What Is Wallenberg Syndrome?
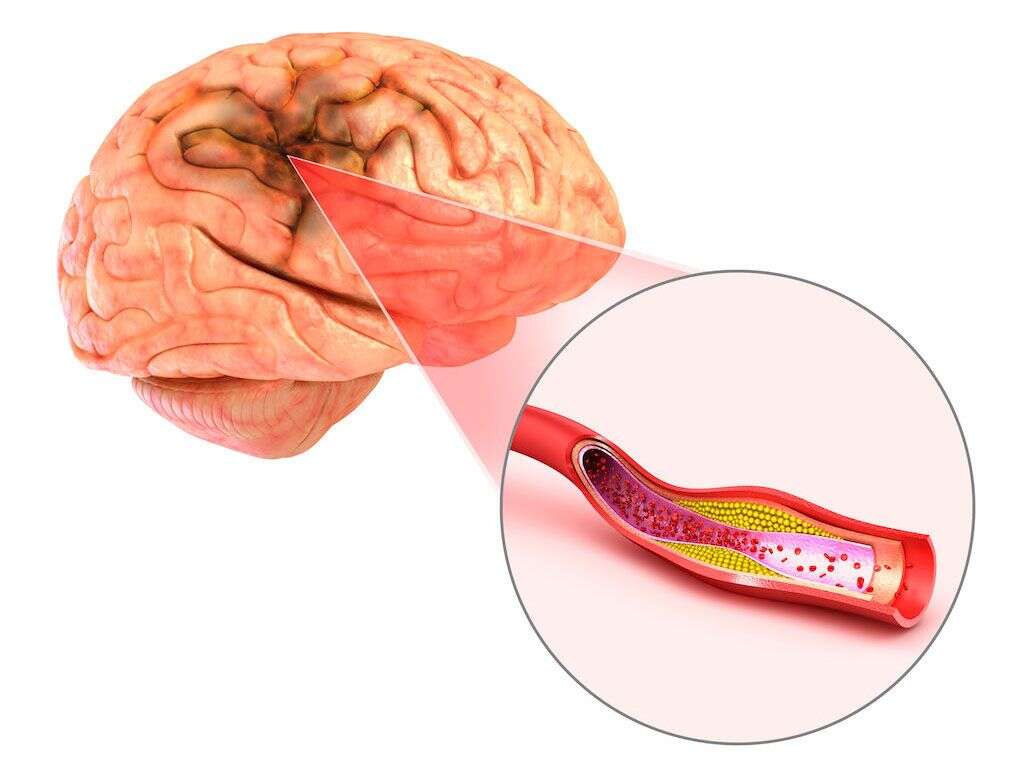
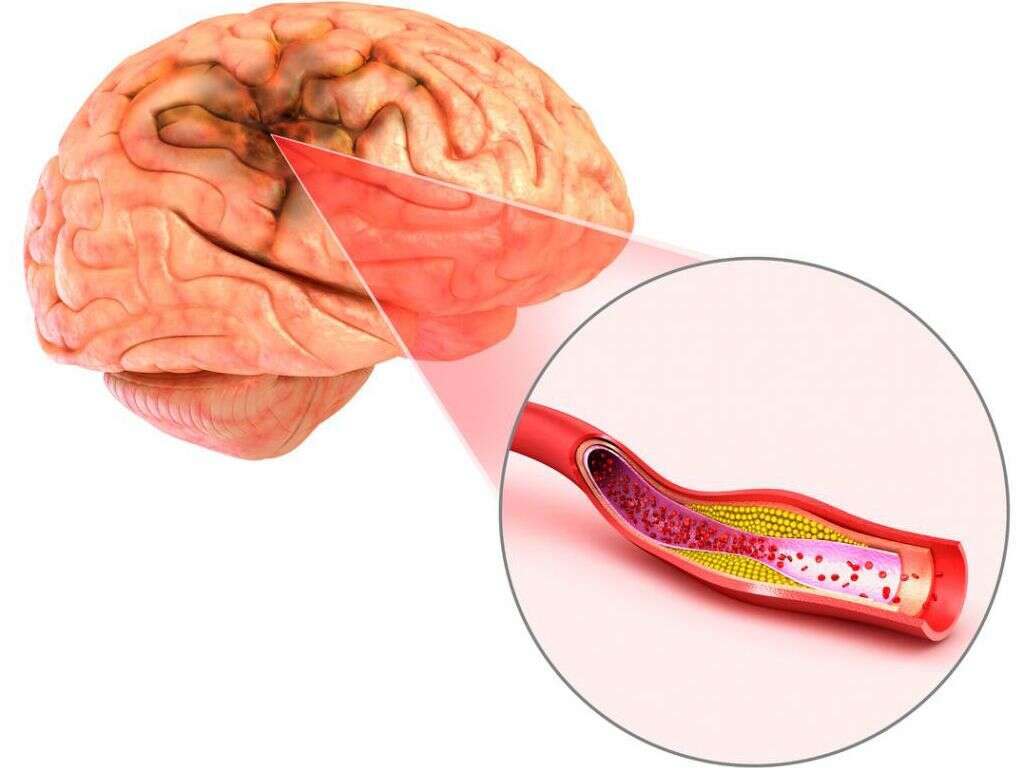
Wallenberg syndrome, also called lateral medullary syndrome, is a type of stroke that affects the stem part of the brain. This is the region comprising the medulla oblongata. The syndrome occurs when blood supply is curtailed due to blockage within either of the two arteries supplying this region of the brain. The two arteries are known as vertebral artery and posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
Similar to other parts of the brain, when starved of oxygen for a length of time, the affected brain cells can no longer function properly and may end up dying. When this happens, it leads to the symptoms associated with Wallenberg syndrome. The condition, whose predisposing factors include smoking, hypertension, and diabetes, is more common in men aged 55 years or older.
