10 Uveitis Symptoms
The uvea refers to the pigmented part of the three concentric layers of the eye. The constituents of the uvea include the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. The uveal tract can be divided into anterior (iris and ciliary body) and posterior (choroid) components. The term “uvea” may be a reference to the almost black color and wrinkled appearance when the uvea is stripped from the eye of a cadaver. The uveal tract is responsible for nutrition and gas exchange as well as light absorption. Some added functions include control of the focus of the eye, secretion of aqueous humour, and retinal illumination optimization.
When the uvea is inflamed, it results in a condition known as uveitis. Uveitis is considered an ophthalmic emergency where an examination and treatment by an ophthalmologist is required to help reduce the inflammation. It is an emergency as it can be serious and result in permanent loss of vision. To prevent the complications of uveitis, early diagnosis and treatment is key. This condition can affect one or both eyes and can be caused by infection (Lyme disease, herpes zoster, cat-scratch disease, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, West Nile virus), autoimmune disease (ankylosing spondylitis, sarcoidosis), injury, inflammatory disorder (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease), or eye surgery. In many cases, the cause is unidentified (idiopathic uveitis). Studies have also shown significant association between cigarette smoking and uveitis. Left untreated, uveitis may result in complications such as permanent loss of vision, cataracts, glaucoma, retinal detachment, and optic nerve damage.
While it affects all ages, it usually affects those between the ages of 20 to 50 years old. It is estimated that there are 200 out of every 10,000 individuals newly diagnosed with uveitis annually. In the United States, uveitis causes about 10 to 15 percent of blindness with 30,000 new cases of legal blindness yearly. In pediatric patients, uveitis affects males more than females while in adults, females are affected more than males.
Symptom #1: Floaters
Floaters are deposits in the eye, specifically in the vitreous humor, that have various shapes, sizes, refractive index, and consistency. In most cases, the floaters occur due to the degenerative changes as the age of the individual progresses.
Floaters are only visible due to the shadows they cast on the retina. They can appear as fragments, cobwebs, threads, and spots. These imperfections float slowly and usually move in the direction where the eyes move. Floaters are more common in patients with intermediate and posterior uveitis.
Symptom #2: Photophobia
Photophobia is a term describing the abnormal intolerance to light. It occurs when one experiences pain or discomfort when their eyes are exposed to light. Some causes of photophobia are related to genetic disorders, issues of the nervous system, or conditions involving the eye.
Some examples include migraine headaches, uveitis, corneal abrasion, cataracts, meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and ankylosing spondylitis. In uveitis, since the uvea is inflamed, it is unable to control the amount of light entering the eyes, resulting in discomfort. Photophobia is a common symptom of acute anterior uveitis. It is rarely seen in chronic anterior uveitis, intermediate uveitis, and posterior uveitis.

Symptom #3: Headaches
A headache refers to pain that is felt in the head or neck. Headaches can occur in migraines, cluster headaches, and tension type headaches. Frequent headaches can cause significant depression as they negatively impact employment and relationships.
Causes of headaches include dehydration, head injury, substance abuse, sleep deprivation, fatigue, colds, and dental issues. Headaches can also affect those with eye issues such as glaucoma and uveitis. If you suffer from constant headaches and experience other symptoms listed in this article, be sure to seek medical attention.
Symptom #4: Blurry Vision
Blurry vision occurs when there is loss of the margins of objects in vision. The affected person loses the sharpness, causing the objects they see to appear hazy and out of focus. Blurry vision is most commonly caused by refractive errors such as presbyopia, nearsightedness (myopia), or farsightedness (hypermetropia).
Blurry vision can also be a symptom of a more serious condition. Most types of uveitis can alter the accommodation (focus) of the eye, resulting in blurry vision.

Symptom #5: Photopsia
Photopsia refers to flashes of light and is most commonly seen in conditions such as migraines, posterior vitreous detachment, occipital lobe infarction, and retinal detachment. Photopsia is most commonly caused by the shrinkage or liquefaction of the vitreous, which pulls on the vitreoretinal attachments, producing electrical impulses and irritating the retina. These impulses are then interpreted by the brain as “flashes.”
When photopsia occurs in pregnancy, it may suggest severe preeclampsia. Photopsia is an important symptom that warrants immediate investigation. Some patients with uveitis have also reported seeing flashes of light. Photopsia is usually seen among patients with posterior uveitis.
