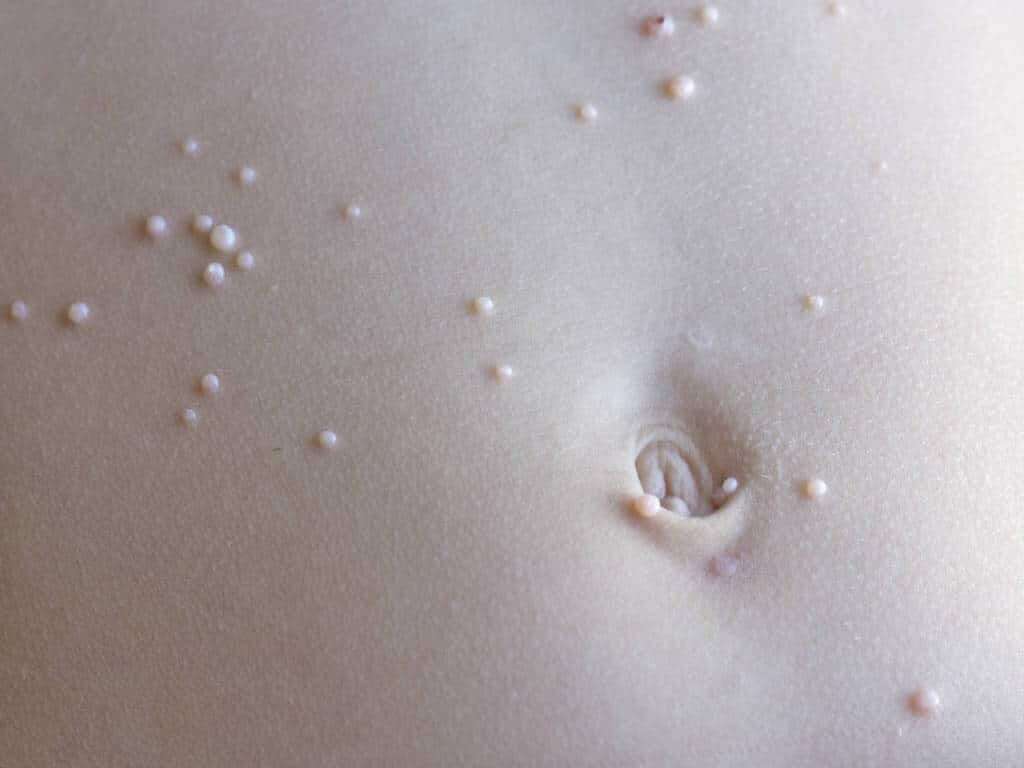
What Is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Our skin is our first barrier of defense against disease. It is effective at this task, helping to keep out pathogens that might do us harm. This does not mean that our skin is invincible, however, and it is prone to developing problems itself. There are numerous different medical conditions that can have a negative impact on our skin.
They can cause rashes, sores, and other blemishes that can be unsightly, uncomfortable, painful, and even dangerous. Most are quite harmless, however, and will do us no harm, even if they do look unpleasant. One example of such a medical condition is molluscum contagiosum.
1. Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a type of viral infection that can affect people of all ages, but is most commonly found in children. When it does affect adults, they tend to be people that have a weakened immune system. It is also a fairly common condition, but is also usually only mild.
The condition can be treated but this can be very uncomfortable, so treatment is avoided in most cases. The condition is very contagious and is spread from person to person, and also from contact with surfaces and objects that are contaminated. Potentially severe complications will arise in just a small number of cases.
2. Skin-To-Skin Contact
Molluscum contagiosum is named after the virus that causes the condition. It causes lumps to appear on the patient’s skin, and these lumps are very contagious. All it takes for another person to become infected is for them to come into skin to skin contact with an infected person.
The virus can also rub off onto items like towels and clothing. Even surfaces that have been in contact with an infected person can pass on the virus if another person’s bare skin comes into contact with them. One of the reasons it is common in children is that children are more likely to be in close contact with other children.

3. Scratching
Molluscum contagiosum will usually infect a single area to begin with, causing a single bump. However, many people will scratch and rub these bumps, and this can cause other areas of the skin to become infected also. At the peak of the disease, the patient can have the bumps all over their body.
The bumps will be itchy in some cases, and it can be very difficult to avoid scratching them. This, in turn, means that the bumps are more likely to be spread to other parts of the body. It is not uncommon for the bumps to appear on the patient’s face from touching their face after scratching a bump elsewhere on their body.
4. Sexual Contact
As mentioned, molluscum contagiosum is a disease that is spread by skin to skin contact. When people have sex, there tends to be a lot of skin to skin contact involved. The disease is often spread through contact with an infected person’s genitals. This is the most common way that the disease will be spread among adults.
In adults, the bumps are most likely to be found in the genital area, although they can spread to other parts of the body. It is not necessary for bodily fluids to be exchanged in order for a person to contract the disease sexually. Wearing a condom will provide some protection, depending on where on the body the bumps are.

