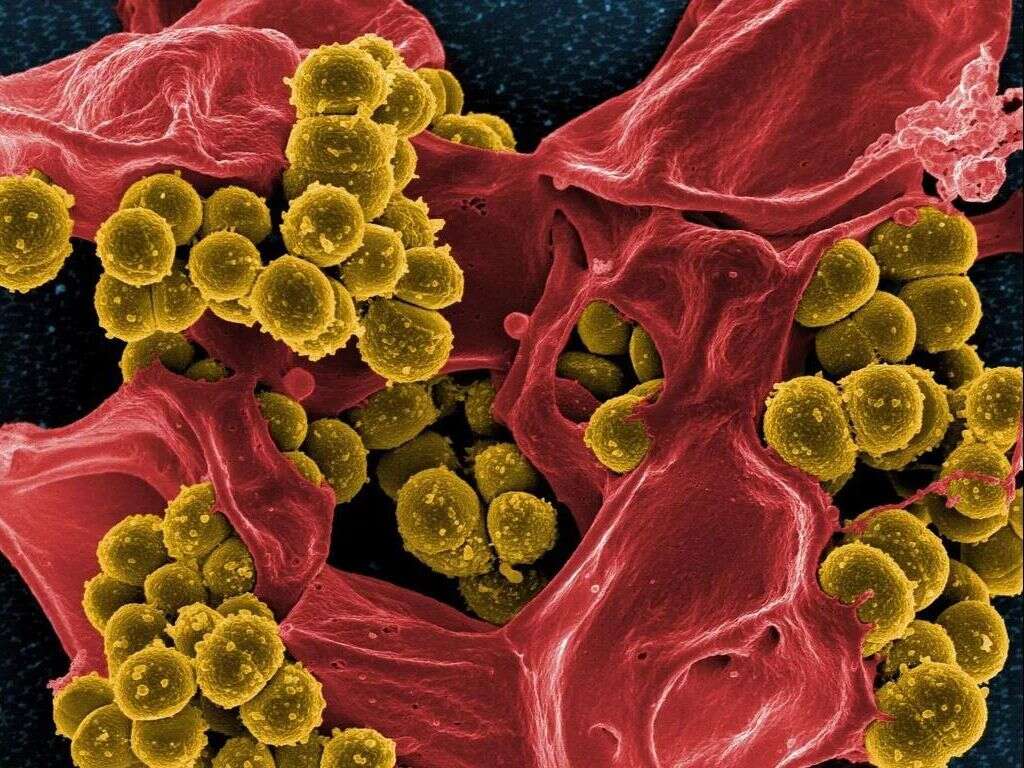
10 Staph Infection Symptoms
Staphylococcus is a group of bacteria that receive their name due to the spherical and grape-like arrangement when observed under a microscope. The most common species to colonize humans are S. Aureus, S. Epidermidis, and S. Saprophyticus. Among the three, S. Aureus is the most common cause of disease in humans and it is known to cause many conditions like skin infections, gastroenteritis, pneumonia, endocarditis, toxic shock syndrome, and many more.
Staphylococcus can be found in our skin and nose without causing any harm to the carrier. Healthcare workers and people with a compromised immune system such as diabetic patients are at a greater risk of colonization. Some species like the Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) have acquired resistance to some antibiotics, becoming a public health issue. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and to prevent further complications.
1. Fever
A fever is an increase in body temperature. Usually, the temperature should be above 38⁰C (100.4⁰F) in order to be considered as a fever, but this depends on the site where the temperature is being measured. A fever is usually a response of the body to a threat. By increasing the body’s thermostat set point, we start to shiver to generate heat in order to reach the new temperature that has been set.
A fever is a common finding among many infectious conditions and a staph infection is not an exception. S. Aureus is known to cause many conditions like skin infections and pneumonia, that may cause a fever to appear.
2. Itchiness
Pruritus is the medical term that describes the feeling of irritation and uneasiness that makes you want to scratch the affected area of the skin. It can be caused by many conditions and depending on the source of the problem it can be very annoying especially at night when we try to sleep.
Conditions like impetigo and folliculitis are known to cause itchiness in the affected area and can become unsettling, especially to younger kids. It is advisable to avoid scratching these lesions to prevent damaging the skin and prevent secondary infections.
