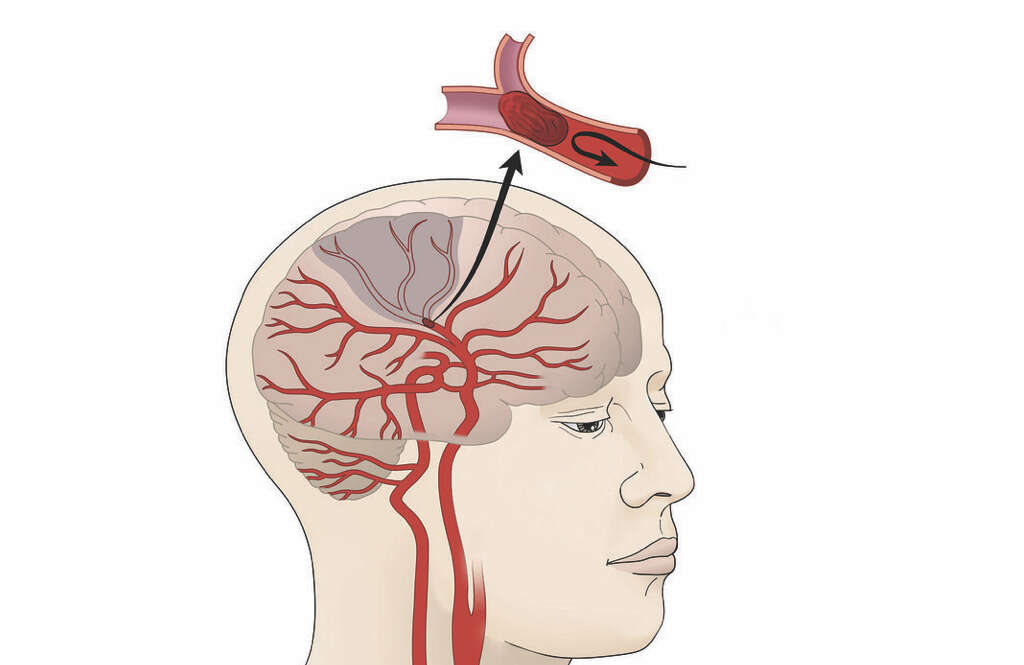
What Is Cerebral Infarction?
Our brains are made of living tissue and, as with all other living tissue; it needs to be fed with a constant supply of fresh blood. If the supply of blood to the brain was cut off, then the patient is going to be in a lot of trouble. They may end up with a cerebral infarction.
A cerebral infarction is a very serious condition that will be fatal in many cases. It is not always fatal, however, and some people will go on to live for long after the incident took place. A cerebral infarction will often be caused by a stroke, and anybody suffering from a stroke should be found medical assistance immediately.

1. A Cerebral Infarction
If brain cells are starved of oxygen for long enough, then they will simply die. This tends to happen in certain parts of the brain and it is known as a cerebral infarction. Part of the brain dying will likely have some very profound symptoms for the patient. It can also, of course, be extremely dangerous.
Cerebral infarctions are typically caused by an ischemic stroke, which means that the blood vessels supplying the brain with blood have become blocked. The deceased part of the brain cannot be revived, but patients will often still be able to restore at least some of any faculties that might have been lost.

