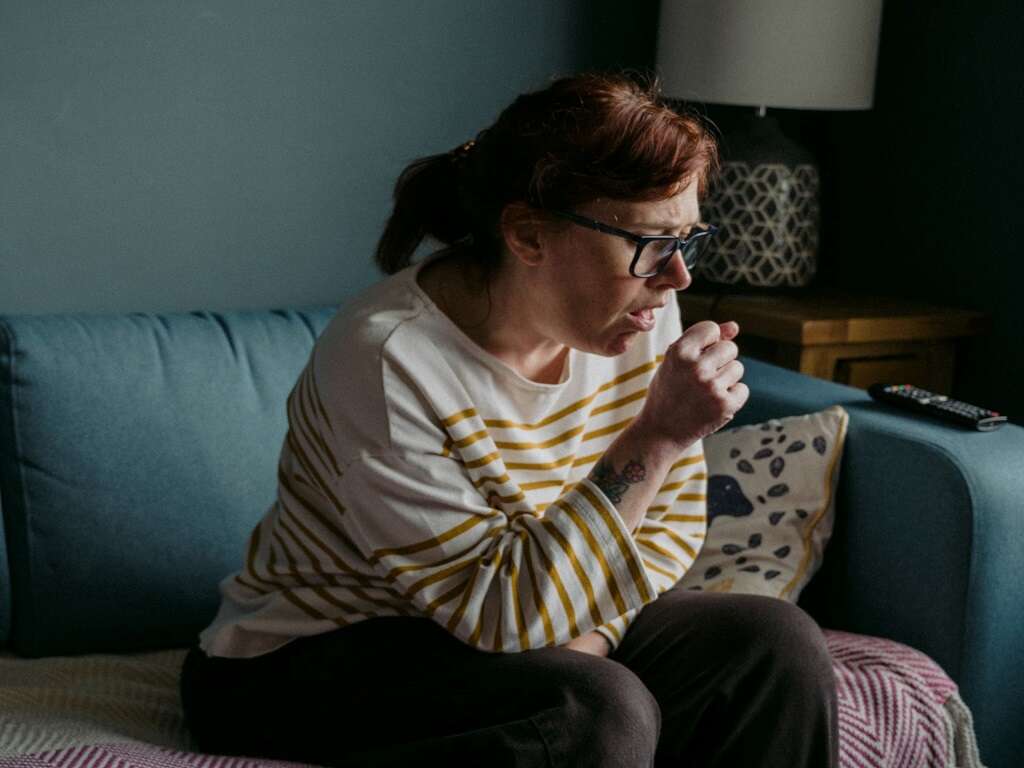

1. Causes
There are many potential causes for orthopnea, from moderate to life-threatening. The most common cause is a heart-related condition, such as high blood pressure, cardiomyopathy and heart failure. In those cases, the individual’s heart isn’t strong enough to redistribute blood throughout the reclining body efficiently. With the increased pressure this causes in the lungs, fluid accumulates and impairs breathing.
Other issues like obesity can make it hard to breathe while lying down. Fluid buildup is another culprit in lung conditions like pulmonary edema, pneumonia or pleural effusion, and ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdomen). Diaphragm paralysis can also lead to orthopnea.
2. Risk Factors
Because orthopnea is typically a symptom of an underlying condition, risk factors include the medical condition that leads to breathing problems when reclining. Issues like sudden weight gain, blood clots and panic disorder can make a person more susceptible to orthopnea.
Medical conditions such as asthma, chronic bronchitis, sleep apnea, polycystic liver disease and heart failure place patients at higher risk for orthopnea. Environmental factors, like high altitude, toxins and drugs, can also play a role in the development of orthopnea.2‘Pulmonary edema.’ Mayo Clinic, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pulmonary-edema/symptoms-causes/syc-20377009

