10 High Blood Sugar Symptoms
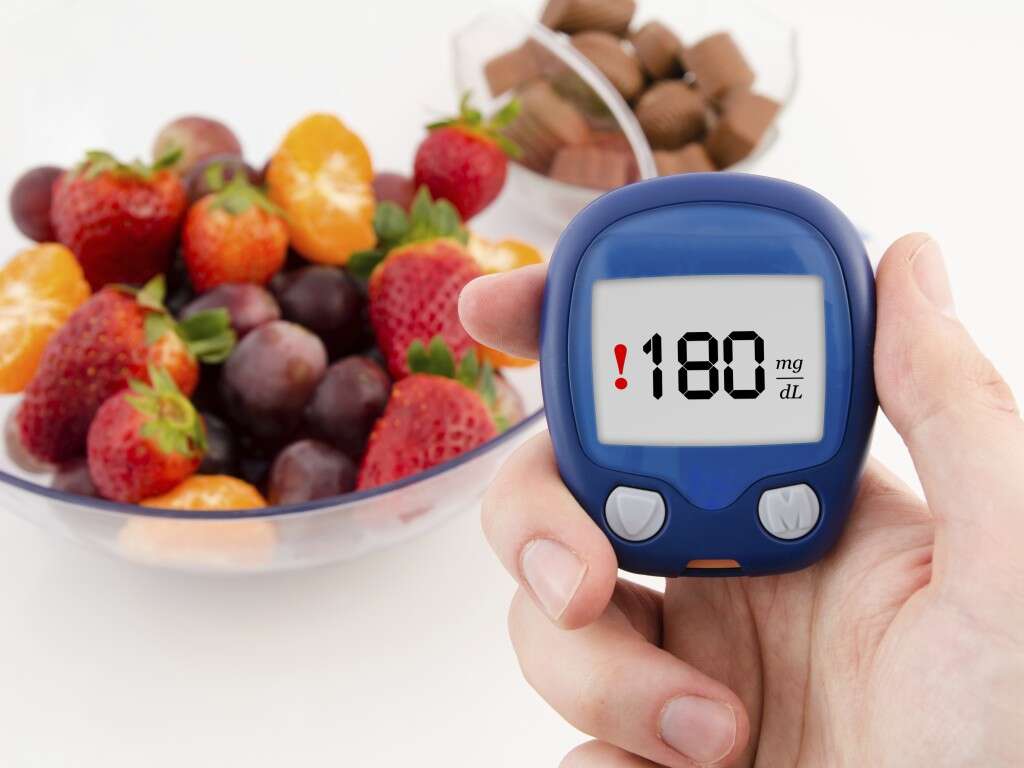
High blood sugar or hyperglycemia is a condition which describes the excessive amount of glucose in the blood. This means that the blood sugar level is higher than 11.1 mmol/l or 200 mg/dl. However, depending on different individuals, there may be little to no symptoms until the blood sugar becomes much higher, such as at 15 to 20 mmol/l or 250 to 300 mg/dl. Chronic levels of high blood sugar can lead to complications such as noticeable organ damage.
High blood sugar is most commonly seen among patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes refers to a group of metabolic disorders where there are high blood sugar levels for a prolonged duration. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is also known as juvenile diabetes as it is more commonly seen among young children and adolescents. It occurs due to the failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes occurs when there is insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes occurs among pregnant women.
Symptom #1: Fatigue
Fatigue can be described as a gradual feeling of tiredness that can be alleviated by periods of rest. Fatigue can be classified into physical fatigue which means the transient inability of the body’s muscles to maintain peak performance, while mental fatigue describes the temporary inability to achieve maximal cognitive performance.
Fatigue is a non-specific and common symptom that can be seen in many conditions such as sleep deprivation, nutritional deficiency, stress, overwork, pregnancy, infections, and other diseases.
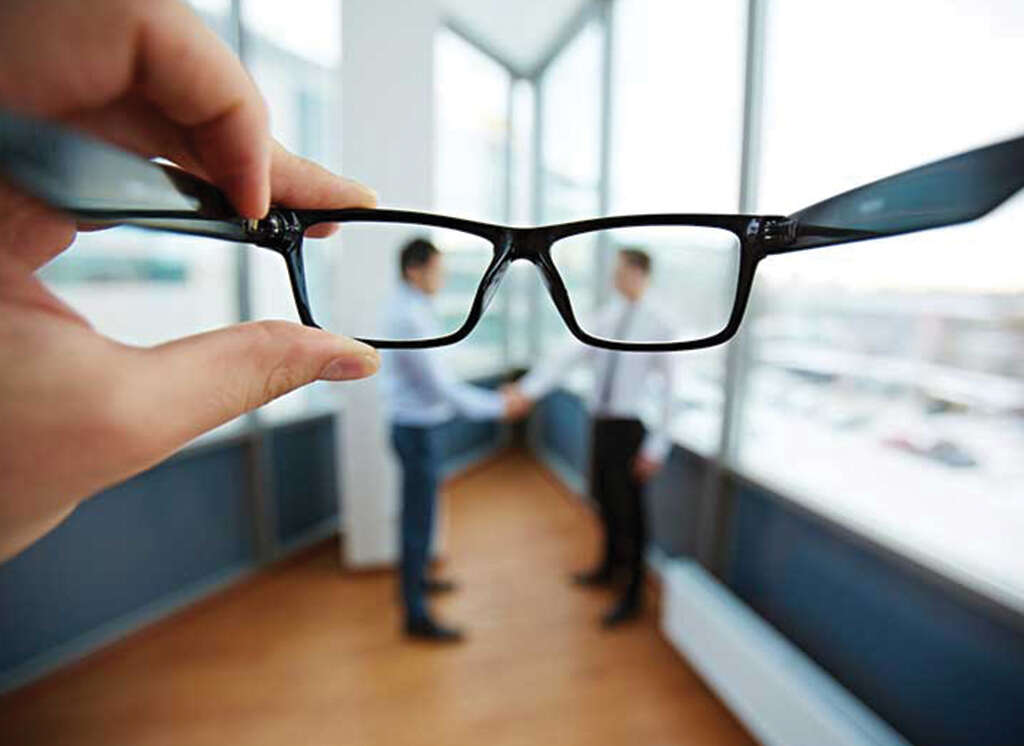
Symptom #2: Blurry Vision
Blurry vision is one of the commonest ocular complaints and can be caused by many issues such as presbyopia, cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, eye infection, retinal detachment, optic neuritis, brain tumor, stroke, and more.
In patients with high blood sugar, it can lead to transient swelling of the lens in the eye which results in blurry vision. Repeated episodes are believed to cause the formation of cataracts.

