10 Causes Of Blurred Vision
Blurry vision refers to vision where there may be fuzzy or hazy lines instead of clear and sharp borders. It can cause navigation difficulty resulting in issues with driving, reading, and writing. Blurry vision doesn’t only affect the line of sight, but also parts of the entire vision. This can involve the peripheral vision.
Blurry vision can affect one or both eyes. Although blurry vision may seem trivial to most, it is important to seek medical attention if the blurry vision is accompanied with loss of muscle control on one side of the boy, severe headache, issues with speech, loss of vision, and facial drooping. The above symptoms are consistent with a stroke and warrants emergent care by professionals.
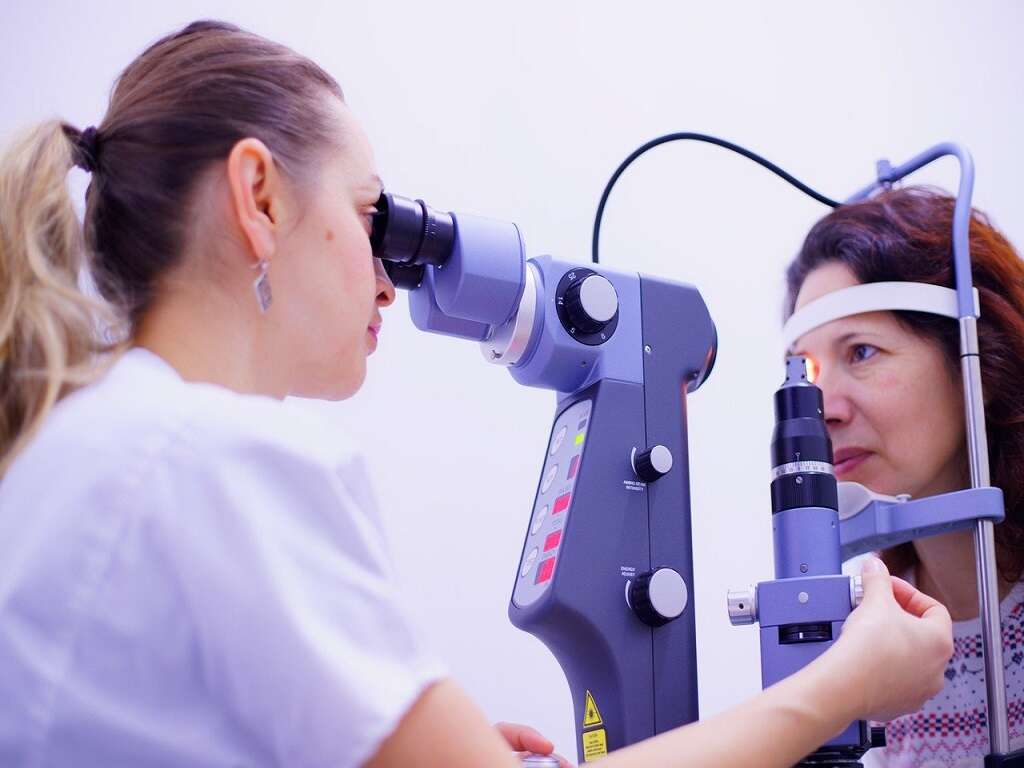
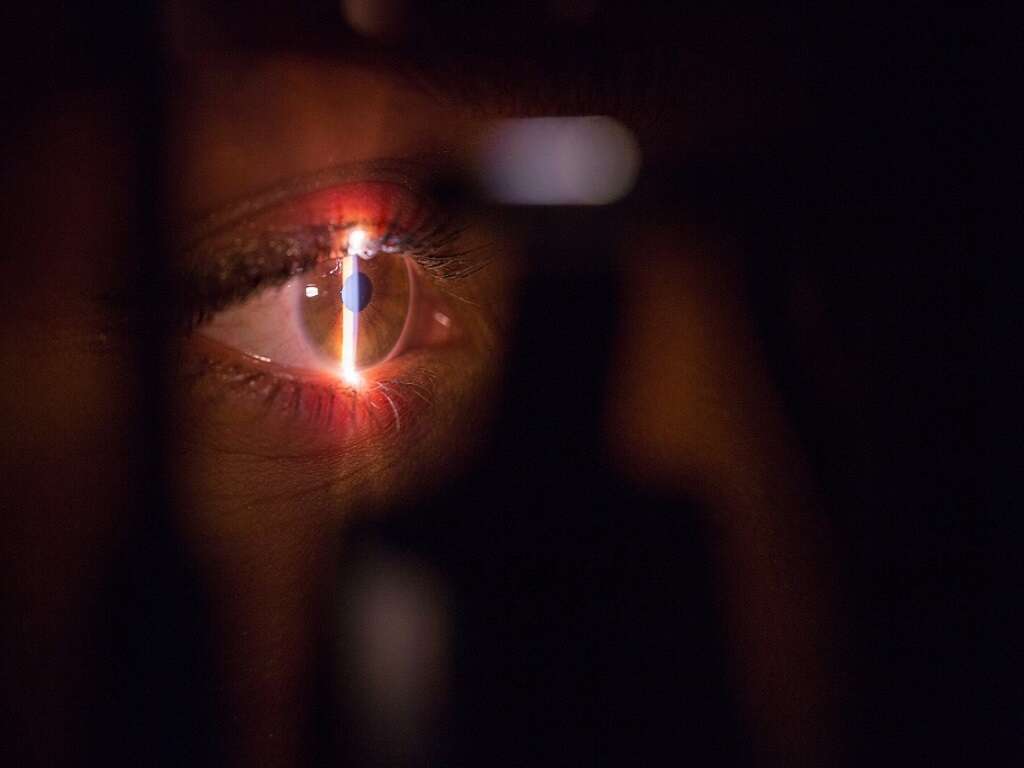
The diagnosis of blurry vision can be diagnosed via the patient’s history and physical examination performed by the physician. Eye tests such as the use of an eye chart, refraction test, ophthalmoscopy, tonometry, and slit lamp examination may be necessary. Blurry vision is treated based on the underlying cause.
Cause #1: Atropine
Atropine is a type of medication used in the treatment of pesticides and nerve agent poisonings. It also helps to decrease heart rate and lowers saliva production during surgery. Used as an eye drop, it can treat uveitis and amblyopia.