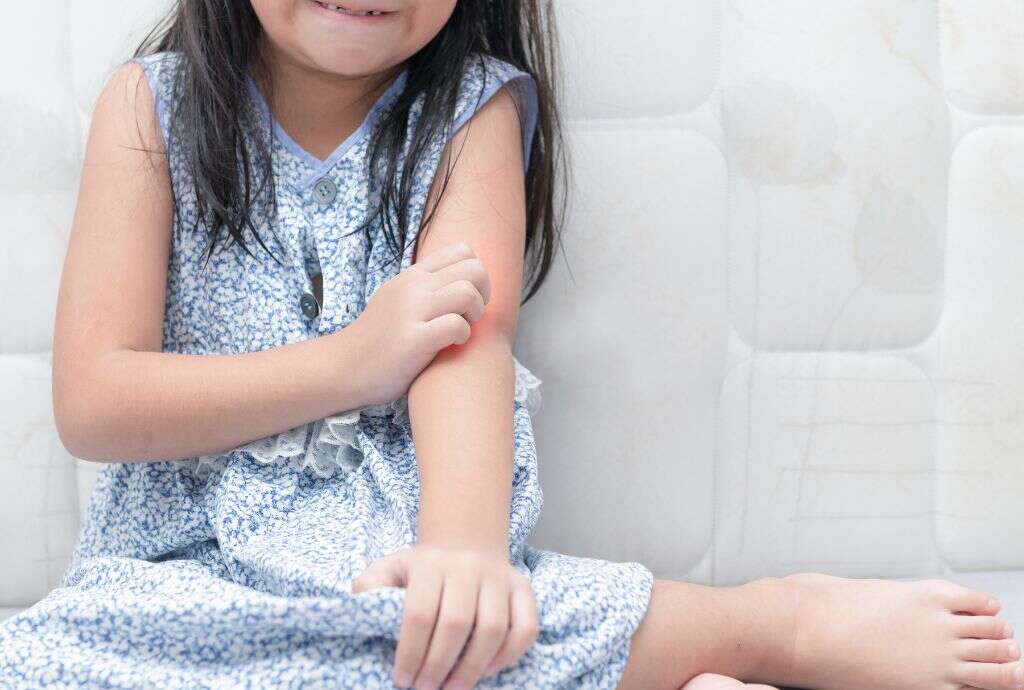
3. Skin Rash
A rash is a disturbance in the normal structure of the skin, usually involving changes in the skin color and texture. It is a non-specific symptom that can be seen in many conditions. Usually, a rash can cause itchiness in the affected area, but this is not always the case.
S. Aureus is the causing agent of many skin conditions like impetigo and folliculitis. Patients with impetigo usually experience small blister-like lesions that are usually filled with a yellow fluid. Eventually, these lesions will turn into a yellowish crust which is a classic finding in this condition. S. Aureus also causes folliculitis which may appear as a red rash surrounding hair follicles.
4. Warm Skin
Localized changes in skin temperature might be a sign of infection or inflammation. During an inflammation process, the blood vessels in the affected area are going to expand, causing more blood to rush into the site. This increase in blood flow is going to cause the affected area to become warm to the touch.
S. Aureus is known to cause skin and soft tissue infections. As the inflammation process progresses, the affected area is going to become red, warm, tender to the touch, and it may even swell-up. If you are experiencing these symptoms, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible for a proper evaluation.
