10 Vitamin B12 Deficiency Symptoms
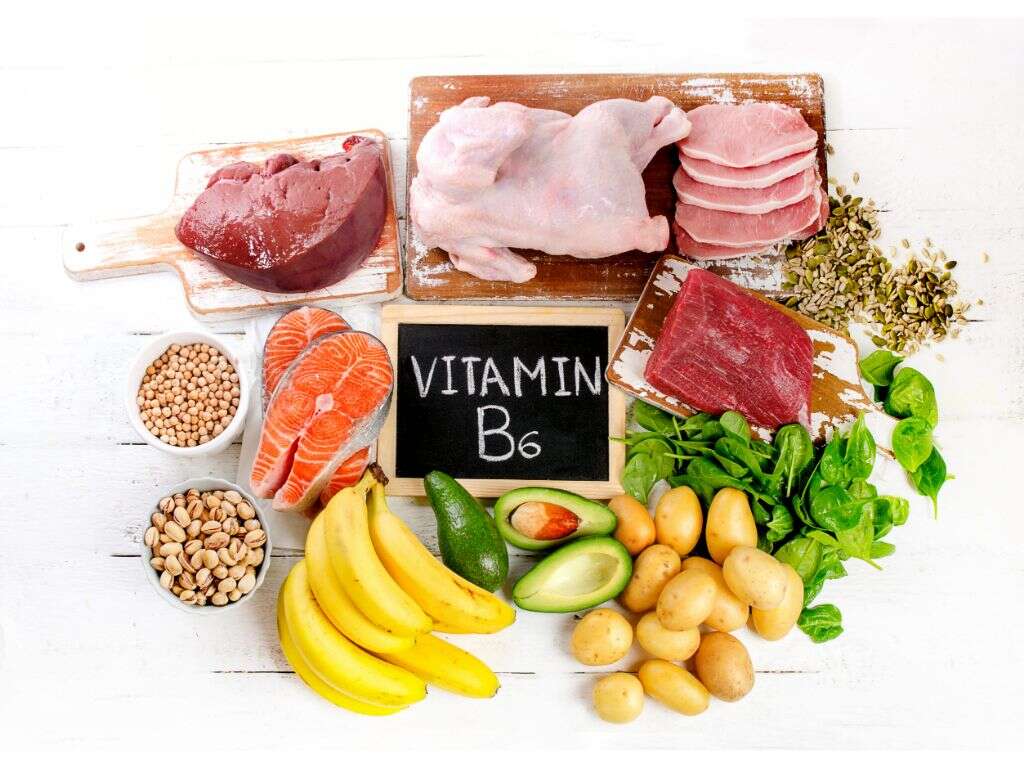
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an important water-soluble vitamin whose roles in the body include generation of DNA and red blood cells. It also helps in the correct functioning of the nervous system.
Foods derived from animals such as red meat, poultry, dairy, eggs, and fish contain the highest amounts of vitamin B12. You can also get significant amounts of cobalamin from food products that are fortified with vitamin B12 such as breads and plant-based milk.
Deficiency of vitamin B12 is more common in the elderly, and in people whose diet does not contain enough cobalamin, including strict vegetarians. It can also affect people who take medications like metformin and antacids in the long term and those who’ve had a portion of their bowel surgically removed. Below are 10 vitamin B12 deficiency symptoms to be aware of.
Symptom #1: Moodiness
Many people with vitamin B12 deficiency complain of sudden changes in their moods. As a matter of fact, low levels of B12 have been linked to mood and brain disorders such as depression and dementia. The “Homocysteine Hypothesis of Depression” has been suggested as a potential explanation for this link.
This theory suggests that high homocysteine due to low levels of the vitamin might cause brain tissue damage, which would then interfere with signals going to and coming from your brain leading to mood changes. The symptom can be reversed by supplementing vitamin B12. It should be noted that the changes in mood can have different causes. Taking a vitamin B12 supplement can help in the improvement of your mood if it is deficiency induced.
Symptom #2: Dizziness and Breathlessness
If you have vitamin B12 deficiency, you may become anemic. This can lead to constant shortness of breath and dizziness, especially when you engage in demanding physical activity. This happens because your body is short of red blood cells, which are necessary for the delivery of oxygen to the cells in every part of your body.
Without adequate oxygen, the cells of your body cannot play their roles effectively. They cannot even produce sufficient energy to function properly. When this happens to brain cells, it can cause dizziness. It is worth noting that, besides vitamin B12 deficiency, these symptoms could be due to other causes. For this reason, if you suffer from bouts of shortness of breath, visit a doctor to find out what might be the problem.