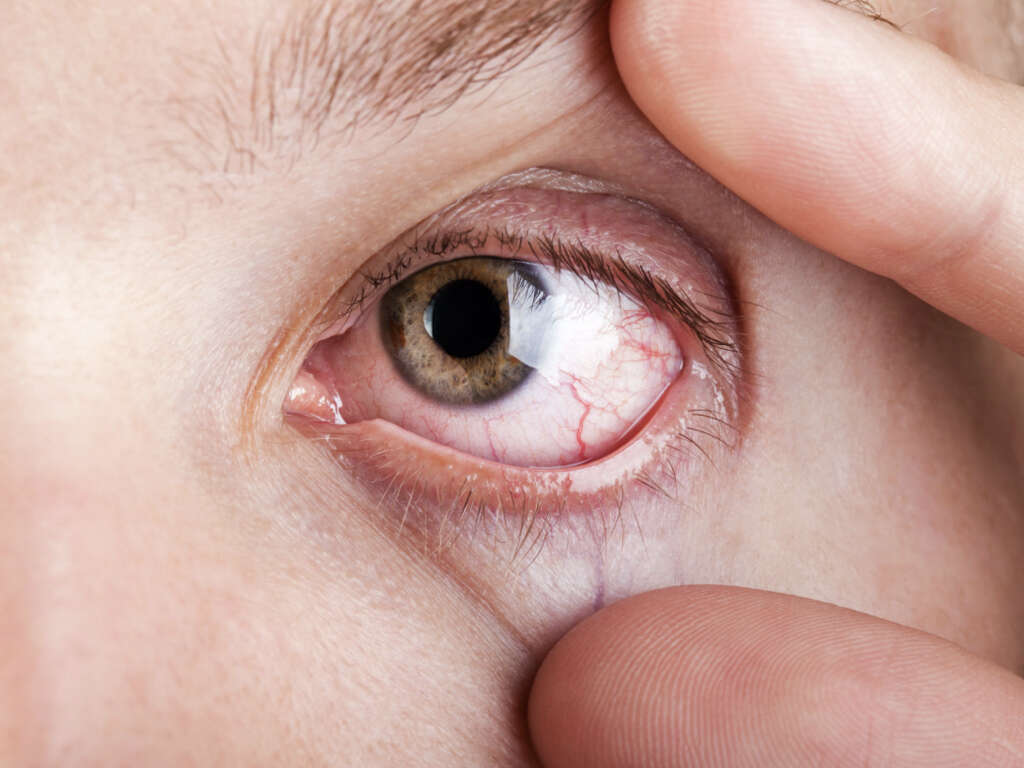
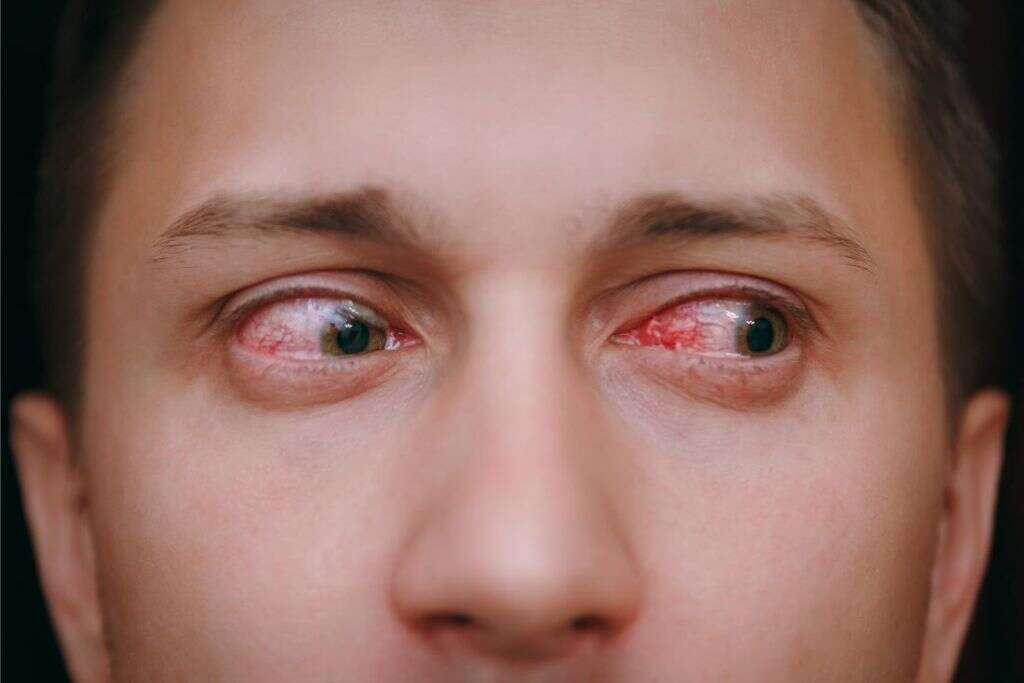
Symptom #6: Redness of the Eye
The presence of redness of the eyes or bloodshot eyes may indicate underlying health issues. While some are benign, there are also serious health conditions that can cause redness.