Large doses help with the treatment of certain poisonings. Side effects of atropine use include urinary retention, large pupils, constipation, dry mouth, and tachycardia. One of the main side effects of atropine include blurry vision if used topically on the eye.
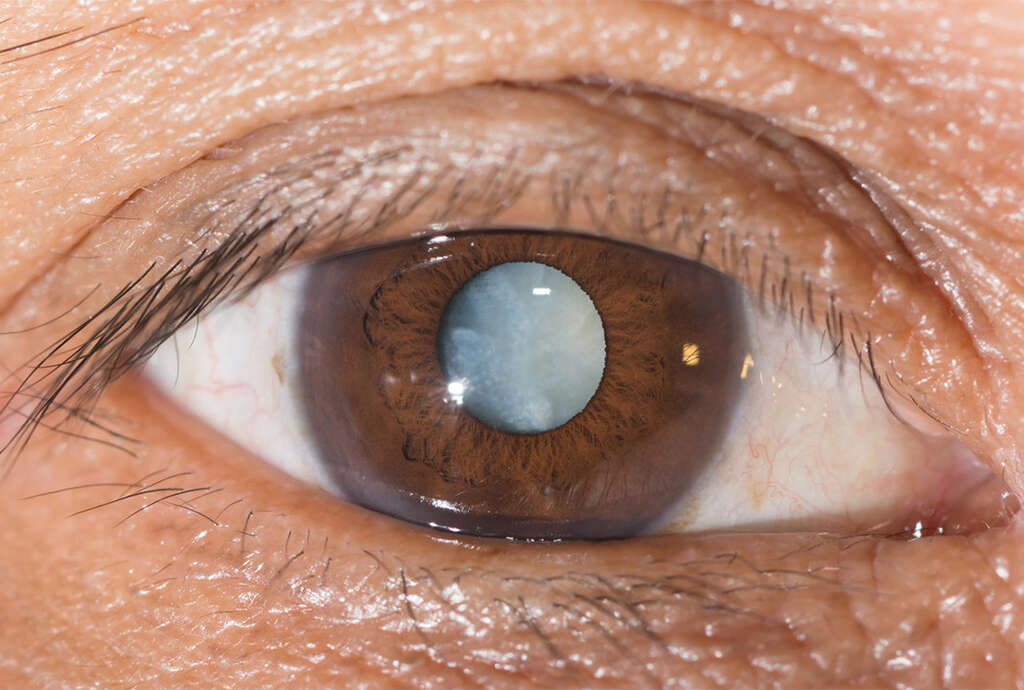
Cause #2: Cataracts
A cataract refers to clouding of the lenses leading to a decrease in vision. It can gradually develop and affect both eyes causing symptoms such as blurry vision, faded colors, halos around light, and trouble seeing at night. Patients with cataracts often experience issues with driving at night, reading, and recognizing faces.
There is also an increased risk of falls and depression. It is one the main causes of blindness globally. The most common causes of cataracts are aging, congenital, trauma, exposure to radiation, or previous history of eye surgery. Those at risk are smokers, individuals who consume alcohol, or those who are excessively exposed to sunlight.
Cause #3: Presbyopia
Presbyopia refers to the condition where aging of the eye leads to worsening ability to focus on close objects. This means that there is difficulty reading small print, which is compensated by holding the reading material further away. Patients with presbyopia also experience eyestrain and headaches.
Considered a part of the normal aging process, presbyopia occurs as the lens of the eye hardens and loses its accommodation capabilities. It can be treated using eye glasses. Signs and symptoms include difficulty reading, visual issues in low light conditions, eyestrain, and blurring of close objects.
Cause #4: Poorly Controlled Blood Sugar
In this case, blurry vision is a temporary issue that may have developed due to high blood sugar issues. The high glucose level causes the lens of the eye to swell, leading to blurry vision. This can occur after a high carb meal. This means blurry vision that occurs after meals can be easily avoidable.
It is important for diabetics to follow the recommendations of their nutritionist or healthcare personnel, as chronic blurriness can take as long as three months before the vision returns to normal.

Cause #5: Glaucoma
Glaucoma refers to a group of eye conditions where there is vision loss and damage to the optic nerve. Broadly divided into open angle, closed angle, and normal tension glaucoma, the management for each subtype differs. However, vision loss from glaucoma is usually permanent.