1. Symptoms of Wallenberg Syndrome
The brain stem is responsible for the control of vital body functions including swallowing, muscle function, heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and consciousness. This communication occurs through the spinal cord. It follows that in the event that Wallenberg syndrome occurs, it will interfere with these functions. The most common symptom of Wallenberg syndrome is the inability to swallow. This can have serious effects if it goes untreated because the affected person may not get adequate nutrition.
Other Wallenberg syndrome symptoms include nausea, vomiting, a hoarse voice, imbalance, and dizziness. The patient may also have difficulty in walking, and suffer with hiccups, decreased sweating, and poor temperature sensation. Other symptoms include numbness and paralysis on one side of the body, which may affect the face, the limbs, or even the tongue.
2. Causes of Wallenberg Syndrome
It is not clear why Wallenberg syndrome occurs. However, the condition develops when the brain stem is starved of oxygen for a period of time. This leads to inflammation of the affected brain cells making them ineffective in carrying out their functions.
When this happens, the body functions controlled from the affected part of the brain can no longer run normally. This is what leads to the symptoms described above.
The cells that make up the brain stem, as indeed the rest of the brain and the body, need oxygen and nutrients to produce energy. These are delivered through blood. If, however, blood rich in oxygen and nutrients does not flow with ease to these cells, they can no longer produce the energy necessary for them to function. If this continues for some time, the cells may even die, making the brain tissue dysfunctional.
3. Blood Clots
Blood clots are the most common cause of Wallenberg syndrome and other types of stroke. When stroke occurs as a result of blockage of blood flow it is called ischemic stroke.
For blood to flow with ease and deliver oxygen and nutrients to the brain and the rest of the body, it needs to have a certain consistency.
The blood vessels should also be flexible and have no impediments or constrictions. If, however, blood becomes too thick, clots may form. Clots may also form as a result of disease or trauma to the neck area. If such clots end up in the blood vessels serving the brain stem, they can block the flow of blood. This can cause Wallenberg syndrome.
4. Wallenberg Syndrome and Chronic Diseases
While an otherwise healthy person can get Wallenberg syndrome, some medical conditions increase the risk of the disease.
For this reason, people who have these conditions are more likely to get Wallenberg syndrome: high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, high cholesterol, arterial fibrillation, and obesity.
For this reason, you should undergo regular medical checks to find out if you have any of these conditions. People with any of these or other chronic conditions should ensure that they get proper treatment. And if you smoke cigarettes or take too much alcohol, you should review these lifestyles and consider quitting in order to reduce your risk of getting the disease.

5. Complications of Wallenberg Syndrome
Although many patients recover significantly from brain stem stroke, in some cases, complications can develop. As discussed earlier on, the brain stem controls several functions in the body. If the syndrome causes serious damage in parts of the brain stem, physical bodily functions may be adversely affected for the long term.
Complications include disruption of speech, eye movement, and general mobility. The extent of these complications varies depending on the severity of the damage. In cases where severe brain stem damage occurs, patients may develop total body paralysis such that, except for the eyes, the rest of the body remains in a locked-in state with no mobility.
6. Disease Process
As mentioned earlier, the brain stem is responsible for various vital functions in the body.
And similar to the rest of the brain, and indeed the body, the brain stem requires a continuous flow of oxygenated blood that also contains nutrients.
