10 Syphilis Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2018. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. - https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats18/syphilis.htm
- 2. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (HIS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd Edition (ICHD-3) – www.ichd-3.org
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is caused by a bacterium called Treponema Pallidum. This pathogen has many ways of infecting people, the most common being through intimate contact with a lesion of an infected person. Additionally, it can be transmitted from an infected mother to an unborn child and through blood transfusions as well. Syphilis is usually seen in young and sexually active males and females aged 20 to 30 years, but it can affect other age groups as well. This condition has been rising in recent years, affecting around 10 people per 100.000 in the US.1Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2018. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. - https://www.cdc.gov/std/stats18/syphilis.htm
Syphilis infections usually develop in stages. Primary syphilis is the first stage of the disease, followed by secondary syphilis which appears a few weeks after the first stage has cleared. If the condition is not treated properly, the disease can go into a latency period that may last for years without showing symptoms until it reaches the late stage of the disease known as tertiary syphilis.
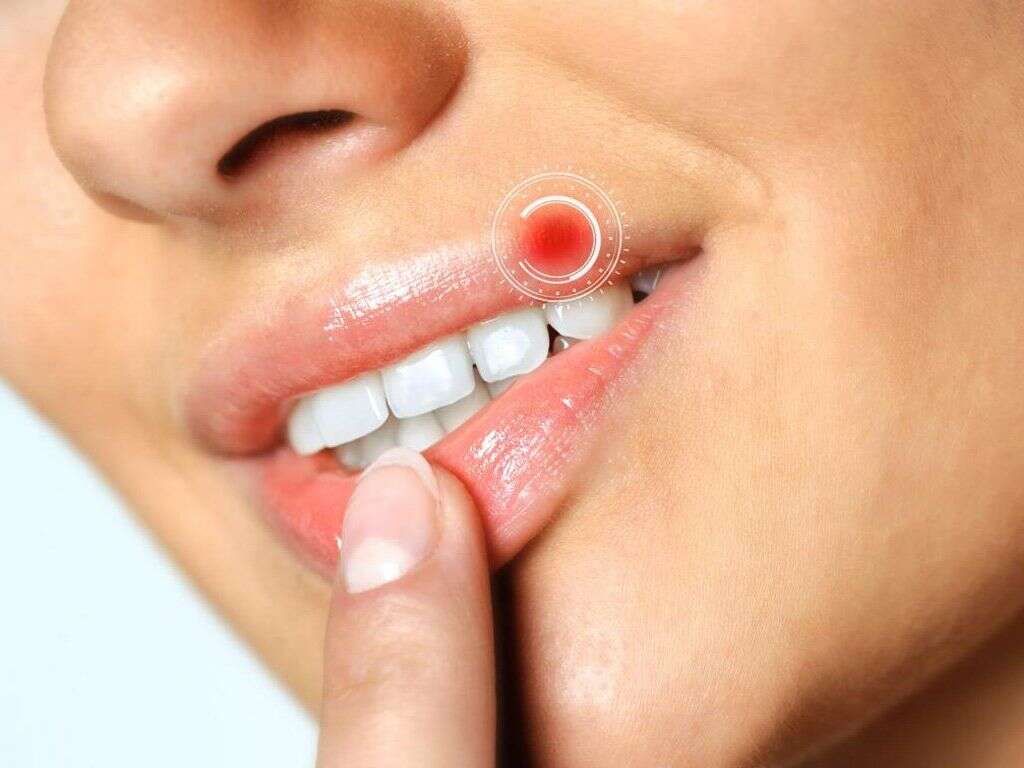
1. Painless Ulcer
The most common symptom associated with syphilis is the presence of a painless lesion at the site of exposure with an infected individual. This lesion is called a chancre. This is a symptom associated with primary syphilis and it usually develops within a few weeks from exposure.
The ulcer usually appears in the penis or the vagina of the affected person and some patients may find them on their anus or their mouths depending on the site of exposure. Most patients will have a single chancre, but multiple lesions have been described as well.

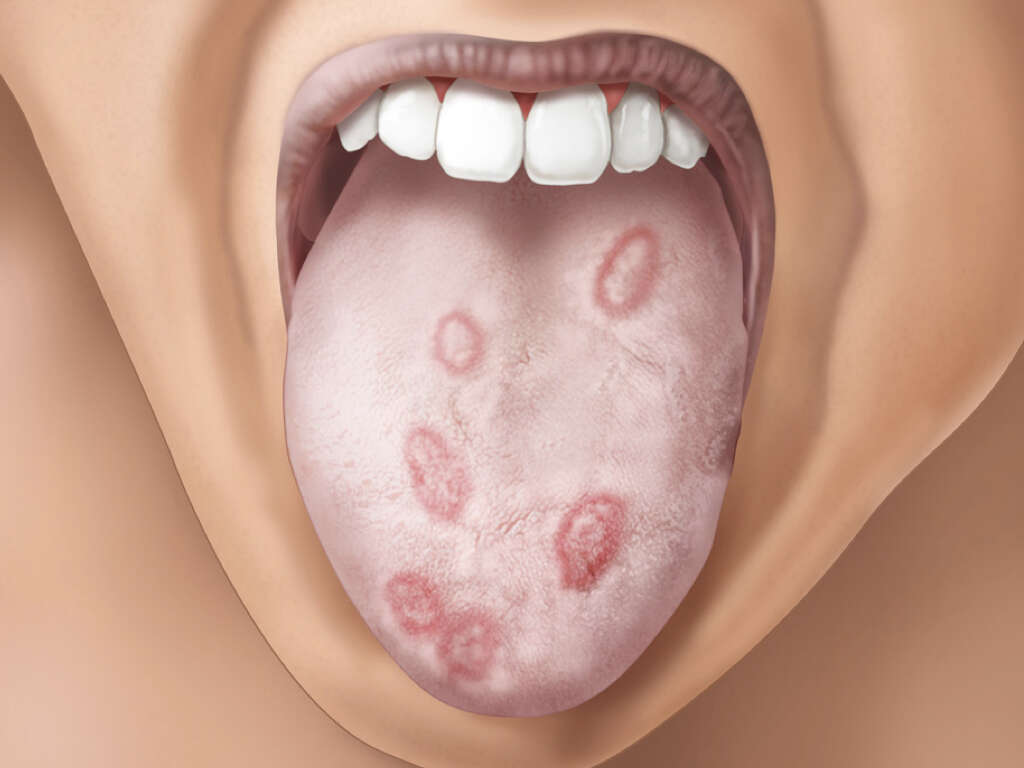
2. Rash
A rash is a disturbance in the normal structure of the skin, usually involving changes in the skin color and texture. It is a non-specific symptom that can be seen in many conditions. Usually, a rash can cause itchiness in the affected area, but this is not always the case.
This is most common symptom associated with secondary syphilis. Several weeks after the patient discovers the chancre, a rash appears in their bodies. Usually the rash causes no itchiness and it can cover a large portion of the patient’s body including their hands and feet. This rash may also be accompanied by the appearance of wart-like lesions in the patient’s genitals and/or mouth.