2. Ischemic Stroke
There are two main types of stroke. One of these is a hemorrhagic stroke, which means that the blood vessels in the blood have burst. Burst blood vessels will mean that blood is leaking out into the brain. With nowhere for the blood to go the pressure inside the brain will increase, potentially causing damage to the brain’s cells.
The other type is an ischemic stroke and, as mentioned, this type is responsible for cerebral infractions. It means that the flow of blood to the brain through an artery has somehow become blocked. There are several potential reasons for this happening.
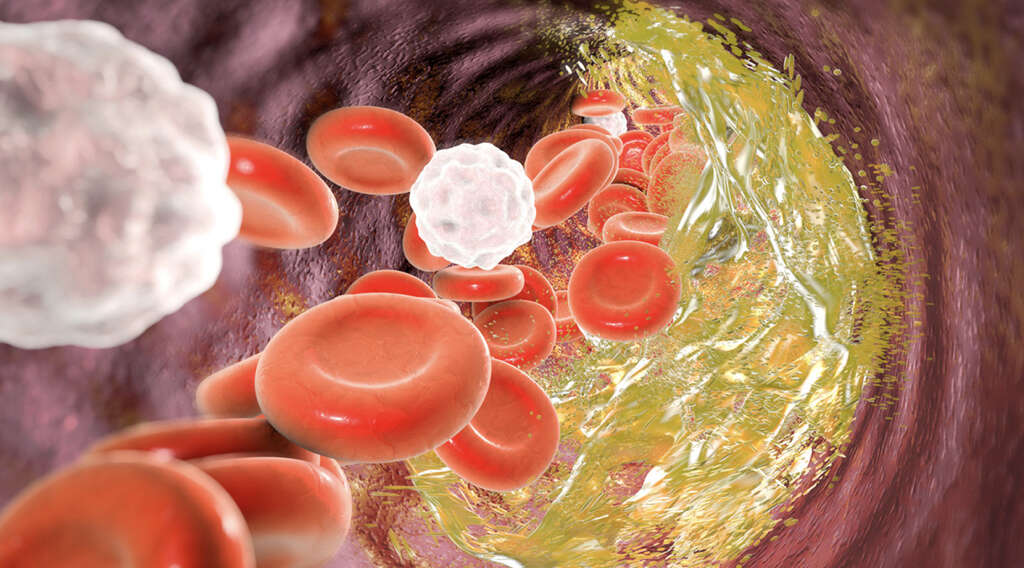
3. Atheromatous Blockage
Our arteries have smooth linings, and this helps the blood to flow through the channel. If this lining was to somehow become damaged, then particles can begin to accumulate on the lining. This can develop into plaque, which is hard material made of fatty deposits, and blood cells, among other things.
This buildup of materials can begin to impede the flow of blood through the blood vessel, in a condition known as atherosclerosis. This can cause a stroke directly as the flow of blood to the brain becomes blocked. It can also result in a stroke by way of producing a thrombus.
4. Thrombus
A thrombus is the technical medical term for a blood clot, and it is a condition associated with atherosclerosis. The plaque that builds upon the walls of the blood vessels will sometimes be torn away by the flowing blood. This tearing can cause a blood clot to form at the site of the damage, and this can be very dangerous.
Atherosclerosis is not the only potential cause of a thrombus. It can also be caused by an injury to the patient, for example. However it is caused, a thrombus will remain in place and potentially cause strokes and other serious conditions as the flow of blood is impeded. A thrombus can also result in an embolus.
5. Embolus
As mentioned, a thrombus is a blood clot that remains in position. They can become dislodged, however, at which point they will circulate through the cardiovascular system. At this point they become what is known as an embolus, which is also very dangerous.
The clot can continue to flow through the system until it reaches a part where it becomes lodged. This will stop the blood from flowing through the blood vessel, cutting off the supply of oxygen further along the system. This very dangerous condition can happen in several places in the body, and it can result in a stroke.

6. Symptoms
A cerebral infarction is likely to cause a number of unpleasant symptoms, and the severity of the symptoms will vary according the specifics of each case. There will also be different symptoms from case to case, depending on which part of the brain is affected.
Many patients will experience a loss of sensation on one side of the body. The side that is affected will be on the opposite side to the cerebral infarction. Other potential symptoms of a cerebral infarction include abnormalities with vision, impaired reflexes, and slurred speech. A stroke can also cause other symptoms like confusion, paralysis on one side of the body, and a loss of balance.

7. Who’s At Risk?
Those people most at risk of suffering from a cerebral infarction are also those most at risk of having a stroke. A stroke can happen to any person at any time, but it is more likely to happen in people that are older. This is partly because the underlying causes of stroke are often those that will develop with age.
People with atherosclerosis are among the people at particularly high risk, as are people with a high blood pressure. Obese people are also at a higher risk, as are people that eat unhealthily and do little exercise. It is a good idea to get regular check-ups to try and identify potential problems early.

8. Prevention
It is not possible to completely prevent cerebral infarctions, but we can at least move the odds in our favor. This mostly means taking good care of yourself overall by exercising regularly and eating healthily. Even modest efforts at living healthily can make a significant difference.
Some people will have medical conditions that make having a stroke more likely. These conditions can often be managed to help reduce the chances of something serious happening. This will often mean using medication to help treat symptoms in addition to living healthily. Some surgical procedures are available that can also help to reduce the chances of a stroke occurring.

9. Diagnosis
It will be necessary for a diagnosis to be reached so that the patient can receive the appropriate treatment. There are some techniques that will help professionals to tell what the problem is. Doctors will also want to ask the patient, or friends and family, about their symptoms and medical history.
It is often important for doctors to rule out other underlying causes of the patient’s symptoms. Imaging techniques like an angiogram will help to identify any blockages that could lead to a stroke. An MRI and CT scan can also be used to help look for physical signs of a cerebral infarction.

10. Treatment
Treating a cerebral infarction will first involve having to deal with the underlying cause. This means removing or bypassing blockages in the blood flow so the brain gets the oxygen that it needs. This will help to prevent further damage being caused to the brain, and must be done as a matter of urgency.
Even in patients that do survive, it is not possible to restore the lost tissues. However, therapy can help the patient to restore at least some of the functions they might have lost. Therapy can be very effective, and some patients that have suffered from a cerebral infarction will go on to live a relatively normal life.