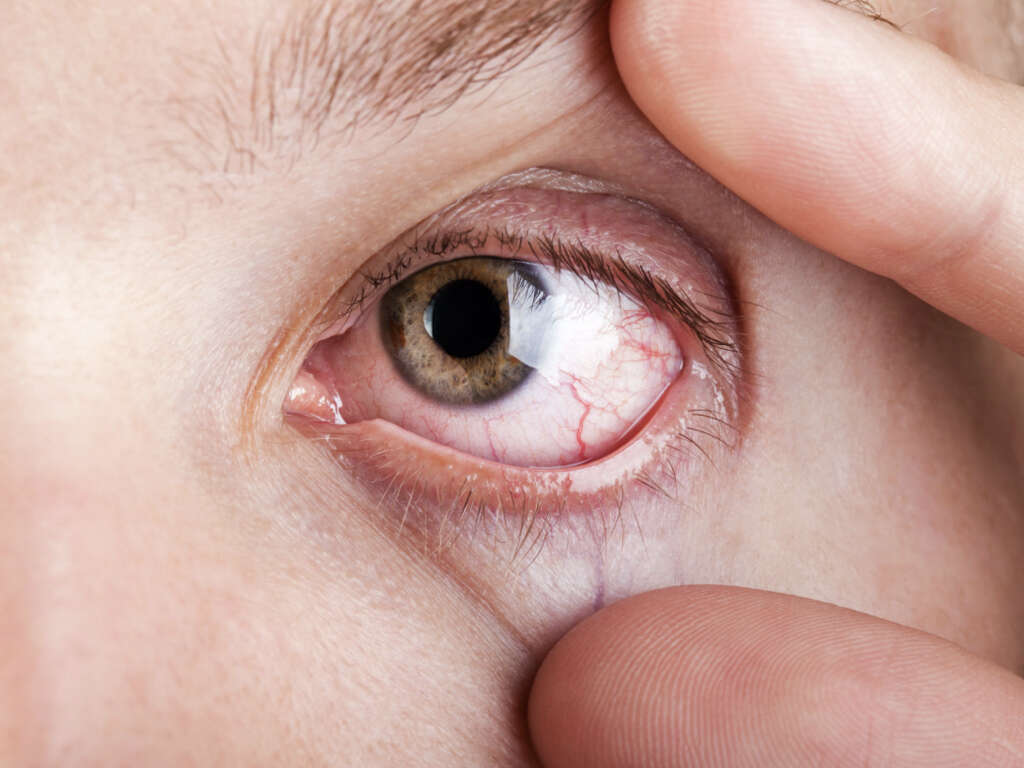
Risk factors include high blood pressure, positive family history, and increased pressure in the eye. It can be treated using medication, surgery, or laser treatment. Some signs and symptoms include ocular pain, blurry vision, red eye, halos, nausea, vomiting, and suddenly decreased vision.
Cause #6: Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a type of eye disease that occurs due to diabetes. It occurs when there is damage to the retina which can be attributed to diabetes. It is also one of the leading causes of blindness. It affects up to 80 percent of patients who have had diabetes for 30 or more years.
About 90 percent of cases can be reduced if there is proper monitoring and treatment of the eyes. Some signs and symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include sudden loss of vision and blurry vision. Treatment includes injection of corticosteroids, laser surgery, or vitrectomy.
Cause #7: Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration or age-related macular degeneration refers to a condition where there is blurry or no vision in the center of the visual field. Although it does not result in complete blindness, the loss of central vision can lead to difficulty driving, writing, and recognizing faces.
It can also cause blurry vision. Macular degeneration most commonly occurs among the elderly, with risk factors such as genetics and smoking playing a role. Prevention involves avoiding smoking, exercising, and having a healthy diet.
Cause #8: Retinal Detachment
Retinal detachment is a condition where the retina has separated from the layer underneath it. It can lead to symptoms such as flashes of light, floaters, and worsening field of vision. Some patients may also describe it as a curtain that falls over part of the vision.
Blurry vision may also occur. Straight lines such as the edge of the wall or road can suddenly appear curved. Retinal detachment is important as left untreated, it can lead to permanent vision loss.

Cause #9: Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis is a condition where there is a demyelinating inflammation of the optic nerve. Commonly associated with multiple sclerosis, optic neuritis can result in partial or complete vision loss in one or both eyes.
Signs and symptoms include blurry vision, pain on movement of the affected eye, slurred speech, lack of coordination, reduced night vision, red eyes, and photophobia. It can be treated with corticosteroids but has limited to little effect.
Cause #10: Transient Ischemic Attack
Transient ischemic attack or TIA refers to a brief episode of neurological dysfunction due to loss of blood flow to the spinal cord, brain, or retina without any tissue death. TIA causes the same symptoms as stroke such as paralysis, numbness, and weakness on one side of the body.
There can also be blurry or loss of vision, slurring of speech, difficulty speaking, issues understanding language, and confusion. In TIA, symptoms usually resolve within 1 to 24 hours. TIA is a recognized risk factor of stroke.