3. Swollen Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are a crucial component of a person’s immune system. They can be found all over our bodies, connected by a complex array of lymphatic vessels. The lymph nodes filter pathogens and play a very important role in cell-mediated immunity. Many condition may cause lymph nodes to become swollen and depending on the cause and location of the inflammation, a specific group of lymph nodes located near the problem will swell.
Given the fact that most cases of syphilis start in the pelvic region, it is common to find swollen lymph nodes in the same area. Nevertheless, other lymph nodes including the ones located in the neck can be affected as well.

4. Fever
A fever is an increase in body temperature. Usually, the temperature should be above 38⁰C (100.4⁰F) in order to be considered as a fever, but this depends on the site where the temperature is being measured. A fever is usually a response of the body to a threat. By increasing the body’s thermostat set point, we start to shiver to generate heat in order to reach the new temperature that has been set.
Most infectious diseases cause a fever and syphilis is not the exception. It usually appears in the second stage of the disease, also known as secondary syphilis. It may last a few days and it is usually not a very high-grade fever.

5. Malaise
Malaise is a very subjective symptom that can be described as a general feeling of discomfort or a state of uneasiness that is quite difficult to describe. Due to its subjectivity, it is not a very helpful diagnostic tool, as it is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions.
This symptom is commonly seen in secondary syphilis. It is one of many constitutional symptoms like fatigue, fever, headaches, and muscle pain, that are associated with this stage of the disease. As the disease progresses into latency, the symptoms usually disappear slowly.

6. Headaches
A headache is described as the sensation of pain in any region of our head. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. Depending on the characteristics and nature of the headache, they can be classified into primary headaches (migraines and tension-type headaches to name a few), secondary headaches (traumatic, vascular, and substance-related headaches to name a few), and a third category reserved for neuropathies and other headaches.2Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (HIS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd Edition (ICHD-3) – www.ichd-3.org
This symptom can be seen in secondary syphilis as part of the many constitutional symptoms associated with this stage of the disease. On the other hand, this symptom can also be found in later stages of the disease, if the infection spreads into the central nervous system (CNS).

7. Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions and also can be a consequence of the normal aging process. Depending on the cause of the problem, this symptom may appear gradually or suddenly. Furthermore, hearing loss can be classified depending on the location of the problem into: sensorineural (if the problem is located in the inner ear), conductive (if the problem involves the outer and/or inner ear), and mixed (when the problem is a combination of the other two types).
Tertiary syphilis is the late stage of the disease and it can affect many organs in the body. As the infection reaches the central nervous system (CNS) the patient may experience gradual hearing loss as one of the most common symptoms associated with this stage of the condition.

8. Neck Stiffness
Neck rigidity is defined as difficulty or inability to properly move the neck due to stiffness and/or pain. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions but it is particularly relevant in cases where meningitis or meningeal irritation is suspected. It is important to know that having a stiff neck is not necessarily associated with an infection of the central nervous system. Many other conditions can cause neck stiffness; therefore, it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.
For patients with syphilis, a stiff neck might be a sign that the infection has reached the central nervous system in a condition known as neurosyphilis. This may happen at any stage of the disease but it is usually seen in tertiary syphilis. Meningitis caused by a syphilis infection is a very serious complication that requires urgent medical care.

9. Hair Loss
Alopecia is the medical term used to describe the partial or complete loss of hair in areas where hair growth is usual. It can happen due to many reasons, both naturally due to the aging process and also due to several medical conditions and medications.
Syphilitic alopecia is a less common symptom of secondary syphilis. The hair loss can follow a patchy type of pattern where the patient has areas with little to no hair known as bald spots in their scalp, or it can be a diffuse pattern characterized by hair loss without bald spots visible.

10. Blurred Vision
Blurred vision can be described as the gradual or sudden loos of visual acuity. This is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions. Depending on the actual cause of the problem, many patients might refer different visual complaints. Patients usually have problems with details and visual sharpness and it can happen on one or both eyes.
In patients suffering from syphilis, the infection may spread into the central nervous system (CNS) in a condition known as neurosyphilis. This can manifest in many ways, but one of the most common symptoms are sensory alterations regarding hearing loss and visual acuity. Patients may suffer from blurry vision and it might progress into complete blindness in some cases.