Symptom #3: Mobility Issues
Damage to your nervous system as a result of vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to changes in your movement and walking style. It could also have an effect on your balance and coordination, which makes it easy for you to fall. This occurs because of the deterioration of the nerves due to B12 deficiency. To prevent this from happening, ensure that your diet contains foods rich in vitamin B12.
This symptom is more common in the elderly because people above the age of 60 are usually more prone to having a B12 deficiency. However, treating or improving such deficiencies will usually improve mobility. This symptom might be also present in young people that have a severe untreated deficiency.
Symptom #4: Pins and Needles Sensations
The most serious side effect of B12 deficiency is damage to the nerves. This could occur over time if deficiency goes on for long because vitamin B12 is an important contributor to the metabolic pathway that produces myelin. Myelin is a sheath that surrounds the nerves, and serves as protection and insulation.
When adequate B12 is lacking, myelin production is affected in such a way that the nervous system might not function properly. The most common symptom for this is paresthesia, which is the sensation of pins and needles. The symptoms associated with B12 deficiency usually occur alongside anemia. Note that this sensation is a common symptom that may also have other causes.

Symptom #5: Fatigue and Weakness
This is a very common symptom of deficiency in vitamin B12. You get weak and fatigued because your body does not have adequate amounts of vitamin B12 to make all the red blood cells necessary for healthy transportation of oxygen throughout the body. Low levels of red blood cells lead to inadequate oxygen, which presents as weakness and fatigue.
For the elderly people, this type of anemia is usually the result of an autoimmune condition called pernicious anemia. People that have this anemia do not produce enough intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is essential for preventing deficiency, as it ought to bind with vitamin B12 in your body so that you are able to absorb it.
Symptom #6: Skin Paleness or Jaundice
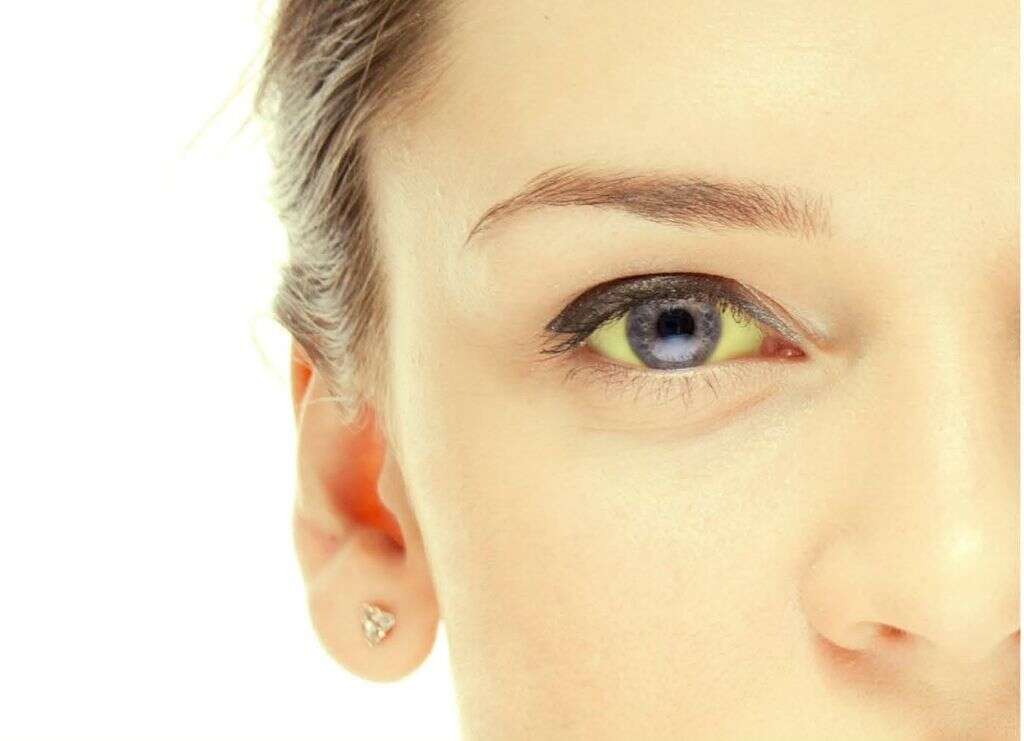
People that have B12 deficiency are usually pale or have a slight yellow tinge to their skin and the white part of their eyes. This condition is called jaundice and happens when a lack of B12 brings about problems in your body’s production of red blood cells. Vitamin B12 plays an essential role in the production of red blood cells.