Some causes include allergies, colds, eyestrain, coughing, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, and uveitis. Ocular redness is one of the most common symptoms of anterior uveitis. While most redness of the eye resolves on its own, it is best to seek medical attention if the symptoms last more than 2 days and are associated with presence of discharge, pain, or light sensitivity.
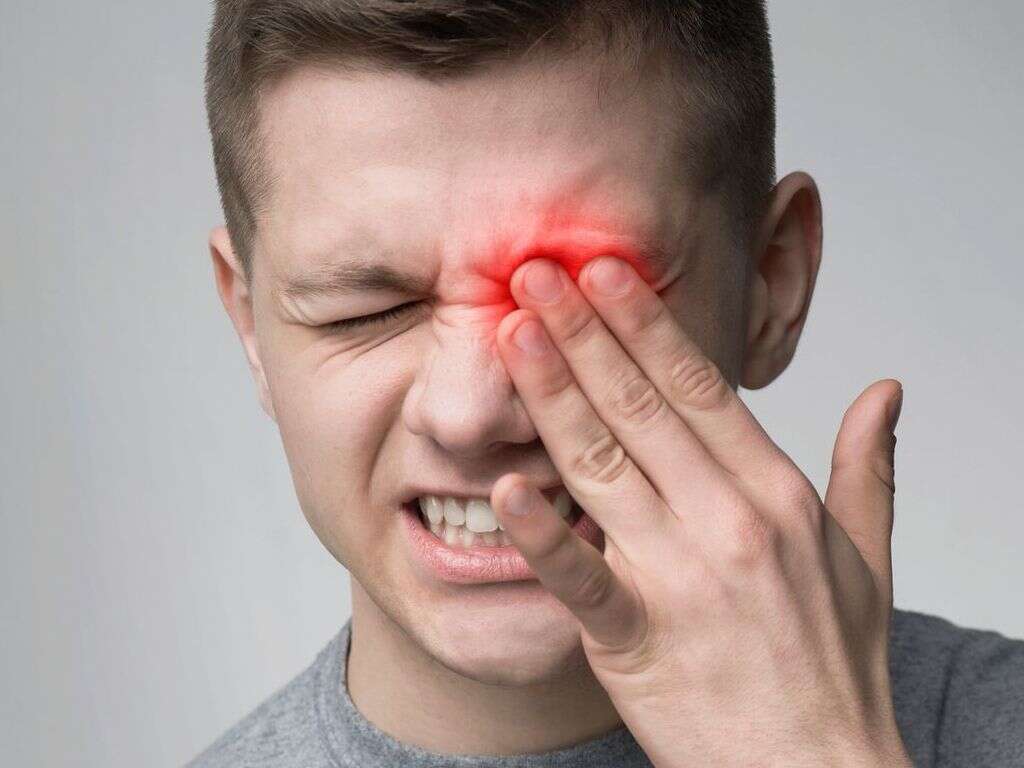
Symptom #7: Eye Pain
Eye pain, or ophthalmalgia, can be divided into pain on the surface of the eye or within the eye. Eye pain is common and is rarely serious. Pain on the surface of the eye is usually due to trauma, foreign objects, or some types of infection. When vision loss accompanies eye pain, it becomes a medical emergency and medical attention should be sought as soon as possible.
Some causes of eye pain include conjunctivitis, irritation from contact lenses, corneal abrasion, and glaucoma. In uveitis, the pain generally develops over several hours and is more common in anterior uveitis.
Symptom #8: Decreased Vision
Decreased vision occurs when there is a loss of vision that cannot be corrected with eyeglasses. The vision loss can be complete or partial. Some common causes of decreased vision include age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and cataracts.
In uveitis, vision loss is often associated with blurry vision. Some may recover with treatment, while damage to the eye can occur in intermediate and posterior uveitis due to the chronic and recurrent inflammation in the optic nerve and retina. Individuals with decreased vision should seek medical attention as soon as possible for early diagnosis and treatment.

Symptom #9: Excessive Tearing
Excessive tearing occurs when there is an overflow of tears. Normally, tears are a necessity as they help to keep the eye healthy. However, excessive tearing can impair vision. It can be caused by excessive production or blocked tear ducts.
In uveitis, excessive tearing occurs due to overproduction of tears as there is irritation and inflammation of the uvea. Treatment of excessive tearing depends on the underlying cause. Increased lacrimation is a common symptom of anterior uveitis.
Symptom #10: Fever
Fever, or pyrexia, occurs when the body’s set point of temperature is higher than normal. A fever is a common symptom and can be seen in various conditions, including infections (viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic).
In uveitis, fever is often an underreported symptom. Some causes of uveitis that may be associated with fever include Kawasaki disease, syphilis, and tuberculosis.