5. Symptoms
The bumps that are caused by molluscum contagiosum are usually no more then ¼ inch across. They can also be much smaller. The bumps are round, flesh colored, and are raised up from the skin. They will also typically have a small recess at the top. They will become itchy for some people, and scratching them can cause them to turn red.
In children, the spots are most likely to appear on the arms, armpits, face, neck, and on the top of the hand. The same goes for adults, although the spots are more likely to be found on the upper thighs, lower abdomen, and on the genitals if the disease was spread sexually.
6. Complications
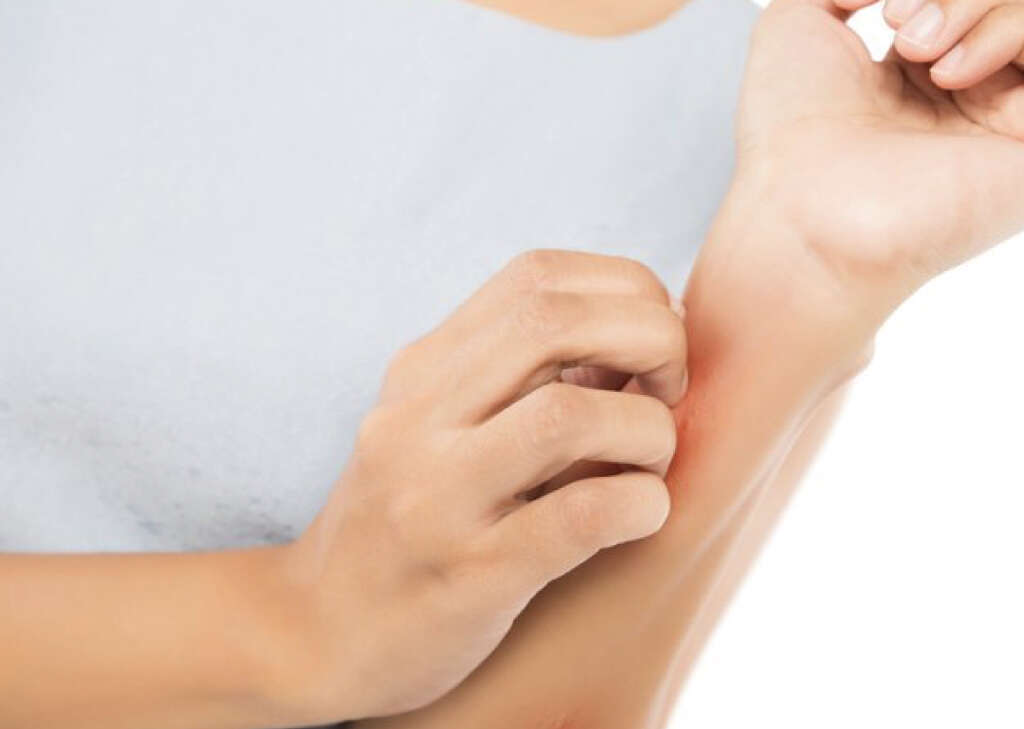
When the bumps become itchy, it can be very difficult to resist scratching them. Excess scratching can break the skin, and the bumps can become infected as a result. Some of the bumps may also leave behind permanent scars after they have disappeared.
If the patient scratches or rubs their eyes after touching an infected area, the bumps can develop on their eyelids also. This will, in turn, develop into keratitis or conjunctivitis in some cases. These conditions are treatable, but they can cause permanent damage to the eyes if they are left untreated so it would be wise to see a doctor as soon as possible.
7. Who’s At Risk
Pretty much anybody is at risk from catching the disease. All it takes is contact with another infected person. However, children are more likely to catch the disease than adults are. This is largely because children tend to be in close physical contact with other children quite a lot when playing with each other.
Other people at risk include adults that have numerous sexual partners. It is also more common in people that have weakened immune systems, such as people that have HIV/AIDS. People with weakened immune systems are also more likely to find that the infection will be widespread over their bodies.
8. Prevention
Because the virus is so contagious, it is very difficult to prevent it from spreading. However, there are steps we can take to help limit the spread as much as possible. One of these is to wash our hands frequently, and using soap and water will be even more effective. We should also try and avoid sharing items with other people.
Avoid touching the bumps as much as possible, and also avoid shaving over them. Bandages, Band-Aids, and clothing can be used to help cover the bumps, thus preventing contact with them. Patients should also try and avoid sexual intercourse if they have bumps on their genitals.

9. Diagnosis
The bumps that are caused by molluscum contagiosum are quite distinct, and it is a common condition, meaning your doctor will likely be well aware of it already. This means that the doctor will often be able to make a diagnosis just by performing a brief physical exam.
The bumps will also resemble symptoms of other medical conditions in some cases, so the doctor might want to request tests to be sure of what the problem is. If necessary, scrapings of the skin can be taken and then sent away for analysis where experts can look for signs of molluscum contagiosum.
10. Treatment
Treatment is usually not deemed necessary, and the patient will often make a full recovery in 6 to 12 months. Some people will continue to develop new bumps for up to 5 years, however. The patient will no longer be contagious once the bumps have completely disappeared.
The highly contagious nature of the bumps means that doctors will sometimes recommend they are removed. This can help to prevent them spreading to other parts of the patient’s body, and also to other people. However, the procedure can be painful, so surgical removal of the bumps is avoided where it is not deemed necessary.