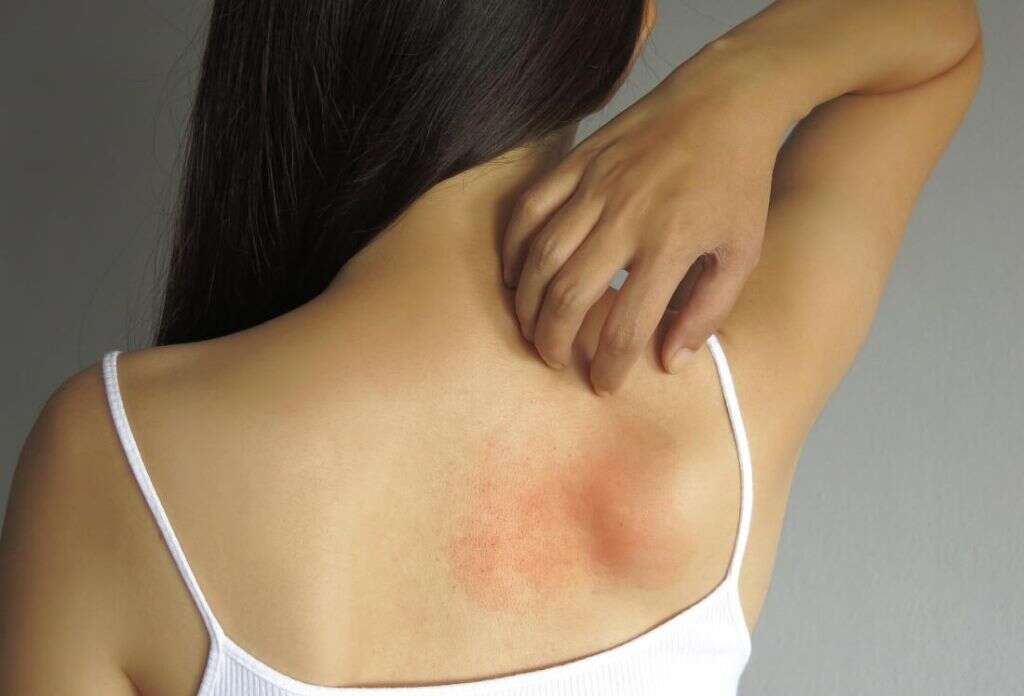

5. Swelling
Edema is defined as fluid accumulation that leads to swelling of the affected tissue. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. Depending on the location and the nature of the edema, it can be a very dangerous sign, like in pulmonary edema, or an annoying symptom like the one seen in venous insufficiency.
Skin infections usually cause the affected area to swell-up. Depending on the type and location of the infection, the area can increase dramatically in size, causing pain and tenderness. Conditions like cellulitis can cause the affected area and the surrounding tissues to swell as well.
6. Diarrhea
Diarrhea is defined as the passage of 3 or more loose or liquid stools in a single day. This is a non-specific symptom that is associated with many conditions. Depending on the duration of this symptom, it can be classified into acute diarrhea (usually lasts a few days) and chronic diarrhea (over 14 days). Diarrhea can lead to dehydration, and this is especially important in young children and elderly patients.
S. Aureus is one of the multiple pathogens that are known to infect the gastrointestinal tract causing gastroenteritis. These bacteria can invade the mucosa of the colon causing severe diarrhea and it may even cause blood to appear in the stools. Food poisoning usually appears after consuming food contaminated with bacteria or toxins that cause the symptoms to appear shortly after exposure.

7. Nausea
Nausea is commonly defined as the urge to vomit. It can appear suddenly but in some cases, it has an insidious onset. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions, but it can also be triggered by certain events or things in our surroundings.
This is one of the most common symptoms associated with food poisoning. Many patients will experience multiple episodes of vomiting as well. It is important to be aware of signs of dehydration, especially in children and the elderly. Patients suffering from bacterial gastroenteritis are also likely to have a decreased appetite and this can be related to nausea and vomiting.
8. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. The location and characteristics of the pain can help to distinguish between different pathologies and it can be very useful information to the clinicians in order to provide an accurate diagnosis.
S. Aureus is known to cause gastroenteritis. As the bacteria colonize the gastrointestinal tract, the patient may experience cramps and diffuse abdominal pain. The symptoms usually appear shortly after eating contaminated food and could last a few days or even weeks. If you are experiencing symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, and diarrhea, you should seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis.

9. Shortness of Breath
Dyspnea is the medical term used to describe sudden shortness of breath. It is characterized by having difficulty breathing which may or may not be associated with a feeling of tightness in the chest. Dyspnea is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with both respiratory and circulatory conditions. It is important to state that exercise-induced dyspnea is usually a normal and transitory state of air hunger which is not directly related to a disease, whereas, resting shortness of breath is usually a sign that something might be wrong.
S. Aureus is one of the many pathogens known to cause pneumonia. These bacteria can invade the respiratory tract causing the patient to develop a cough, fever, and eventually shortness of breath. Chest pain may appear as well in people with a respiratory tract infection.
10. Pain During Urination
Dysuria is the medical term used to describe the presence of pain during urination. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions such as urinary tract infections (UTI), kidney stones, and sexually transmitted infections (STI) to name a few. This symptom is often described as a burning sensation during urination and it can be quite a painful experience.
S. Saprophyticus is known to cause urinary tract infections, especially in young sexually active women. It usually causes a non-complicated UTI known as cystitis. Due to anatomical reasons, females are more likely to experience urinary tract infections than males.






-06.jpg)