What Is Melanin?
4. Physiology of Melanin in Humans
Granules of melanin are inserted by melanocytes (cells) into vesicles (melanosomes). These vesicles are then transferred into keratinocyte cells in the skin (epidermis). These then accumulate on top of the cell nucleus to protect the nuclear DNA from mutations that can be caused by ionizing radiation of ultraviolet rays.
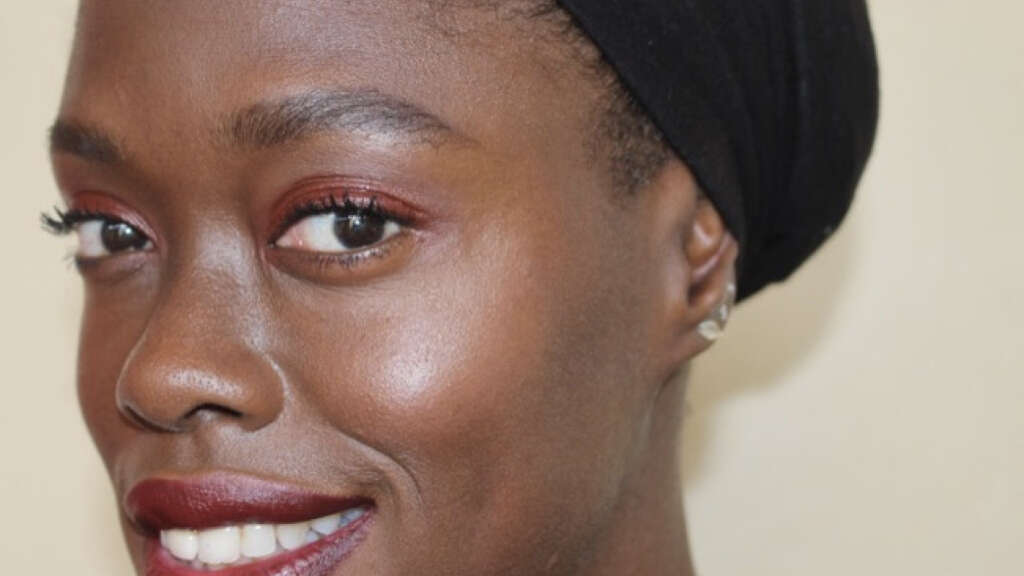
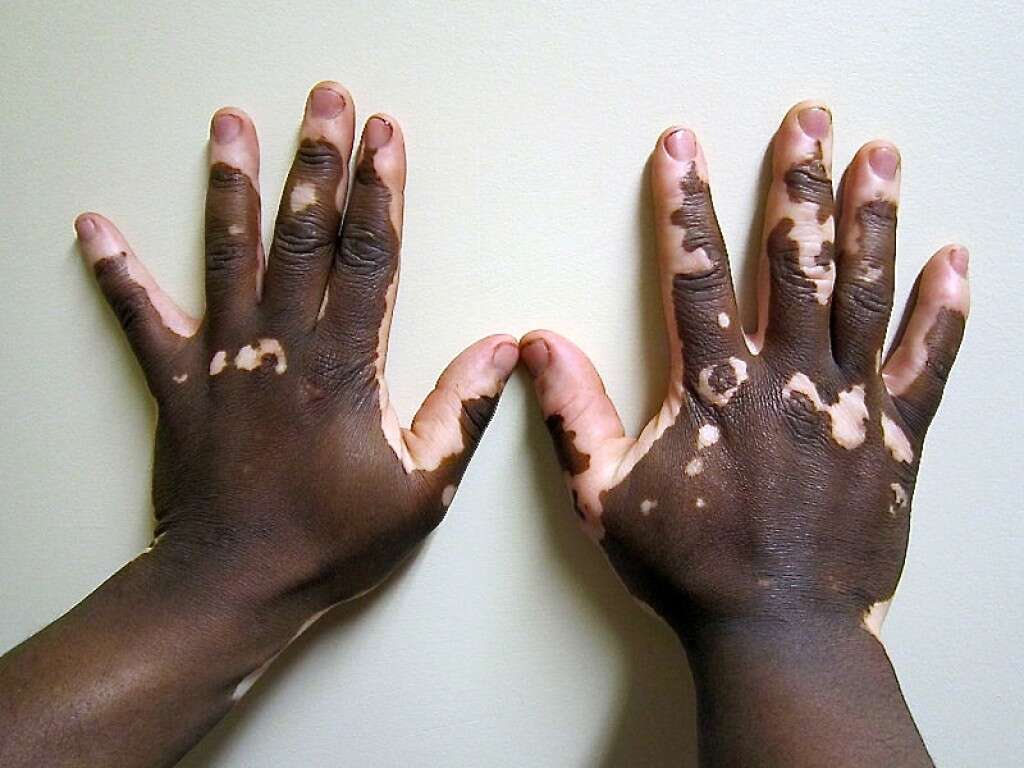
Generally those who live near the equator have more eumelanin, resulting in darker skin (brown or black) to protect them against the higher exposure to the sun. Since they have better protection, melanomas (skin cancer) are more commonly seen among those with lighter skin. However, increased pigmentation also increases the amount of heat absorbed from sunlight compared to individuals with lighter skin. Increased pigmentation also interferes with the synthesis of vitamin D, leading to increased incidences of rickets in dark-skinned children.
Advertisement