There is a type of anemia known as megaloblastic anemia that causes the red blood cells located in your bone marrow to be large and fragile such that they cannot pass out of your bone marrow and into circulation. This denies blood the supply of these red blood cells. The shortage causes the skin to appear pale in color. Because of their fragility, many of these cells break down and cause excess bilirubin and yellowing of the skin and the white parts of the eyes.
Symptom #7: Blurred Vision
Blurred or disturbed vision is another vitamin B12 deficiency symptom. This usually results when an untreated B12 deficiency progressively damages the nervous system in various parts of the body including the optic nerve which connects the eyes to the brain. When this happens, visual signals no longer travel effectively, hence the disturbed vision. The name for this type of damage is optic neuropathy.
If you notice that your vision is deteriorating and getting blurred, there are chances that this may be a result of deficiency of vitamin B12. If you think that you don’t take adequate amounts of B12, you should consider supplementing. Note that optic neuropathy is largely reversible by supplementing with vitamin B12.
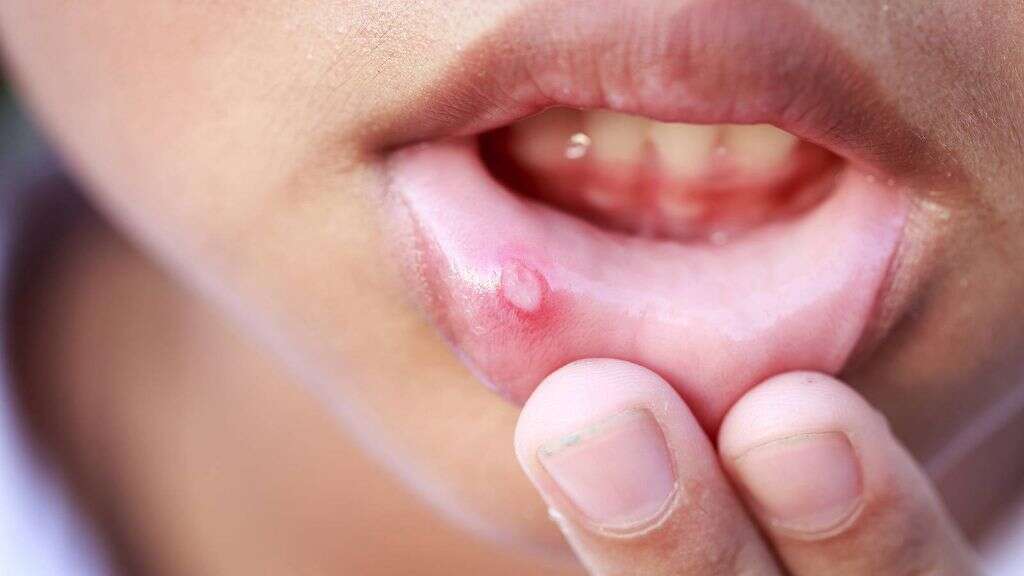
Symptom #8: Mouth Ulcers
When you have a mouth inflammation known as glossitis, your tongue begins to change shape and color. It may become really red, swollen, and very painful. The ulcer makes the tongue feel and look smooth because the little holes on the tongue, which act as taste buds, are covered due to the swelling.
Apart from the pain that comes with glossitis, it can also change the way you eat or speak. It has been proven that an inflamed tongue that has long straight lesions on it could most likely be a very early sign of vitamin B12 deficiency. Also people with the deficiency might experience other oral symptoms like itching and sensations of pins and needles.
Symptom #9: Fever
Fever is a rare vitamin B12 deficiency symptom, although it occurs occasionally. It is not clear how this symptom occurs, but it can arise due to serious and long-term deficiency of B12. Some cases of fever are known to eventually clear after increasing intake of vitamin B12.
It is also worth to note that in most cases, fever is a sign of an infection or illness. For this reason, it is not enough to take vitamin B12 supplements and assume that your condition will improve. If you suspect a case of fever to result from deficiency of vitamin B12, you need to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptom #10: Decreased Appetite
Due to the other digestive issues such as nausea and diarrhea, deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to loss of appetite, which may lead to weight loss in the long run. When your stomach is upset, you are getting recurrent diarrhea or nausea, and you feel weak, you may find it difficult to eat enough food to maintain a healthy weight.
It is important to note that besides low intake of the vitamin, deficiency can also arise due to underlying health conditions that might interfere with its absorption. Such conditions include Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, atrophic gastritis, and pernicious anemia. For this reason, you need to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of the problem.