10 Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is also known as ischemic heart disease, the most common of all cardiovascular diseases. It can lead to dangerous episodes such as myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death, stable angina, unstable angina, abnormal heartbeat, and heart failure. Symptoms of coronary artery disease are usually aggravated by exertion, exercise, or emotional stress. It may or may not improve with rest.
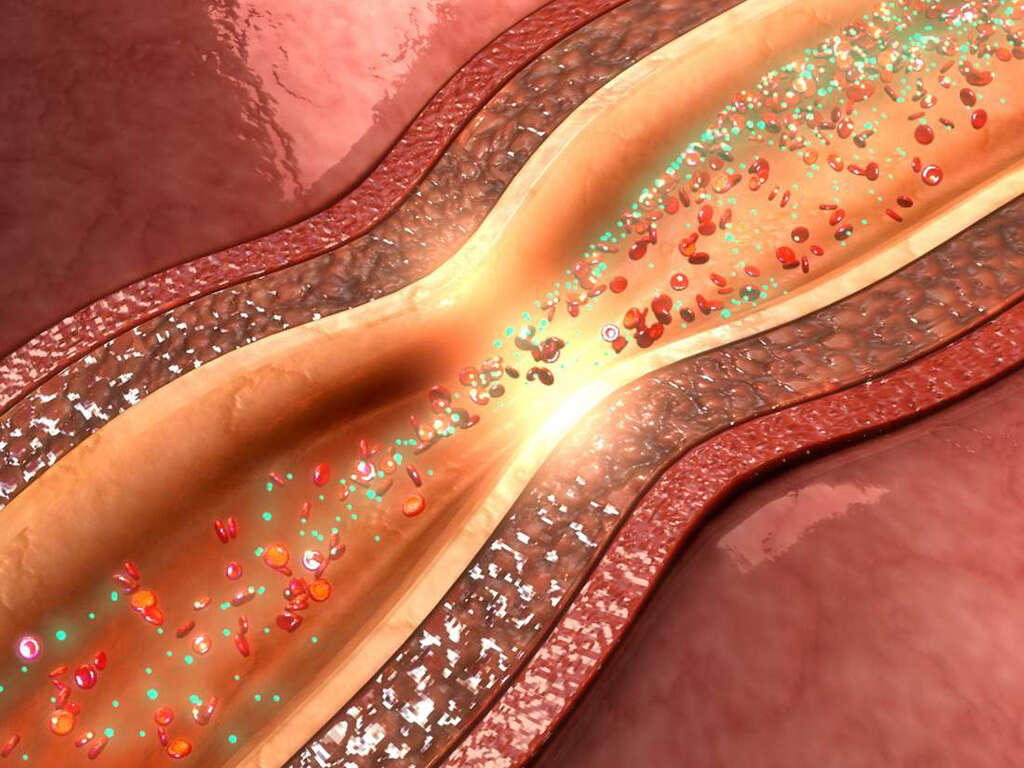
The risk factors for coronary heart disease are obesity, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, a sedentary lifestyle, and high blood cholesterol. Excessive alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, depression, and stress are also factors. Coronary artery disease can occur when there is reduction of blood flow and oxygen to the heart which may be attributed to the presence of plaque in the arteries. The diagnosis of coronary artery disease may involve electrocardiogram, coronary computed tomography angiography, cardiac stress testing, and coronary angiogram.
To lower the risk of coronary heart disease, individuals can start a regular exercise routine, comply with a healthy diet, maintain a normal weight, and avoid smoking. The treatment of coronary artery disease is similar to prevention. It involves medication such as beta blockers, antiplatelets, nitroglycerin, or procedures like coronary artery bypass surgery and percutaneous coronary intervention. In 2015, as many as 110 million individuals were affected by coronary artery disease which resulted in 8.9 million deaths. It has been estimated that coronary artery disease has contributed to about 15.9 percent of all deaths globally. In 2010, approximately 20 percent of individuals in the United States were thought to have coronary artery disease. Rates are usually higher among men compared to women.
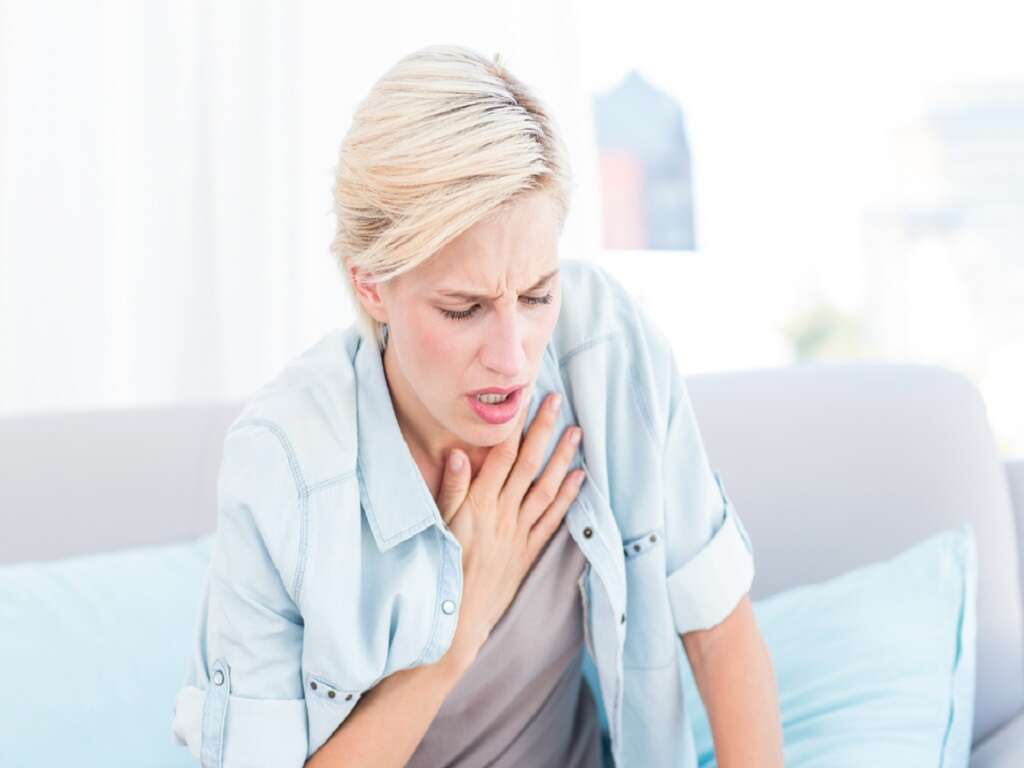
Symptom #1: Chest Pain
Chest pain refers to pain that is felt in any region of the chest. It may be due to various causes and is considered a medical emergency. Chest pain can be differentiated into cardiac related and non-cardiac related chest pain.
Non-cardiac related chest pain can be due to the gastrointestinal, lung, or musculoskeletal issues. The management of chest pain ultimately depends on the underlying cause. Cardiac related chest pain may be associated with nausea, sweating, vomiting, and weakness. Patients usually complain of a crushing or squeezing sensation over the chest.