3. Orthopnea and Heart Failure
Orthopnea is frequently a sign of progressive heart disease. It’s one of the main symptoms of heart failure.3Rakesh K. Pai, MD, FACC; Martin J. Gabica, MD; E. Gregory Thompson, MD; Adam Husney, MD; Stephen Fort, MD, MRCP, FRCPC: ‘Heart Failure Symptoms.’ UMHS Michigan Medicine, August 31, 2020, https://www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/tx4082abc Other common signs include excessive fatigue, fluid retention, and swelling of the feet, legs and ankles.4Biykem Bozkurt; Douglas L. Mann: ‘Shortness of Breath.’ AHA Journals, July 15, 2003, https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.0000075956.36340.78
When these symptoms accompany orthopnea, the risks of heart failure are higher. The heart may be damaged, making it too weak to pump blood effectively when in the recumbent position. A cardiologist can help diagnose and treat the cause.

4. Diagnosis
Because orthopnea is both a condition and a symptom of a medical problem, diagnosis of this breathing issue is fairly simple. Essentially, the patient’s description of their breathing difficulties is enough information for a physician to diagnose orthopnea.
One key criterion is that shortness of breath occurs when the individual lies down and goes away when the individual sits up or stands. Another condition for diagnosis is that the issues happen right away or very soon after reclining.

5. Signs of Orthopnea
People suffering from orthopnea often cough or wheeze when reclining. They have shortness of breath, finding it hard to breathe when they recline. The flatter they lie, the worse the symptoms. Therefore, they usually need extra pillows to prop them up in order to fall asleep.
Other signs depend upon the cause of the orthopnea, such as heart failure, polycystic liver disease and chronic bronchitis. Sufferers are likely to exhibit symptoms related to the conditions causing breathing difficulties. Symptoms usually get progressively worse over time.

6. Complications
Orthopnea can lead to fatigue during the day and weight gain. As the orthopnea gets more extreme, many people are unable to sleep in bed at all. Instead, they can only rest while sitting in a chair.
Other complications are tied to the cause of an individual’s orthopnea. In serious cases, such as heart failure, if the person doesn’t seek treatment, it can lead to severe complications. The results may be severe heart failure and death.

7. Management
Individuals with orthopnea may attempt to manage the problem by propping up their upper body with pillows or sleeping in a sitting position. But treating the root cause of this breathing condition is the best way to obtain lasting relief.
Identifying the source is essential for effective management. For example, obesity-related orthopnea can be alleviated with a successful weight loss program. Once a diagnosis of the underlying cause is made, the individual’s medical provider can establish an effective treatment and management program.

8. Prevention
While there are no direct preventative measures for orthopnea, a healthy lifestyle can help. That’s due to the range of conditions that can cause orthopnea. Exercise, a healthy diet and avoiding harmful lifestyle habits can lessen the risks of heart failure and obesity.
Some conditions show a genetic predisposition , but even in these cases a healthy lifestyle can help people stay as healthy as possible. Regular health care checkups, following doctors’ recommendations and timely medical follow-ups are essential and may help lessen the impact of serious medical conditions.

9. Prognosis
As with most aspects of orthopnea, the outlook depends a great deal on the cause of this condition. Severity, timing and available treatment options are all factors. Early medical intervention can often yield encouraging results.
Naturally, serious conditions like advanced heart failure and COPD are more complex and difficult to treat than an acute infection or altitude sickness. So, prognosis varies. Sometimes, medication and oxygen supplementation are used to address the immediate breathing issues of orthopnea while treatment for the underlying cause is ongoing.

10. When to Seek Medical Attention
Because orthopnea is one of the major symptoms of heart failure, its occurrence is cause enough to see a doctor.5Cara Martinez: ‘Shortness of Breath: When to See Your Doctor.’ Cedars-Sinai, September 30, 2019, https://www.cedars-sinai.org/blog/shortness-of-breath.html When accompanied by other risk factors, the urgency grows. Some examples of high-risk factors for heart failure are obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure and a family history of heart problems.
African-Americans, smokers, seniors and individuals who drink excessively or abuse drugs are at higher risk of heart disease.6‘Heart Failure: Risk Factors.’ University Health Care System, https://www.universityhealth.org/heart-failure/risk-factors/ Even without these risk factors, people experiencing orthopnea should seek medical attention.