The nutrients and oxygen are necessary for the production of energy required for proper brain and body functions. If, however, blood flow is disrupted due to a blockage in the blood vessels, the affected cells can no longer function normally, a condition called infarction or stroke. When this happens in the brain stem, the resultant condition is called Wallenberg syndrome.

7. Diet and Lifestyle Changes in the Management of Wallenberg Syndrome
Some dietary and lifestyle changes can have positive effects after suffering from Wallenberg syndrome.
As with other types of stroke, lateral medullary syndrome usually occurs as a result of poor blood flow to the affected part of the brain.
It follows that a patient affected by the condition should make some dietary and lifestyle changes that support good circulation. These include drinking adequate amounts of water, eating foods rich in fiber, cutting out on greasy fast foods, reducing alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and exercising regularly. It is also worth to note that incorporating these changes can help reduce the risk of stroke in the first place.
8. Diagnosis
When a patient visits a doctor, the doctor will first review the symptoms and take medical history of the patient. If the symptoms are indicative of a case of Wallenberg syndrome, the doctor will then order tests.
Computed tomography, also called a CT scan, and magnetic resonance imaging, also known as MRI, are the most common methods used to determine whether or not a patient has lateral medullary infarction.
Once a CT scan or MRI is taken, the doctor is better able to make a diagnosis. This is possible because the resultant image can show signs of blockage of blood vessels associated with stroke in the brain stem.
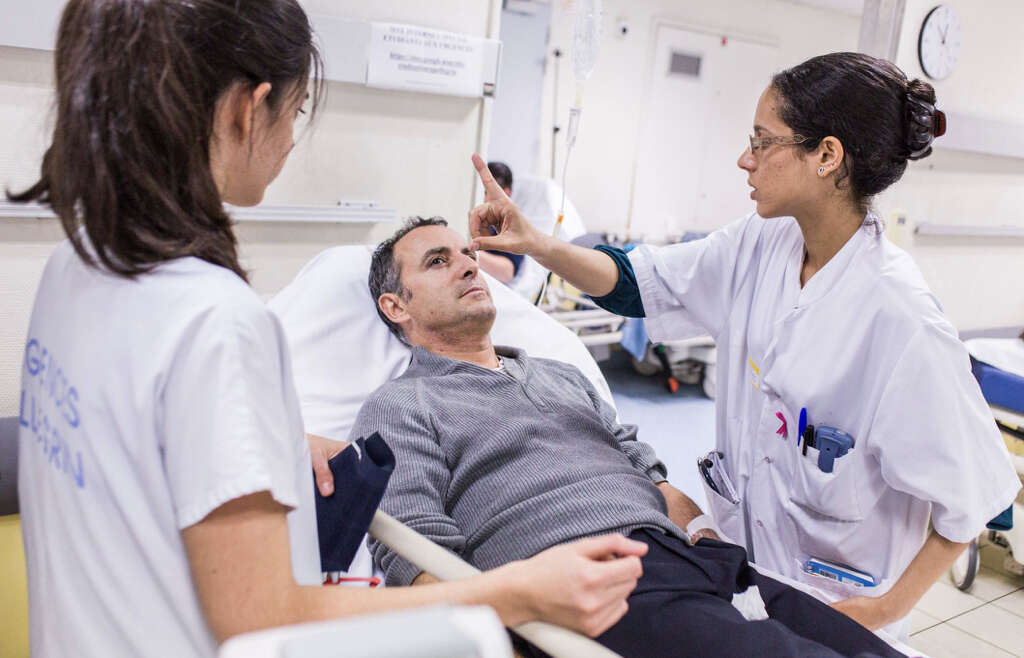
9. Treatment
Treatment of Wallenberg syndrome depends on its severity and the affected parts of the body. In general, however, treatment is intended to offer relief from the symptoms and to help the brain and body to recover. Because this type of stroke usually affects swallowing, a feeding tube is inserted to ensure that the patient gets the necessary nutrition.
Additionally, the patient is put through swallowing and speech therapy to help regain these abilities.
Blood thinning medication such as warfarin is also given to help dissolve clots so that blood flow is improved. The patient may also be given pain relieving medication such as gabapentin. In some cases, surgery may be necessary for the removal of blood clots.
10. Long-Term Outlook
In most cases, the long-term outlook for Wallenberg syndrome is good with most patients achieving significant recovery within weeks and up to six months. This, however, depends on the affected part of the brain stem, the extent of damage, and the length of time before treatment was commenced.
Less damage and immediate commencement of treatment can mean that the patient recovers sooner.
In cases of more serious damage, and delayed treatment, recovery may take longer. It could also lead to permanent damage and disability. To reduce the risk of long-term disability, it is necessary to seek treatment as soon as possible following the appearance of symptoms suggestive of Wallenberg syndrome.