Symptom #2: Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath or dyspnea is a feeling where one is unable to breathe well enough. The individual with shortness of breath may require extra effort to breath, or experience chest tightness and air hunger.
Dyspnea can be caused by issues such as congestive heart failure, interstitial lung disease, cardiac ischemia, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, anxiety, and panic disorder.

Symptom #3: Sweating
While sweating may be a normal phenomenon, pathological sweating or diaphoresis can be associated with abnormal conditions such as shock, hyperthyroidism, and heart disease. It occurs due to the increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system.
It can also be seen in infections and may be accompanied by fever and chills. It is also one of the primary symptoms of heart attack that prompts patients to seek treatment.

Symptom #4: Palpitations
Palpitations refer to a patient’s perception that there is abnormality with their heartbeat. It can be perceived to be excessively fast, hard, or irregular. Palpitations can occur due to various reasons such as anxiety, coronary heart disease, hyperthyroidism, asthma, cardiomyopathy, among others.
They are usually associated with symptoms such as sweating, headaches, breathlessness, and dizziness. Palpitations that are accompanied by chest pain usually mean that there is underlying coronary artery disease.

Symptom #5: Tachycardia
Tachycardia refers to heart rate that is above the normal resting rate. A heart rate above 100 beats per minute is defined as tachycardia. Some of the causes of tachycardia are amphetamine use, alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, caffeine use, exercise, fever, hyperthyroidism, infection, anxiety, and anemia.
The management of tachycardia depends on the type of tachycardia and the stability of the patient. The management of unstable narrow complex tachycardia may involve the use of intravenous adenosine or cardioversion.

Symptom #6: Weakness
Weakness is a non-specific and common symptom seen in many different conditions. Weakness can be divided into true and perceived muscle weakness. In true muscle weakness, it is often a symptom of skeletal muscle diseases such as inflammatory myopathy or muscular dystrophy.
Perceived muscle weakness occurs when the individual feels that there is more effort required to perform an action despite having normal muscle strength.

Symptom #7: Dizziness
Dizziness refers to impairment in spatial perception. It is a broad term that can be used to refer to presyncope, vertigo, and disequilibrium. Some of the common causes of dizziness are fall in blood pressure, inadequate blood supply to the brain, disorders of the inner ear, side effects of medications, and loss of visual cues.
Dizziness can increase the risk of falls and injuries. Patients, especially the elderly, should refrain from activities if experiencing dizziness.

Symptom #8: Nausea
Nausea is a term describing an uncomfortable and unpleasant sensation with an urge to vomit. Although there is no pain, nausea can be a debilitating symptom as it causes discomfort in the abdomen, chest, and throat.
Nausea is nature’s way of discouraging an animal from repeating their actions that may have caused the unpleasant sensation of nausea. It is a non-specific symptom that can be seen in pregnancy, food poisoning, gastritis, anxiety, extreme pain, dizziness, and depression. It can be managed using antiemetics such as promethazine, metoclopramide, and ondansetron.

Symptom #9: Pedal Edema
Edema occurs when there is excessive and abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitium. Clinically, patients present with swelling of the affected parts. When coronary artery disease progresses to heart failure, “pitting” edema occurs. This refers to the pits that appear when pressure is applied to the affected area.
The indentation persists despite the release of pressure. Other causes of pedal edema include varicose veins, dermatitis, and pregnancy. It can be managed with fluid restriction and the use of diuretics.

Symptom #10: Fatigue
Fatigue refers to the feeling of gradual tiredness where it can be alleviated by periods of rest. It can be divided into physical and mental causes of fatigue. Physical fatigue occurs when there is a temporary inability to achieve peak physical performance while mental fatigue is the transient reduction in maximal cognitive performance.
Fatigue can manifest in patients as lethargy or somnolence. It is a non-specific symptom that can be seen in various patients who are feeling unwell.