Symptom #3: Polyphagia
Polyphagia is also known as hyperphagia which means an increased appetite or excessive hunger. This results in an abnormally large consumption of food. It can be caused by many conditions such as Kleine-Levin syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Bardet-Biedl syndrome, hyperthyroidism, and diabetes.
When the blood sugar levels remain high, glucose cannot enter the cells as there is insulin resistance or inadequate insulin. Therefore, the body cannot convert the food consumed into energy resulting in a constant state of hunger.
Symptom #4: Dry Mouth
Dry mouth is medically known as xerostomia. It can be due to a change in the saliva composition or a reduction in the flow of saliva. It is a common and non-specific symptom that is commonly seen as a side effect of medications especially among older individuals, those who breathe through their mouths, radiotherapy that involves the salivary glands, dehydration, chemotherapy, and more. Management includes the use of saliva stimulants and saliva substitutes.
Usually, the increased levels of blood glucose may cause the patient to become dehydrated, causing the dry mouth to appear. Dehydration can be quite a serious condition so it is important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Symptom #5: Stupor
Stupor is defined as the lack of mental function or consciousness. This means the affected individual is unresponsive and only responds to base stimuli. It can be seen in infectious diseases, mental illnesses, severe hypothermia, complicated toxic states, epilepsy, vascular illness, neoplasms, shock, trauma, and more.
Patients with stupor usually appear sleepy most of the time. Severe cases can result in loss of appetite, patients becoming motionless, and becoming mute.
Symptom #6: Coma
Coma refers to the state of unconsciousness where the afflicted patient cannot be awakened and does not respond to any stimuli. There is absence of wakefulness and the patient is unable to speak, feel, move, or hear.
A patient in a coma usually scores between 3 and 8 on the Glasgow Coma Scale. There are many causes of coma such as severe hypoglycemia, hypercapnia, traumatic brain injury, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intoxication, and more.

Symptom #7: Polydipsia
Polydipsia refers to excessive thirst or drinking. It is a non-specific symptom that can be seen in many disorders such as diabetes mellitus, diabetes insipidus, hypokalemia, low blood volume, and more. Polydipsia is not a disease but instead a symptom of a disease.
Polydipsia is often associated with other symptoms such as polyuria. Excessive water intake can result in a low serum concentration of blood urea nitrogen, red blood cells, and sodium.
Symptom #8: Polyuria
Polyuria describes an abnormally large production or excessive passage of urine, often greater than 2.5 to 3.0 liters a day. One of the normal accompanying symptoms is increased frequency of urination. It can be associated with excessive thirst.
There are many causes of polyuria but is most commonly due to uncontrolled diabetes mellitus where there is high blood sugar. Other causes include adrenal cortical tumor, central diabetes insipidus, primary polydipsia, and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.

Symptom #9: Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is also known as impotence. It describes the inability to maintain or develop a penile erection during sexual activity. There can be psychological consequences that result in relationship difficulties and issues with self confidence.
Besides psychological causes of erectile dysfunction, organic causes of impotence are poorly controlled diabetes where there is high blood sugar, cardiovascular disease, neurological issues, hormonal insufficiencies, side effects of medications, and more. It can be managed through medications such as sildenafil, injections into the penis, or the use of penile prosthesis.
Symptom #10: Poor Wound Healing and Recurrent Infections
Patients with poor wound healing and recurrent infections often have poorly controlled diabetes where there is constant high blood sugar. Since high blood sugar weakens the patient’s immune system, diabetics are more susceptible to recurrent infections and poor wound healing. The hyperglycemic environment favors immune dysfunction such as humoral immunity, damage to the neutrophil function, and depression of the antioxidant system.
This is also the reason why diabetics are recommended to be immunized with influenza and pneumococcal vaccines to lower the rates of hospital admissions and mortality.